I have thought a lot about the phrase “speaking truth to power” over the last few days. Perhaps my musings have a lot to do with the free space I have in my mind now that my thesis is complete. Or it could be the anger I feel knowing that children of Hollywood actresses and the like scammed their ways into colleges and universities while I sacrificed, saved, budgeted and continually sought/seek to maintain my integrity on my significantly less flexible income. What did it mean for me to know that some people have no idea or care about the struggle of other people? What did mean to have someone blatantly disrespect the work ethic of millions of people? Nearly one year ago, my colleague Lindsey wrote a blog about The True Cost of fashion as highlighted in a Netflix documentary. For me, it was an eye-opening read as I found myself confronted by my disrespect for the work ethic of millions of people. After reading her blog, I was committed to shopping differently, but I honestly did not know how or where to begin. You see, I like clothes. I use the word like instead of love because love affirms a commitment whereas like can be fleeting and fickle; therefore, I like clothes and love colors, patterns, and fabrics. I agree with Orsola de Castro’s declaration that “clothes are the skin we choose.”
I cannot say that I have gone this year without purchasing new clothing, but I have not bought as much as I have in years past. I have also become mindful of my giving to charity stores because as the film points out, unsold clothing goes to other countries and overwhelms their local industry; thereby limiting the jobs and transferrable skills like sewing and tailoring. Watching the film, I realized that the core of this change was the shift in my paradigm which subsequently caused a shift in my values. De Castro asserts that our choice of clothing is the manifestation of our communication – fundamentally a part of what we seek to communicate about ourselves. So, I began to ask myself, “What did I want to communicate about myself? Did it matter to me that some of my clothes are years old if they still fit and have been well maintained?” No, but the change in my values was not merely about not caring about the durability of my clothing from years ago. It was about the lives of those on the other end of the stitches and sewing machines.
A downside of globalization is the increase of fast-fashion at the expense of the lives of garment factory workers. Globalization has allowed for the outsourcing of fashion to low-cost economies where the wages are low and kept low; therefore, those at the top of the value chain get to choose where the products are made based upon where they can compete and manipulate the cost of manufacturing. The only interest companies have in countries like Bangladesh is for the exploitation of the people, most of whom are women. The result of the Bangladeshi factory worker is that the “budget conscious shopper” can now purchase clothing that is “cheap enough to throw away without thinking about it” as proclaimed by Stephen Colbert. Last year I began questioning how my consumption of fast-fashion had continued to perpetuate the injustices of the gouging of low-wage countries experiencing the exploitation of their citizens while I claim to advocate for liberty and justice for all. Was I true to myself by ignoring the plight of millions of people making the $20 pair of jeans I brought with my e-coupon? I began to think about it.
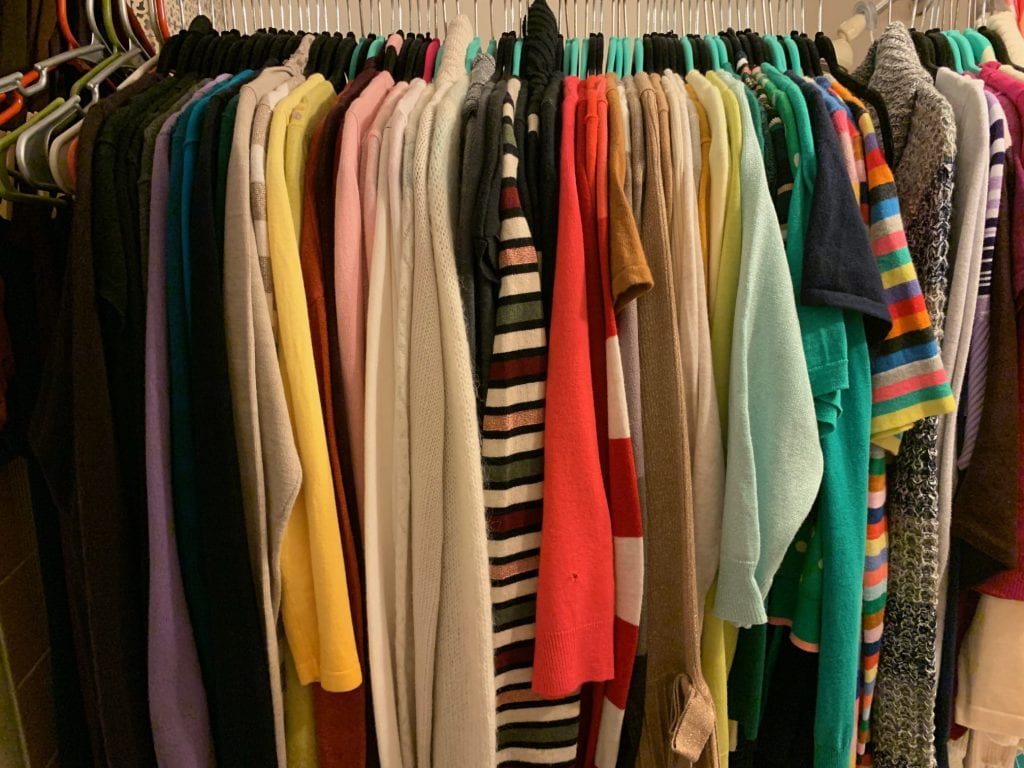

According to the film, Bangladesh is the second largest fashion producing market in the world after China. In 2013 the Rana Plaza took over 1,000 lives and had been noted as the worst garment disaster in history. In the year following the tragedy, the fashion industry had its most profitable year. Despite the trillions of dollars made globally by the industry, the lives of the workers are disposable. There is no standard wage or guarantee of work conditions. In Cambodia, garment workers protested and demanded a living wage of $160 US a month. The protesters met with aggressive government force that resulted in the deaths of five workers and several others injured. Companies in low-wage countries do not own the factories or hire the workers. Therefore, they are not officially responsible for the treatment of workers and the human rights violations they endure as a byproduct of their need to work. The research of Kevin Bales reveals the depths of the impact of the global economy on human lives in his books on disposable people.
As consumers in a capitalistic society, we distance ourselves from the devastation of poverty and inequality by comforting ourselves with the notion of ‘at least it’s a job’ and ‘sweatshops have the potential to bring about a better life for workers eventually.’ In a Fox News interview highlighted in the documentary, Benjamin Powell of the Free Market Institute defined sweatshops as “places with very poor working conditions as us, normal Americans would experience. Very low wages by our standard. Maybe children working; places that might not obey local labor laws. But there is a key characteristic of the ones I want to talk to you about tonight, Kennedy [the host of the show], and that’s they’re places where people choose to work. Admittedly from a bad set of other options.” There are several things worth noting about Powell’s statement. First, he acknowledges that the conditions are deplorable. Second, he knows that ordinary Americans have not experienced any situations like this. Third, he knows that there is a possibility that children are employed in these factories because there is no enforcement of local labor laws. Lastly, he soothes his conscious and those of the viewer by suggesting people choose to work there. In an article, Powell and Zwolinski argue that the anti-sweatshop movement fails in at least one of two ways: internally by failing to maintain their allegiance or externally but uncontroversial by yielding to objections that should be viewed as legitimate concerns. They insist that sweatshop workers voluntarily accept the conditions because it is a better alternative for them. Is it American pride that allows us to assume that a citizen of another country would willingly choose to work in a job to feed and clothe their children/family that Americans would not do? Have we become so full of ourselves that we willfully accept the sweatshop conditions for others but not ourselves for a $5 t-shirt or $15 dress?
The documentary states that fashion is the most labor dependent industry with nearly 1 in 6 working globally in some part of it. Most of the work is done by those with no voice in the supply chain. Many factory working parents must leave their children to be reared by other family members who live outside of the city or factory area due to the long hours and low-wages; eventually seeing them only once or twice a year. Shima, an Indian garment worker, tearfully states, “There is no limit to the struggle of Bangladeshi workers. People have no idea how difficult it is for us to make the clothing. They only buy it and wear it. I believe these clothes are produced by our blood. A lot of garment workers die in different accidents. [Regarding Rana Plaza] A lot of workers died there. It’s very painful for us. I don’t want anyone wearing anything, which is produced by our blood. We want better working conditions so that everyone becomes aware.” Livia Firth, creative director of Eco-Age, chides that we are profiting off their need to work. They are not different from us, but we treat them with disrespect and like slaves. Economist Richard Wolff concludes that American desire for profit at all cost is in direct competition to the values we claim to possess as Americans. In other words, as consumers of fast-fashion, we are perpetrators of injustice because we assist in the exploitation of workers through the violation of their human rights. Our capitalist economy thrives on our insatiable greed, our irrational fear, and our thirst for power all at the expense of someone else’s survival in poverty and inequality.
Am I anti-capitalism? Perhaps. I am anti-inequality and the continuation of needless injustice at the expense of those most vulnerable so if the divide between the haves and the have-nots continues to widen because of capitalism, then yes, wholeheartedly I am against it. Beyond whether I am anti-capitalist lies the question of whether I can remain unchanged when faced with the narrative of someone surviving in an unjust situation? Put another way: can someone with less social and economic power speak into my life and cause me to change? Yes.
If our economic system thrives on our individual and collective materialism, then any change in our behavior and values will change the system. Changes in our individual and collective action and values mean changes in the individual and collective lives of those on the other end of the thread and sewing needle. This year I have learned that challenging myself to live in a way that keeps the narratives of those who cannot speak up for themselves t the forefront of my mind is—I joined with them—our collective way of speaking truth to power.
You can join us!