by Delisha Valacheril

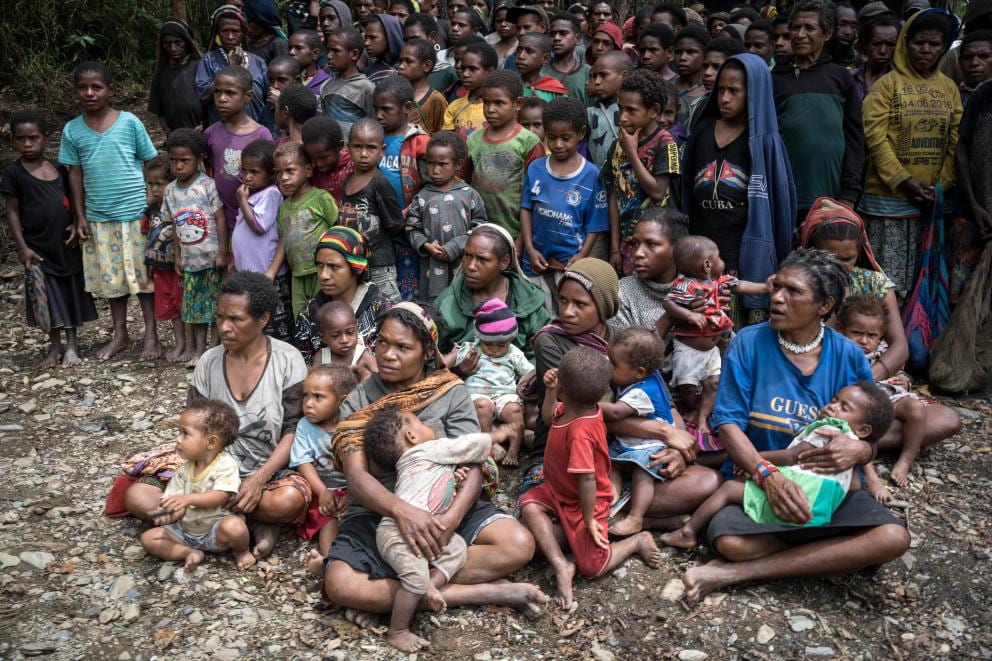
Chinese vlogger captured a horrific, viral video of a woman chained outside to a hut in January of 2022. This woman was mentally incapacitated and had been without clean water, food, and electricity for an extended time. Xiao Huamei had been taken from her home province of Yunnan and sold to a farmer in Jiangsu for 5,000 yuan – or $790 at the time. She managed to escape him only to be sold into marriage trafficking two more times. The last time occurred in June 1998, when Dong Zhimin bought Xiao Huamei and subsequently tortured her, forced her to bear children, and subjected her to barbaric conditions. At the hands of Dong Zhimin, her husband, she was forced to have eight children in nine years, the firstborn in 1999. From when she was sold in 1998 to when she was found in 2022, Xiao Huamei had been a victim of marriage trafficking for 24 years. Claiming she had schizophrenia, Dong Zhimin subjected her to inhumane treatment, such as chaining her up outside like a dog. Dong Zhimin was sentenced to only nine years in prison. Sentences for trafficking crimes are typically capped at ten years. This spurred public outrage online because many felt the punishment did not fit the crime. Ten years is not even enough time to conceive and carry eight children. This case raised awareness about the lack of reforms for marriage and human trafficking.

What is marriage trafficking?
Marriage trafficking is an international problem that continues to grow and must be handled domestically. It is defined by the transfer or receipt of a person; the means may include deception, threats, or coercion, and the purpose may be sexual exploitation and/or servitude. Cases like Xiao Huamei’s are not isolated to domestic women because foreign women are also exploited and sold to Chinese men to be abused and breed children. Traffickers target vulnerable young women and children in their country as well as neighboring countries. Women in Myanmar, Cambodia, and Vietnam who are trying to flee political unrest and economic instability are highly exploited in this situation. Vulnerable, job-seeking women are tricked into entering the arrangement through a broker that is offering well-paying jobs across the job, thus meeting the criteria for an overt act of marriage trafficking. Traffickers smuggle these women in using coercion, violence, and threats. The process used to transport these women also constitutes human trafficking.
The prevalence of trafficking in China is exacerbated by the lack of accountability among government officials. Chinese officials have allegedly turned down the appeals of women who have been trafficked, held them for extended periods, deported them without their children, and, in certain instances, returned them to their husbands in exchange for bribes. Chinese authorities rarely, if ever, pursue prosecutions against marriage trafficking charges. It is difficult to investigate due to the underground, illicit nature of marriage trafficking. In China, marriages between foreign-born women are not usually officially registered, which leads to their children being lost in the system.
The intent behind this industry is apparent from the illicit means used to facilitate the business. The purpose of the financial transaction of young women and children to Chinese men as brides is to uphold cultural values of marriage, family, and children. Based on sociological exchange theory, women enter the relationship expecting stability and support that is gained from marriage, while the men enter the relationship expecting a personal benefit that is gained from maintaining the cultural values of marriage. Most of the time, traffickers promise a better future to young women seeking to better their situation. This is not always the case, but it is the case of Xiao Huamei and foreign brides who are trafficked for marriage. While they migrate voluntarily, knowing that they are to be married, they are also often times deceived or trapped in their situations. Forcing these women into marriage means exerting power and control over them. The exploitation of vulnerable women and lack of individual freedoms constitute these cases as marriage trafficking.
What is responsible for this?
Given China’s longstanding one-child policy with a preference for boys, broader socioeconomic and political factors drive the marriage trafficking illicit market. Due to this, China experiences a gender imbalance, with about 35 million more males than females. The lack of eligible brides creates a demand for the marriage trafficking illicit market. An estimated 7,400 women and girls were victims of marriage trafficking in the Yunnan Province along the border, which is where Xiao Huamei was from. In rural areas, the proportion of women in society has declined. Among them, more than 5,000 females were compelled to bear children with their Chinese spouses. Bride trafficking in China constitutes human trafficking because there is an overt act, a thorough process, and an intentional purpose behind it. China, with its vast population and growing economic and regional disparities, experiences nearly every manifestation of marriage trafficking.

What is China’s response?
Under Chinese law, people face more fines for selling parakeets, a protected species, than for selling women. The government realizes there is an issue, and they have pledged to crack down on the illicit industry. Chinese police arrested more than 1,300 people suspected of assisting in marriage trafficking. However, women are still trafficked from Cambodia, Myanmar, and Vietnam. There needs to be safe passage for refugees from these countries so they do not fall victim to trafficking schemes. Despite past efforts, ongoing commitment is needed to fulfill these pledges and protect vulnerable individuals. To combat marriage trafficking, China needs to enforce stricter laws around forced marriage, childbearing, and immigration.
Victims of marriage trafficking were 6.5 times more likely to experience intimate partner violence compared to women in autonomous marriages. They are 4.7 times more likely to suffer a miscarriage or stillbirth and 4.6 times more likely to suffer the death of at least one child. There are many more women like Xiao Huamei. To protect them, there needs to be active, continued efforts to educate society about the harmful consequences of marriage trafficking. Coordinated programs with neighboring countries to address cross-border cases of marriage trafficking are essential. Providing social services at risk of being trafficked and offering safe entry into China will significantly impact the illicit economy. By addressing marriage trafficking through these comprehensive strategies, we can shape a world where everyone has the freedom to choose whom they marry and live a life free from coercion and violence.