by Caileigh Moose
Since the 1960s, the demographics of immigrants entering France have shifted. In 1968, the largest immigrant groups included Spaniards, Italians, and Portuguese, and were primarily Christian in faith. Today, the majority of these groups come from North African nations like Algeria, Morocco, and Tunisia, where Islam is the predominant religion. Thus, with these immigration shifts, in recent years, Islam has become the second largest faith in France, accounting for 10 percent of the French population, second to Christianity, which rests at almost 30% percent.
This diversification of society has unleashed reactive backlash, with many on the French right driving up what many have called anti-Islam and Islamophobic policies. Recent examples include the 2004 French law forbidding “conspicuous” religious symbols in France and the 2021 French separatism law, which extended the “neutrality principle” (under which civil servants are, among other things, prevented from wearing religious symbols like hijabs) to all private contractors of public services. One political science researcher with the National Centre of Scientific Research has deemed current French president Emmanuel Macron’s first term “gloomy” for French Muslim citizens, referring to the ever-darkening outlook for religious protections that has colored the tone of French policy during Macron’s time in office.
All these fears have culminated in the newest piece of legislation targeting France’s growing Muslim population, so that this year, as French schools started back earlier this September, their female students faced a new, highly controversial restriction: a ban on the abaya.
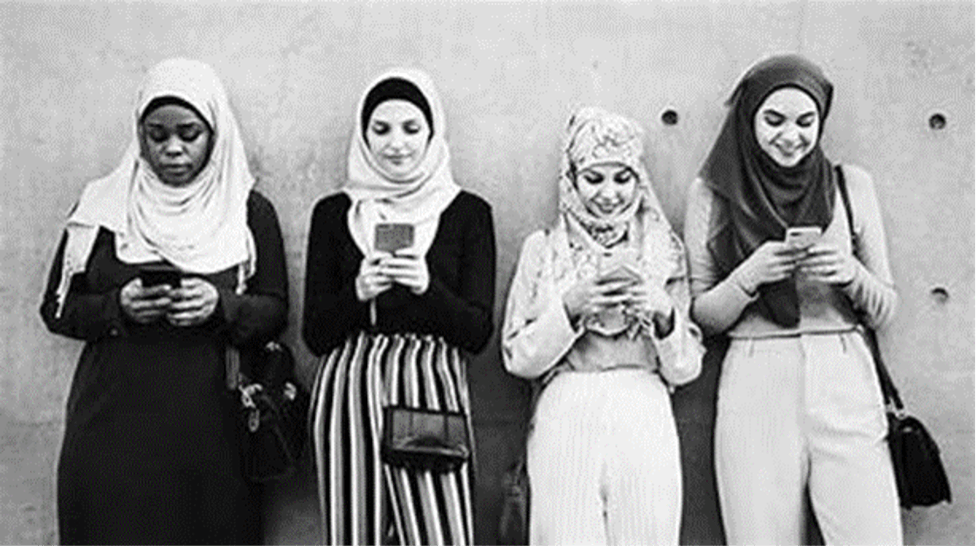

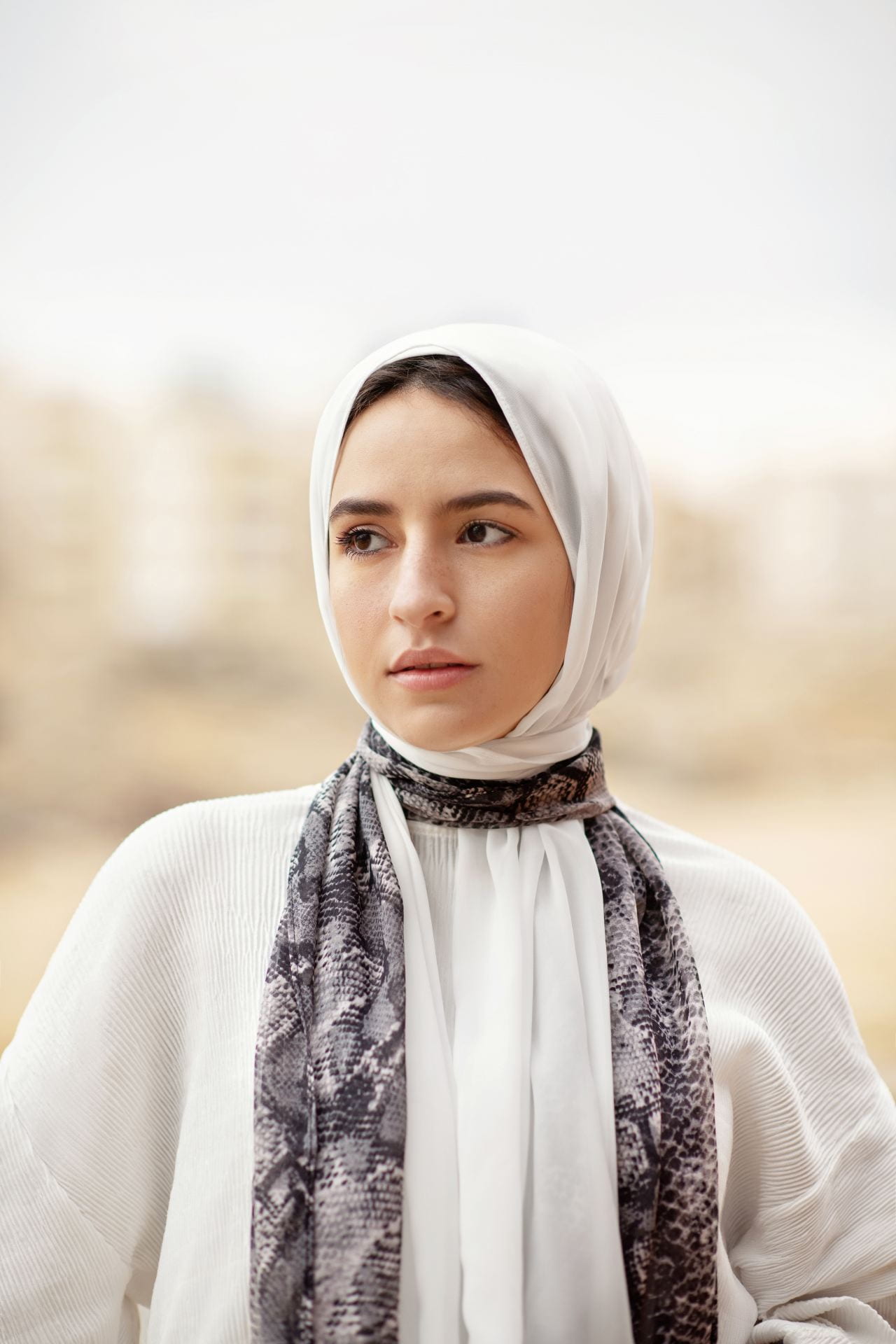
The abaya, which is sometimes simply referred to as the aba, is most commonly known as a loose, typically black, floor-length dress worn primarily by Muslim women. The word itself, translated from Arabic, means simply “dress.” The abaya is mainly popular in the Middle Eastern region of the world, in nations like Saudi Arabia or Yemen, where the garment’s prevalence can be attributed to its alignment with cultural and religious preferences towards modesty within the area.
Its ban was justified by French Education Minister Gabriel Attal through the French concept of “laïcité.” This term essentially defines the ardent secularism that France has in relation to its public institutions, arguably much stricter than an average American’s idea of what the separation of church and state looks like. For example, this idea of laïcité has previously led to the ban of all overtly religious symbols within French public schools, including large Christian crosses, Jewish kippahs, and Islamic hijabs. Now, it is being used to target the abaya. French Education Minister Gabriel Attal attempted to explain the decision through the reasoning that “when put in the framework of a school, it is very clear: you enter a classroom, and you must not be able to identify the religious identity of students just by looking at them.”
Those who celebrate the law are quick to draw this religious connection between the abaya and Islam. However, it is important here to recognize that the abaya is not itself directly connected to the religion of Islam but to select Muslim cultures. Despite what the French Ministry of Education claims about how wearers of the abaya are “immediately recognizable as belonging to the Muslim religion” and, as such, violate the standards for secularism within the French educational system, opponents of the ban have protested that the abaya has no direct religious affiliation. Its wearing is not mandated by any Islamic text, nor is it compulsory dress for the religion; it merely fulfills the religion’s requirements regarding modesty.
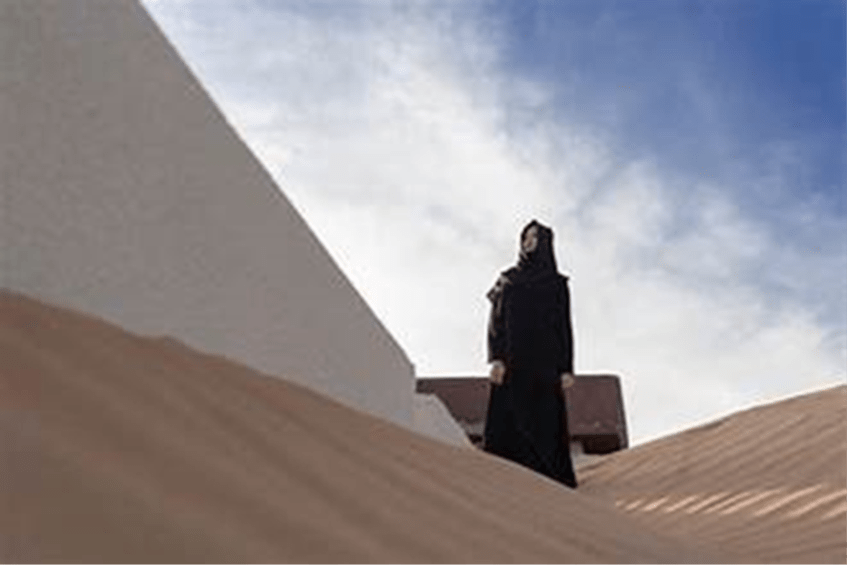

In 2018, a Saudi senior religious scholar of Islam drew mixed reactions when he stated that the abaya shouldn’t be expected or necessary dress for Muslim women, citing the statistic that over ninety percent of practicing Muslim women do not, in fact, wear the abaya. Instead, most women will simply choose to wear loose-fitting dresses, ankle-length skirts, long-sleeved shirts, and anything else that meets the modest standards of their religion, all of which are typical in Western culture and all of which are completely acceptable to wear inside a French school. This may lead some to ask the question: Is this ban truly in keeping with France’s educational goals of secularism, or does it simply originate from a xenophobic attitude surrounding Muslim culture and the modest standards they practice?
Many members of France’s Left would argue the latter. Jean-Luc Mélenchon, a 2022 French presidential candidate, accused the ban of initiating an “absurd, entirely artificial religious war about a woman’s dress,” and Clémentine Autain, one of La France Insoumise’s MPs, called it “characteristic of an obsessional rejection of Muslims.” The ADM (Action Droits des Musulmans), a group that advocates for the rights of Muslims within France, expressed concerns about the risks of ethnic profiling in schools and how the ban might create a target on the backs of Muslim children, especially since the ban includes no clear legal definition of what an abaya is. It will now be up to the school officials and administration to determine what constitutes an abaya and what does not, further fueling speculation that the ban is discriminatory in nature and will only encourage one-sided racial and ethnic stereotyping based on “the supposed origin, last name or skin color” rather than what they wore.
However, despite bringing legal challenges and these concerns over its implementation, France’s highest administrative court, The Council of State, upheld the law in early September, finding that the abaya “was part of a process of religious affirmation” based on the comments from student discussions. France’s new school year has already seen some resistance to the new legislation, with almost 70 Muslim girls sent home on the first day of school for refusing to change their attire in accordance with the new dress code. Whether it serves to reinforce or deteriorate the rights of all French students, time will tell.
If you would like to learn more about the potential social justice impact of this new legislation and what resistance the ban will see in the future, you can visit ADM’s website.