by Pam Zuber
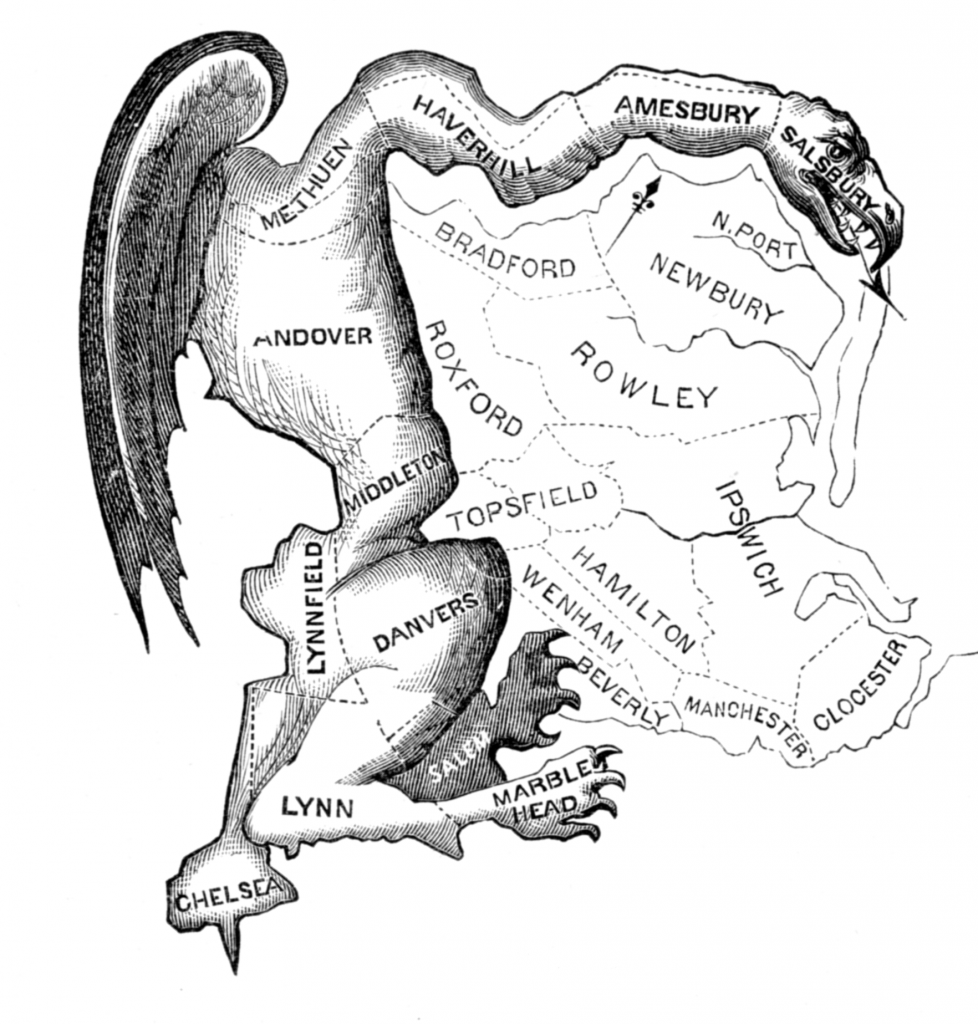
The Gerry-Mander is a name for a creature that appeared in editorial cartoons in 1812 and 1813. Given how gerrymandering has shaped and can shape politics in the United States, calling a Gerry-Mander a monster is no mere exaggeration. Gerrymandering takes its name from Massachusetts governor Elbridge Gerry. In 1812, legislators in Massachusetts’s Democratic-Republican Party redrew the map of a senatorial district to concentrate voters of its party in certain geographic areas. The same map dispersed voters of the rival political party, the Federalists, to separate districts.
Governor Gerry signed this map into law in 1812. This map drew the wrath of the opposing Federalists and spawned the cartoon that criticized the redistricting. The practice and the cartoon gave us a term for politically based redistricting that political bodies still use. We continue to use the term because the practice continues to this day. Politicians still reshape voting districts to suit their political purposes, much as they did in Gerry’s day.
Why Does Gerrymandering Violate Human Rights and the U.S. Constitution?
Creating electoral districts that skew political party representation contradicts democratic principles and human rights. Gerrymandering provides the illusion of democracy but actually denies it. The process still perpetuates voting districts. People in these districts have the ability to vote and usually have their choice of candidates. But, which candidates can they support? People in one district who traditionally vote for one party might not be able to fully support the candidates they would have seen if their districts were more traditionally configured. The voters might have choices, but false choices.
These false choices can undermine their lives. For example, voters might want to vote for candidates who support government-sponsored health insurance, but find that gerrymandering is affecting their choices. Their choices and their voices might be muffled because their votes do not count as much as they could have counted when combined with additional votes for the same candidates and causes. Their votes might not count since they are dispersed among other districts and not concentrated like the votes of other parties in gerrymandered districts.
Redistricting appears to be unconstitutional. It denies basic rights granted by the U.S. Constitution. The Fifteenth Amendment states that “The right of citizens of the United States to vote shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or by any State on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude.” Shifting geographic precincts to highlight or downplay specific candidates appears to abridge the right to vote, a direct violation of the Constitution.
Do People Gerrymander Today?
Yes. Politicians of both parties continue to create electoral districts that blatantly benefit their political parties. A federal court declared in August 2018 that the state of North Carolina’s map of Congressional districts favored Republicans. The court declared that the map “constitutes an unconstitutional partisan gerrymander in violation of the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment, the First Amendment, and Article I of the Constitution.” The next month, the same federal judges ruled that although this map did feature gerrymandering, there would not be enough time to change the map in time for the elections planned for November 2018. North Carolina would not be able to not use this map after these elections, so North Carolina will need to use a new Congressional map for elections in 2020.
Gerrymandering has occurred in other regions of the country. In 2016, the United States District Court for the Western District of Wisconsin ruled that the Wisconsin Legislature drew electoral maps that favored Republican Party candidates in the state in 2012 and 2014. The case made it all the way up to the U.S. Supreme Court. But, in June, 2018, the Supreme Court refused to hear the case, stating that the bodies bringing the case lacked the legal standing to do so. It sent the case back to lower federal courts. This meant that Wisconsin would use the same maps in November 2018 elections.
A number of political insiders expect that voters throughout the United States will use their votes in the November 2018 elections as a way to protest U.S. president Donald Trump and his fellow members of the Republican Party. But, if gerrymandered maps remain in place, they could skew results from the state. They could prevent candidates from certain parties from receiving the majority of votes in their districts and winning their elections.
Gerrymandering harms political parties as well. Both parties engage in such blatant practices for obvious purposes. Such practices tarnish the reputations of the parties as well as the democratic process. The electorate might view such tactics as political dirty tricks, which could discourage voters from supporting political parties, candidates, elections, and causes.
The U.S. Supreme Court addressed the topic of gerrymandering in Maryland in 2018 by not hearing cases about redistricting in that U.S. state. Maryland legislators redrew this map in 2010. Just two years later, a Democratic Party candidate beat a longtime Republican incumbent in a race for a U.S. Congressional seat in Maryland, leading to charges that the state’s Democratic Party redrew Congressional maps to give itself advantages that led to such electoral victories.
How Can Gerrymandering Affect Politics?
It is clear, then, that parties do redraw maps and create new electoral districts. It appears that they do this to try to produce political advantages. But, does this redistricting really create such results? In the case of Maryland, it appears that redistricting has made a significant difference. In 2012, Democratic Party candidate John Mulaney beat Republican Congressional representative Roscoe G. Bartlett. At the time of his defeat, Bartlett had served eleven terms (twenty-two years) in the U.S. Congress. Bartlett blamed redistricting on his loss. “We had the most gerrymandered district in the country.” This is significant in a number of ways. Mulaney was a new challenger while his opponent was an entrenched, longtime incumbent. It is often difficult for challengers to beat politicians who have been in office a long time. Incumbent politicians have
- Name recognition
- War chests of money to help fund their campaigns
- Fellow established politicians who are colleagues who can campaign and vouch for them
- Reputations and accomplishments from their administrations that they can cite in campaigns
Election campaigns are expensive and time-consuming. They require money, connections, and clout. Working in established offices can help people accomplish all three. How hard is it to unseat an established candidate? According to economics reporter John W. Schoen, in 2012, the year of Maryland’s Bartlett/Mulaney race, 90 percent of the people serving in the U.S. Congress kept their seats. This means that Mulaney was one of the minority of 10 percent of challengers who unseated a Congressional representative. His redrawn district could have helped him overcome such long odds.
Are People Fighting Gerrymandering?
Ending gerrymandering restores people’s votes, which helps restore their voices. Groups and individuals hope they can help people restore their voices. Since gerrymandering is about voting rights, it is only fitting that some groups are using electoral means to fight the practice. A Michigan-based group called Voters Not Politicians wants to end gerrymandering in the state. It appears that opposing groups want gerrymandering to continue.
In 2017, Voters Not Politicians collected thousands of signatures on petitions that supported ballot initiatives against gerrymandering in Michigan. The organization needed to collect 315,654 signatures from August to December 2017. In a possible sign of widespread support for anti-gerrymandering efforts, almost 450,000 people signed the petitions. A number of experts say this proposal is sorely needed in the state. For example, a June 24, 2018 headline in the Detroit Free Press noted that “Michigan is an extreme example of gerrymandering.”
Michigan’s Board of State Canvassers approved the ballot proposal. But, organizations such as Save Michigan’s Constitution opposed this ballot proposal as overly broad and took their opposition to the Michigan Supreme Court. The court rejected this opposition, paving the way for the proposal to be on the ballot for state elections in November 2018. The Michigan proposal calls for shifting responsibility for drawing electoral maps from the Michigan Legislature to an independent commission that includes independent private citizens who are not affiliated with political parties.
This proposal aims to take redistricting responsibilities from political parties and giving them to (ideally) nonpartisan private citizens. To implement such goals on a practical level, the proposal suggests:
- Creating a thirteen-member restricting board. The board would consist of five members who are not affiliated with a political party or are independent, four Republicans, and four Democrats.
- Choosing the redistricting board members randomly among people who apply for the positions.
The balanced composition of this group would provide equal representation from major parties. It would allow significant input from people who do not affiliate with any party. It would help ensure that one party’s politics does not take precedence over another’s. It would promote inclusiveness and democratic fairness. But, will party politics shape the outcome of this election and the future of the anti-gerrymandering proposal? After all, voters in districts that are already gerrymandered will encounter this ballot proposal. The gerrymandered districts in Michigan largely favor Republicans after the Republican-controlled Michigan Legislature redrew electoral maps in 2011 and Republican governor Rick Snyder approved them.
Republicans who want things to remain the way they are would likely vote against the ballot proposal. Gerrymandering, thus, would perpetuate political divisions by working to defeat proposals that fight gerrymandering and political partisanship. It may sound like clichés, but that’s why voting is important and why every vote counts. People might not vote because they assume that certain proposals may pass or that certain candidates may win with or without their votes. But, if they and others don’t vote, they don’t contribute ANY votes to the election. The status quo continues because nothing changes.
But, if enough people vote, their candidates and proposals may win. Even if they don’t win, the large number of votes will illustrate the popularity of these candidates and proposals. The large number of votes can encourage others to take notice, to support such people and causes, and maybe even to run for political offices themselves. Citizens can also use the courts to fight gerrymandering. The U.S. Supreme Court refused to hear recent cases on gerrymandering. It didn’t issue definitive rulings on it. While it’s unlikely that the Supreme Court will hear further cases on gerrymandering in the near future, it has not issued a final word on the topic. This means that it might hear other gerrymandering cases in the future, especially after the U.S. Census of 2020 might contribute to further political redistricting.
According to Erick Trickey in Politico, it is more likely that individual U.S. states will tackle gerrymandering: “[I]f gerrymandering’s opponents want better, fairer maps, they’ll have to demand them, state by state.” This is happening across the country. In addition to the Michigan Voters Not Politicians initiative, Better Boundaries (Utah) and Clean Missouri are groups demanding an end to gerrymandering. Colorado voters will vote on an anti-gerrymandering proposal in November 2018, while Ohio voters overwhelmingly approved their state legislature’s anti-gerrymandering proposals earlier in 2018.
In a strange way, then, gerrymandering unintentionally encourages the sort of political engagement it’s trying to squelch. Who knew that the Gerrymander could be both a monster and an ally?
About the author: Pamela Zuber is a writer and editor who has written about a wide variety of topics, including politics, addiction, and gender.