by Pam Zuber

“That’s how we can end this dangerous cycle — by making sure that every single person we know makes their voice heard, in this election and in every election. Because when we all vote, we all do better.” –Michelle Obama, Shondaland, 2018
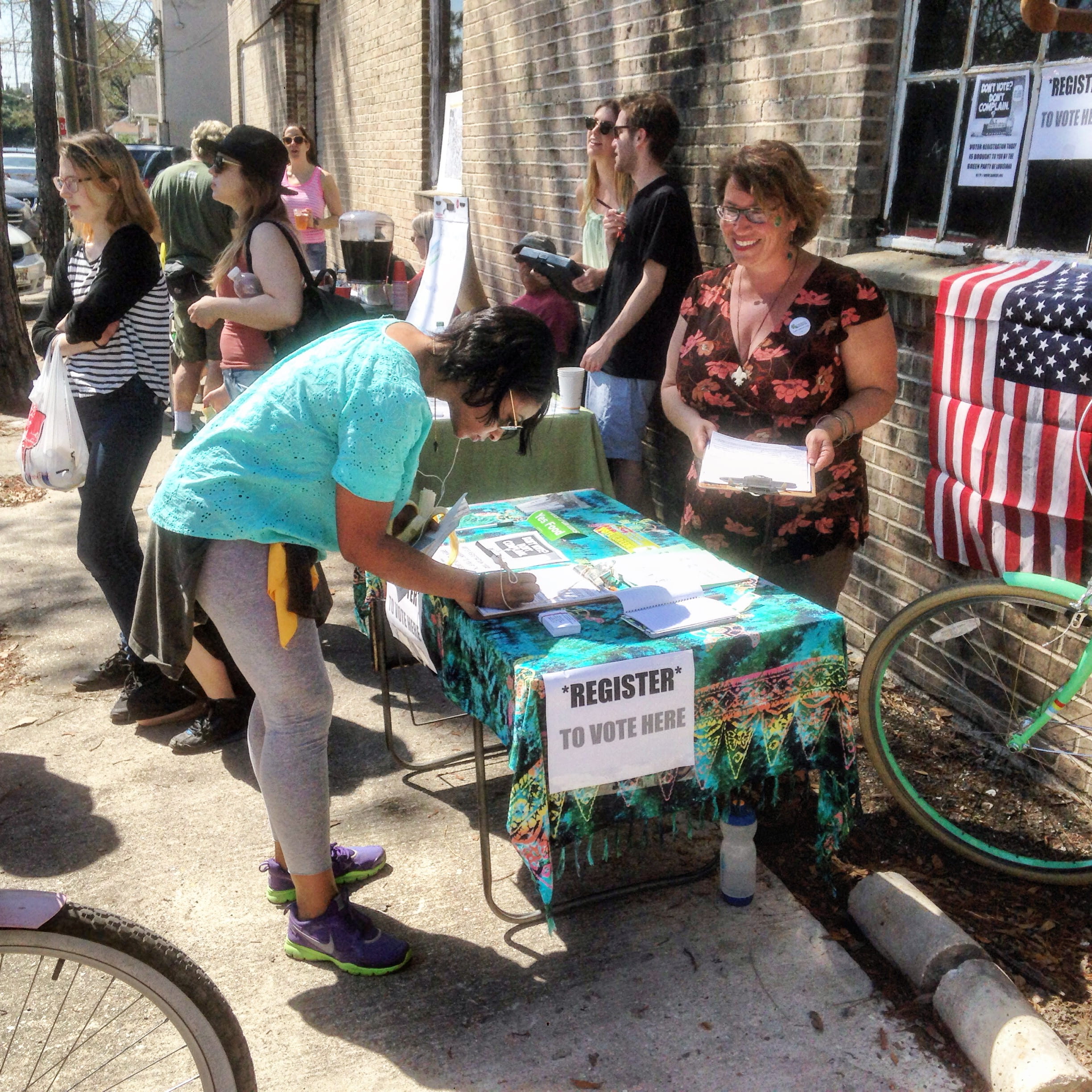
On November 6, 2018, we did do better in many areas. That’s because it was the day of the midterm election, a day that featured elections in several U.S. states. Voters in many of these states voted for proposals and candidates that promoted human rights and represented advancement. A few of the highlights:
Florida
Voters in the Sunshine State approved Proposal 4, a measure that will restore voting privileges to people who have completed serving their sentences for felonies that don’t include murders or felonious sexual assault. This measure is expected to restore the voting rights of more than one million Floridians. A significant number of these Florida residents are minorities. According to Vox, “In 2016, more than 418,000 black people out of a black voting-age population of more than 2.3 million, or 17.9 percent of potential black voters in Florida, had finished sentences but couldn’t vote due to a felony record.” Florida’s Proposal 4 thus will enfranchise people and create a voting pool that more accurately reflects the population of the state. Such voters might elect candidates and approve measures that resemble their lives and their desires, which could make the state more of representational democracy.
Colorado
Did you know that slavery is a punishment that is still legal in federal prisons? Slavery as a punishment is also legal in the constitutions of many U.S. states. But, this won’t be the case in Colorado. On November 6, 2018, voters in that state approved Amendment A, a proposal that would include language that bans slavery in its state constitution, two years after a similar proposal failed in the state. While banning all slavery for all reasons on both the state and the federal levels would obviously be a more humane and empowering decision, banning language that forbids slavery is a good first step. A small step, to be sure, but still a step in the right direction.
New York
Midterm elections in other states featured candidates who are sympathetic to human rights. New York voters elected Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez to the U.S. House of Representatives. Ocasio-Cortez is a woman of Puerto Rican descent and a self-described socialist whose platform endorsed criminal justice and immigration reform, expanded Medicare health coverage, gun control, LGBTIA+ and women’s rights, the promotion of peace, and support for senior citizens and Puerto Rico. Ocasio-Cortez stunned her home state and the nation when she defeated longtime Congressional representative Joe Crowley in the New York Democratic primary in June 2018. The representative’s political views thus place her in the company of fellow progressives such as independent senator Bernie Sanders of Vermont. This means it also places her in opposition to U.S. president Donald Trump. The 2018 midterm election gave Ocasio-Cortez and her fellow Democrats a majority in the U.S. House of Representatives. The U.S. Senate, meanwhile, retained a Republican majority, and the presidential administration is also Republican. Will these different political perspectives lead to bipartisanship? Conflict? How will they affect the politics and governance of the country?
Arizona
Arizona’s race for U.S. Senate may have been as interesting as its ultimate results. That’s because the race featured two women running for a Senate seat. Even though the results of the 2018 election means that a record number of women will serve as U.S. senators, this still means that twenty-four women will be U.S. senators. That makes the U.S. Senate 24% women. The population of the entire United States is 50.8% female, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. Women, then, are still underrepresented in the U.S. Senate compared to their overall totals in the general population. Since Arizona’s race featured two female candidates, it represented a more inclusive sort of political race, one that a female was bound to win, no matter what. And the race? It pitted Republican Martha McSally and Democrat Krysten Sinema. McSally also served as the first woman to fly in combat for the U.S. Air Force. Sinema won, receiving approximately 50% of the vote to McNally’s approximately 47.6%.
Georgia
Another new Congressperson, Lucia “Lucy” McBath of Georgia, has supported LGBTIA+ and women’s rights, immigrants, and the Affordable Care Act. Another focus of her work, gun safety, is sadly personal. That’s because, in 2012, a man shot and killed McBath’s unarmed seventeen-year-old son, Jordan Davis, arguing that the teen was playing music too loudly. The first trial for the crime ended in a mistrial in February 2014 after juror disagreements. After a second trial later that year, Davis’s murderer, Michael Dunn, was convicted and received a sentence of life imprisonment with no chance of parole. Her son’s death and further tragedies such as a 2018 mass shooting at a Parkland, Florida high school led McBath to become what she calls a reluctant activist and prompted her to run for office. McBath supports a host of gun safety measures, such as raising the age requirement to purchase firearms and banning weapon access for people convicted of domestic abuse.
Michigan
Women swept the top executive seats in the state of Michigan. Voters elected Gretchen Whitmer as governor, Dana Nessel as the attorney general, and Jocelyn Benson as the secretary of state. Openly gay Nessel also gained fame as the attorney in the case that legalized gay marriage and adoption in Michigan and helped pave the way for marriage equality in the nation. Whitmer, Nessel, and Benson joined Debbie Stabenow, who held her position as one of Michigan’s U.S. senators. They also join newly elected Rashida Tlaib, a Michigan attorney and civil rights advocate who was one of the first two Muslim women elected to the U.S. House of Representatives (newly elected Ilhan Omar of Minnesota was the other). Michigan voters also approved proposals that could impact state politics in the future. Proposal 2 was a measure that will establish a board of political party members and independent voters that will create legislative maps. This measure hopes to fight gerrymandering, the practice of creating maps to produce voter patterns that are favorable to specific political parties. Another voter-approved measure, Proposal 3, aims to make voting easier and fairer by making absentee ballots more available, automatically registering voters at state government offices, and enacting other measures.

Voters chose more diversity
Many other states elected women. In fact, so many women won their races that there will be a record number of women in the U.S. House of Representatives and the U.S. Senate. Two of these women are New Mexico’s Deb Haaland and Kansas’s Sharice Davids, who became the first female Native American members of the House of Representatives. Haaland, in fact, is a thirty-fifth generation New Mexican.
This surge of female power isn’t just confined to the legislative and executive branches. Nineteen black women campaigned to become judges in Harris County, Texas in 2018. All nineteen will serve as judges. Their campaigns have been dubbed Black Girl Magic and are emblematic of the growing power of African American women in political affairs. Observers hope that the Harris County judges will bring their diverse experiences to represent and work with the people of their area.
Speaking of diverse life experiences, U.S. Representative Ilhan Omar of Minnesota is a woman, a Muslim, and a refugee from Somalia. She wears hijabs, headscarves that some Muslim women wear, which has prompted members of the U.S. Congress to reconsider the legislative body’s ban on head coverings. Her experience as an immigrant could be crucial in shaping or fighting legislation relating to immigration and asylum in the coming years.
More members of the LGBTIA+ community are also running for and holding office. U.S. congressperson Sharice Davids and Michigan attorney general Dana Nessel are lesbians, and Colorado’s Jared Polis became the first openly gay man elected governor of a U.S. state. Previously, he was the first openly gay man elected to the U.S. Congress. And, although Christine Hallquist did not become Vermont’s governor, she did make history as “the first openly transgender gubernatorial candidate in the nation’s history,” according to Politico.
This is not to say that the results of the 2018 midterm election entirely supported inclusion and human rights. Alabama and West Virginia both approved measures that restrict abortions. Mississippi voters elected a senator, Cindy Hyde-Smith, who said she’d attend a public hanging in her enthusiasm for a supporter. Since Hyde-Smith’s competitor was an African American man, the senator-elect’s comments recalled the horror and ugliness of racially motivated lynchings in Mississippi and elsewhere in the nation.
But, even despite these developments, the election elected candidates from many different backgrounds with many different experiences and perspectives. It supported measures that aim to make life more inclusive for more U.S. residents. It approved candidates and measures that represent voters, acknowledge them, and give them agency. Michelle Obama was right. People who vote are broadcasting their voices. They’re working to help make life better for themselves, their fellow citizens, and future generations.
About the author: Pamela Zuber is a writer and editor who has written about a wide variety of topics, including physical and mental health, addiction, human rights, and gender.