By Eva Pechtl
In my introductory blog on ‘How Stigma Hurts,’ I reviewed the opium crisis and the stigmatization of opium smoking by Chinese immigrants. I highly recommend reading this to better understand how addiction was viewed differently depending on the communities using drugs, and usually viewed negatively if that person is already seen as an ‘other.’ While anti-opium sentiment was centrally anti-Chinese, the anti-marijuana sentiment that developed in the 1900s was also, in ways, spurred by racist notions. It may be hard to hear, but the history of drugs has cultural complexities. In this blog, I will continue exploring the history of Marijuana stigmatization and how it intertwines with ethnic bias. I will review current information on the effects of marijuana, explain the shift from referring to weed as ‘marihuana’ to ‘marijuana,’ and display how the criminalization of marijuana has had a heavy toll relevant to Mexican and Black communities in the justice system.

History of Marijuana Propaganda
Marijuana, or cannabis, is a type of cannabinoid drug commonly known as weed, pot, or dope. The dried flowers from the cannabis plant contain compounds or cannabinoids, which can be impairing or mind-altering. Medical marijuana is prescribed for chronic pain relief, nausea relief, managing diseases, and stimulating the appetite. Marijuana is used to manage the side effects of cancer and cancer therapies, relieving nausea and vomiting from chemotherapy and severe nerve pain. Marijuana produces a euphoric, relaxing effect and affects the brain more rapidly if smoked, and the Center for Disease Control estimates that 10% of cannabis users become addicted. However, marijuana can cause disorientation and negative effects on mental health, especially when used frequently and in high doses. Smoking, in general, increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and vascular diseases, and marijuana smoke carries many toxins similar to tobacco smoke. Today, marijuana legality is increasingly accepted but still controversial in the US, and is currently regulated by each state separately.
Before accurate information was provided about its effects, marijuana was highly questioned and feared in the US. In 1930, the Federal Bureau of Narcotics was created to address rising problems with many drugs, but with a particular focus on Marijuana. When alcohol prohibition was repealed, people in power and policymakers found marijuana as the next appropriate target to deem as detrimental to the country, as well as the communities using it. Weed was strongly stigmatized to be associated with Mexican immigrants since it was presumed to have been brought with those fleeing from the Mexican Revolution in the early 1900s. This is despite weed being farmed in North America since the 1600s and used generously in over-the-counter medicine since the 1840s.

Mass propaganda was produced by the federal government to induce fear about weed, linking marijuana with the devil, the degradation of women, and insanity. A notable example of this is the film Reefer Madness, an exploitation film showing high school students becoming addicted to marijuana and then committing various crimes such as manslaughter and attempted rape. The film misrepresents the realistic effects as the teens experience hallucinations, more relevantly representing the desire to demonize and, in that way, oppress drug users. When high, the teenagers in the film descend into unpredictable and insane behavior, perpetuating the notion that those who use marijuana, and interchangeably certain communities, were violent and criminal threats to the US.
From ‘Marihuana’ to ‘Marijuana’
The ‘Mexican Hypothesis’ of drug prohibition demonstrates how the extreme prejudice already well-developed against Mexicans was then attached to their drug of choice. In Mexico, in the 1900s, the common notion of marijuana users was dangerous and unpredictable behavior concentrated among prisoners or soldiers. However, a sort of “Mexican marihuana folklore” was instilled in Americans, and this racist sentiment only grew when immigrants’ effects on the economy made them more threatening. In the context of unemployment increasing public fear of immigrants, many acknowledge that the fear of marijuana was tied to intentional racist undertones, specifically associating Mexican communities with violence and crime. The change in spelling from marihuana to marijuana in legislation, plus references to Mexican ‘locoweed’ or ‘crazy weed’ from Spanish to English, reflects the deliberately xenophobic choice to associate the drug with Mexican immigrants and, frankly, any Mexican communities. Referring to weed or hemp as a foreign, unrecognizable word caused actual confusion, and some Americans did not realize the “new Mexican drug” was the same plant that had already been farmed and used in the US for many years.
Harry Anslinger was a leader in the Bureau of Narcotics and, unfortunately, a notable proponent of repressive anti-drug measures. Some sources reflect that before Anslinger took office, he expressed that claims of marijuana inciting violence or insanity were absurd. His immediate change in opinion when he began his leadership seems to reflect a political power’s interest in finding something and someone to strictly prohibit rather than using his own opinion to advance regulation purposes. Anslinger used his position to defund, discredit, and prevent the publication of research that contradicted his reasoning for marijuana penalties, claiming the drug was something to fear to an extreme. This is an early example of actions by the government raising assumptions that the drug wars weren’t really meant to increase public safety. Anslinger expressed throughout his campaign that marijuana users were infectious and even that they caused white women to be sexually promiscuous with men of color. Overall, Anslinger and related anti-drug propaganda associated drugs with people of color and induced panic and fear about both.
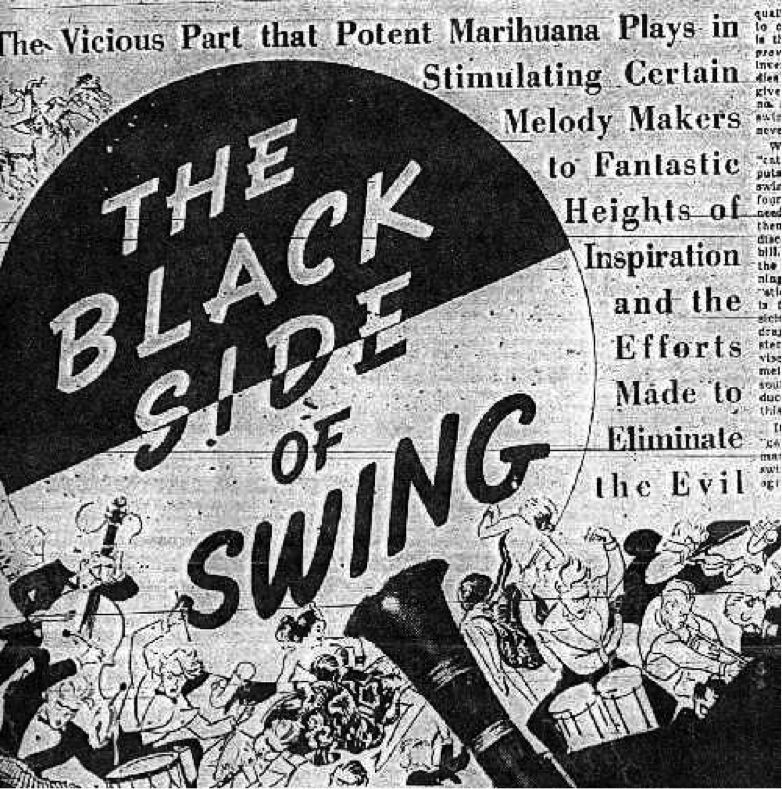
From another perspective, marijuana was specially connected to jazz music and the Harlem Renaissance, a creative movement in Black culture in the 1920s. This period embraced the reconceptualization of Black identity apart from the negative stereotypes that had impacted their relationship to their heritage and communities. Harry Anslinger also publicly complained about Black people, claiming the music of the cultural revolution was satanic and that “jazz and swing results from marijuana use.”
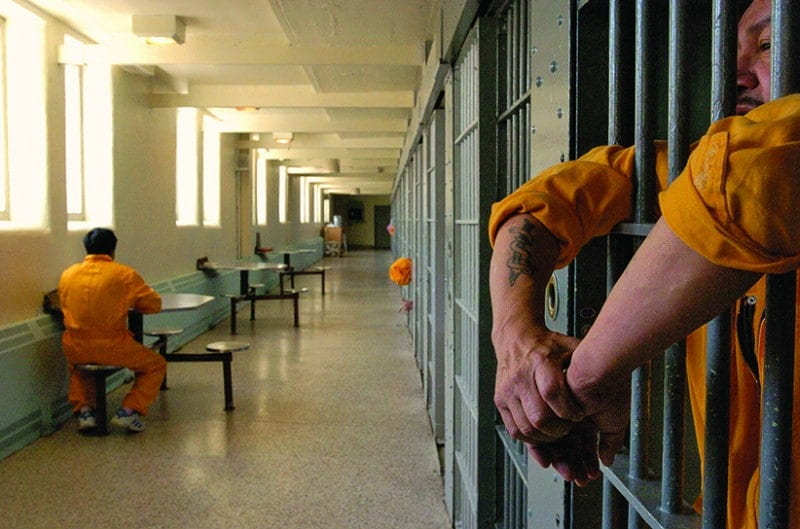
Understanding Criminalization
In 1937, the Marijuana Tax Act criminalized and regulated marijuana use, including an expensive stamp requirement, which made legal compliance nearly impossible for people living in poverty. Income inequality disproportionately affected communities of color due to the racial wealth gap, which was about 10 to 1 for White to Black in 1920, with Latinos unrecognized. No longer being able to afford this drug led to the emergence of illegal markets among communities of color. In the meantime, wealthier White communities could still purchase and use marijuana without violating the law. One’s race and class contribute to their risk of criminalization, and the overrepresentation of certain groups easily invites stigmatization. White communities were not subject to the bias or policy that racial and ethnic minorities faced, and still, in this century, people of color are overrepresented in marijuana arrests. Institutional factors like financial means, neighborhood of residence, and unconscious bias in policing practices are said to contribute to continued discrimination.

The government continued to strengthen cannabis regulation, with the Boggs Act in 1951 establishing 2-5 year minimum sentences for first-time drug offenses. This essentially treated weed as harshly as heroin, and representatives clarified that repressive legislation on marijuana belonged in the Narcotics Control Act of 1956, later classified as a Schedule 1 dangerous drug by the Controlled Substances Act in 1971. Prejudice against Mexican immigrants played a fundamental role in federal prohibition, as some employers and stakeholders feared Mexican people as a source of crime and drugs. Legal scholars Bonnie and Whitebread acknowledge past federal law, noting that as immigrants supposedly introduced marijuana smoking to the US, anti-marijuana statutes followed in the states along with Mexican migration patterns. Around the 1960s, marijuana became popular among the middle class and mostly white college students, a movement that I will explore in my coming blog about the counterculture movement and Peyote in Indigenous culture. Similarly to that topic, existing punishments for marijuana appeared inappropriate once people of different classes and communities advocated for its free use. What is highlighted in Isaac Campos’ reassessment of prohibition is how extremely stigmatized a drug was that was so historically used and relatively mild in effects. Discrimination was even clearer cut in news sources, with claims that Mexican peddlers would distribute marijuana samples to children and the idea that marijuana was a direct product of unrestricted immigration.
So far, in the ‘How Stigma Hurts’ series, exploring bias in responses to early drug crises has revealed similarities across the criminalization of Chinese people and opium smoking and the scare about Mexican and Black people over marijuana. Especially strong was the idea that immigrants and these drugs would harm the purity of white women. Since bias was so ingrained in society, it was simple for people to follow along with repressive legislation because it made sense to them to criminalize these minorities. Importantly, government responses to these issues demonstrate the dangerous effects of a lack of knowledge, especially the tendency to falsely attribute national issues to international people. In times when information about novel drugs was scarce, the same drugs were viewed and criminalized differently because of the groups using them.