There is a common misconception among people that environmental rights are necessary, but they have nothing to do with human rights. Some consider environmental rights as something that is another genre of human rights, not recognizing that without the environment, we as humans seize to exist. Human rights are dependent on the environment, and we can address many environmental rights issues to bring about a better world for all those who live on this green and blue planet that we call home. In this sense, environmental rights ARE human rights, and taking a human rights approach to addressing these environmental rights can close the gaps of inequality between the Global North and the Global South countries. I am dedicating a series to deep dive into this human rights approach to environmental rights, starting with how food, water, and air, the essential needs for all living things, can be transformed with a human rights approach to address some of the most egregious practices in these fields.
Food insecurity, food shortages, and healthy food consumption in general

Food Insecurity
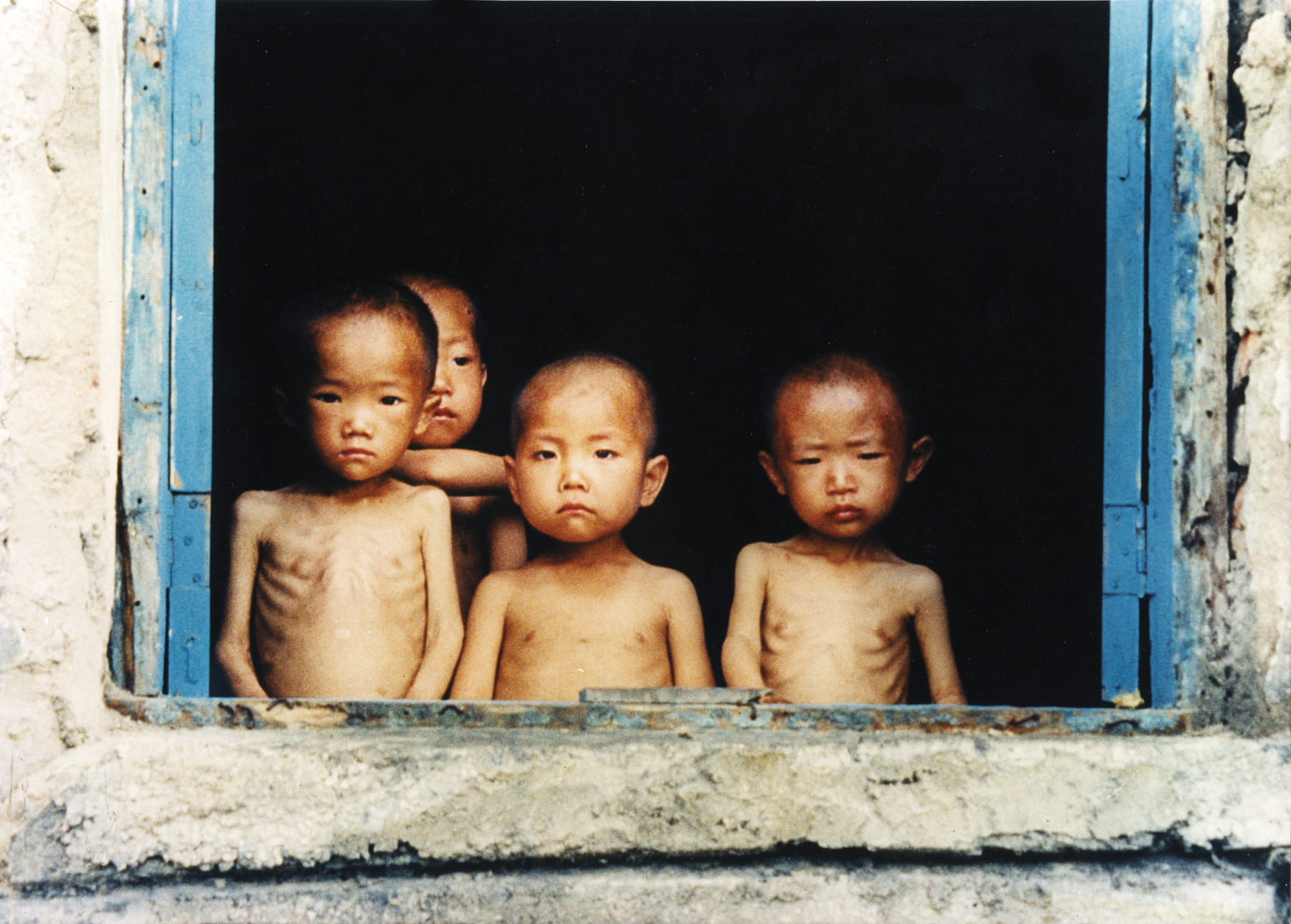
The issue of food insecurity is widespread in many nations worldwide, and it has only increased due to the supply-chain issues that were experienced during the pandemic. While many of the nations that face food insecurity are from the Global South, it is just as prevalent in America, one of the richest nations in the world. For more on food insecurity in America, check out this blog.
Community Gardens
One way to address this issue with a human rights approach would be to encourage the cultivation of community gardens locally to avoid supply chain issues. This would alleviate the issue of transporting the necessary products to and from places (reducing the carbon emissions in the process), provide jobs to local community members, and even cut down costs for the produce. Furthermore, members in charge of taking care of the community gardens would be trained on how to avoid the use of harmful pesticides that are known to cause health issues in humans. These chemicals are not only harmful to humans, but they are also causing bees and other pollinators to go extinct. These pollinators are largely responsible for producing crops around the world, and without them, we would have to engineer mechanical pollinators or manually perform the pollination process, both of which would cost a lot of time, energy, and money.
Alternate forms of Agriculture – Hydroponics

For those communities that do not have rich soil, they can use the technology of greenhouses and other indoor cultivation technology to meet their needs. In fact, there are three types of indoor farming that are currently common in the agricultural industry – aquaponics, aeroponics, and hydroponics. Hydroponics eliminates the need for rich soils by making use of water and a mixture of liquid nutrients to supplement the plants’ needs as they grow. This technique can be used for everyday households and industrial-level agriculture, and it has quite a lot of benefits for the environment as well. For one, it uses less water than traditional agricultural practices, and it does not require soil, so it is not impacted by conditions of soil erosion. It also yields greater produce and eliminates the need for pesticides and herbicides which in turn make the crops safer for consumption and reduces the risk of health issues as a result. Also, plants can grow almost twice as fast as the ones that are grown in soil.
Alternate forms of Agriculture – Aeroponics
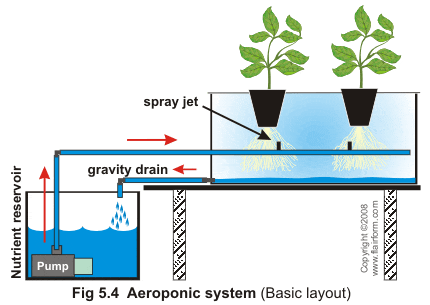
Another indoor cultivation system is Aeroponics. Aeroponics uses water and a mixture of liquid nutrients like hydroponics, but in this technique, the roots are suspended in the air and are misted on a timer to keep them from drying out. This requires a lot of technical precision and uses a lot of energy. While it is a technique that utilizes a lot of energy, according to NASA, it also reduces the use of water (similar to hydroponics) by 98%, and pesticide use by 100%, and still maximizes the yields these crops produce. Additionally, plants grown using this technique have added health benefits, as they absorb more minerals and vitamins. Some setbacks to this method are the fact that this technique needs experts who can monitor the plants and the pH levels of the air. This method is also vulnerable to electrical shortages and requires a lot of advanced technologies to perform successfully, and yield crops. As a result, it is very expensive to initially set it up.
Alternate forms of Agriculture – Aquaponics
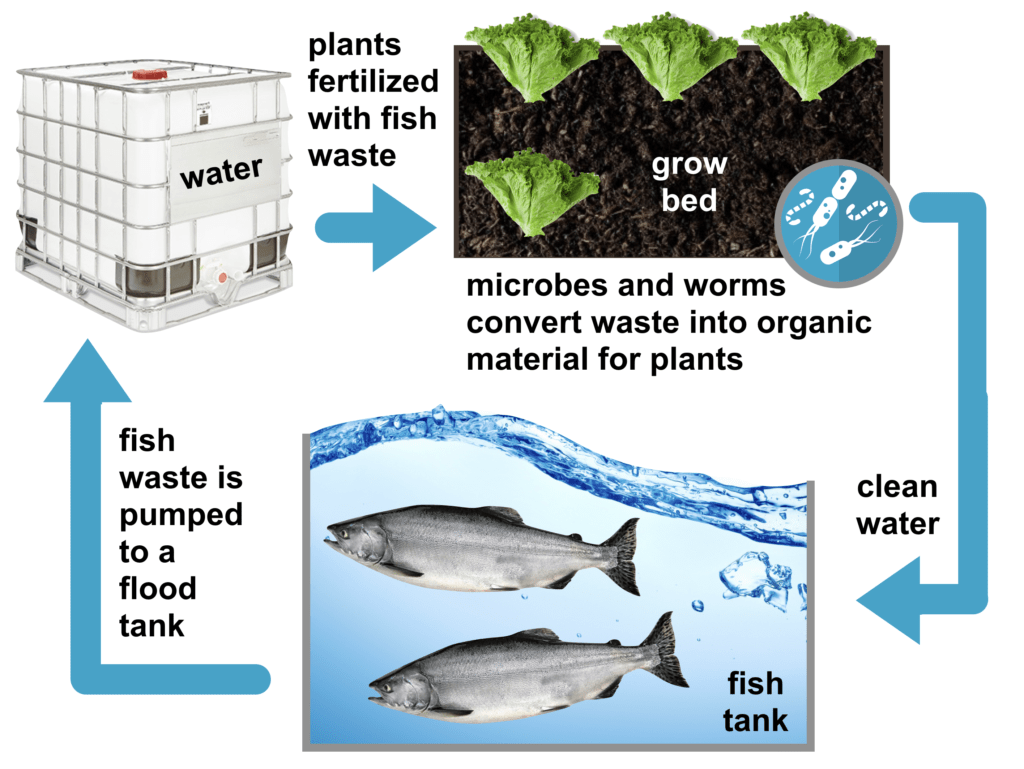
Finally, Aquaponics is another indoor cultivation technique that has become popular today. Similar to hydroponics, aquaponics also has a reservoir where the plants are stored, yet in aquaponics, the reservoir also contains fish. Instead of using a mixture of liquid nutrients, the fishes provide those nutrients naturally to the plants. This may sound a bit strange, but the ammonia that is released by the fishes (particularly their feces) gets converted into nitrates which provide nutrition for the plants. One thing to be careful of when using this method is to constantly check on the ammonia levels, because really high levels of ammonia will actually end up killing the fish. Other than that, the whole process takes about 6 months for the plants and fishes to form their own ecosystem that can operate without much maintenance or monitoring. There are also many benefits to using this system, including the fact that you are able to cultivate plants and fish, two food sources instead of one. Due to the fact that the water is recycled through natural processes, this method does not waste any water, and there is no need for chemicals to upkeep the plants either. The fishes provide all the nutrients that the plants need, so there is no need to top off any liquid nutrients like in the other two methods, saving a lot of money in the long run. This method is great for the environment, and because it has its own ecosystem, it is also sustainable on its own. Of course, with this method, in the winter, the reservoir needs to be kept warm, so that the water and all the fish and plants do not die off from the cold. It also requires the monitoring of pH levels like the aeroponics method does, and since this method uses fish, it requires that you know how to take care of the fish for the greatest success.
These are just some ways to address the need for better food-producing systems, as well as the elimination of harmful chemicals within our produce. As an added bonus, these systems use less water than traditional farming techniques, produce greater yields, and are healthier for consumption, all while taking up less space than farming on a field.
Wasteful Practices – GMOs and Food Waste

Additionally, a wasteful practice that the current agricultural companies invest in is the selling of genetically modified seeds known as “terminator seeds“. These are seeds that are genetically modified to yield crops for only a single generation. This means that the seed cannot reproduce again, and the farmers have to continue to buy new seeds every year. This is an attempt by Big Agricultural companies like Monsanto to increase their profit margins. This greedy practice on the part of Monsanto and other Agricultural companies, replace the natural, sustainable regrowth of crops to ensure that the farmers have to continue to purchase new seeds from the companies instead of using the seeds that are yielded with their crop. This practice is egregious, and addressing this is yet another way to ensure that we promote the natural functions of our environment.
Food waste is another major issue that we face in today’s society. As discussed above, food insecurity is an issue that impacts over 34 million Americans today. Hence, it is unfortunate to find out how much food is wasted in this nation, whether it is unused food, crops left unharvested due to price drops or abundance of crops in the market, or even supply chain issues. Residential consumers in homes and those in restaurants and other stores that sell produce may not be able to sell all the products they have available, especially if the produce does not appear to be picture-perfect. Farmers may not harvest many of their crops if there is an abundance of the crop they have grown in the market that season, wasting the produce that was grown but never made it to the market. As we saw during the pandemic, supply chain issues can cause a lot of food waste as well. Many farmers had to waste their crop yields as they had no way to transport these products to the local grocery stores. Many industries halted during the pandemic, making the products they produced go to waste. Every year, 40% of the food available to Americans ends up being wasted. This is painfully wasteful, especially when we consider how many people across the world, including children, go hungry every day.
Conditions in Meat and Dairy Farms
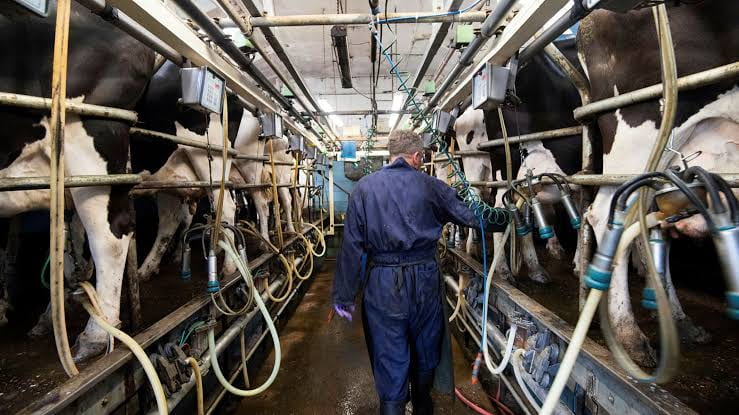

For those who are meat eaters, having a few local farms provide the meat you consume (with regulations of course) can ensure that your meat is not contaminated and that the livestock was treated in ethical ways. Currently, the meat industry produces in bulk, and their practices are cruel and inhumane toward their livestock. Chickens and pigs are forcibly held in cages barely enough for them to stand in, and they live their lives inside these cages stacked on top of each other to save space. This means that they are urinating and defecating on top of each other, which is not only unsanitary and inhumane, but it can also cause the animals to develop diseases and illnesses. Additionally, cows that are not raised on grazing land are usually held in large factory farms, where they are used as dairy cows until they can no longer produce milk, in which case, they are sent to be slaughtered for meat. Certain practices used today, like genetically modifying cows to produce more milk outside of their normal milk-production periods, can lead to an increase in health risks for these animals as well.
These practices are cruel and inhumane, and they are also very bad for the environment. Not only do these farm animals add to the increasing amounts of greenhouse gases present in our atmosphere, but their wastes are also polluting the nearby waterways, making the water unsafe for the locals who live near these factory farms. All this cruelty and unsanitary conditions also carry over when these animals are slaughtered and distributed for mass consumption by companies like Tyson. During the pandemic, there were many reports about the unsafe and unsanitary conditions for the workers inside these meat distribution companies, and stories went viral of contaminated meat with fingernails and other disturbing elements found inside the meat packages. Many of the workers within these meat packaging factories actually lost their lives due to the companies’ negligence regarding their workers’ safety during the pandemic.
Food is a Human Right

Food is a necessity for all human beings, regardless of who you are, or where you live. The type of cuisine you prefer may vary from region to region, from culture to culture, and from one environment to the next, but the fact still remains that every human being needs to eat to survive. By definition, food is a human right, and this is indicated in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) under Article 25. Though this article does not specify this detail, it should be the right to healthy and nutritious food, rather than the generalized term food. This minor change in language would ensure that higher regulations are maintained on food and agricultural industries and eliminate harmful chemicals and ingredients within our food sources. There is an unequal distribution of food just like there is an unequal distribution of wealth and wages across the world. These food shortages can be addressed using these various techniques of indoor farming and community gardens, while safer produce can be cultivated by avoiding the use of pesticides and herbicides. Livestock can be treated more humanely instead of being stuffed in factory farms, and there needs to be a shift from a mindset of profit to a mindset of proficiency within these food industries.
This is one blog out of a series of blogs that will focus on how environmental rights are human rights. The next installation of this series will focus on how water is a human right, and how issues surrounding access to clean water can be addressed with a human rights approach.