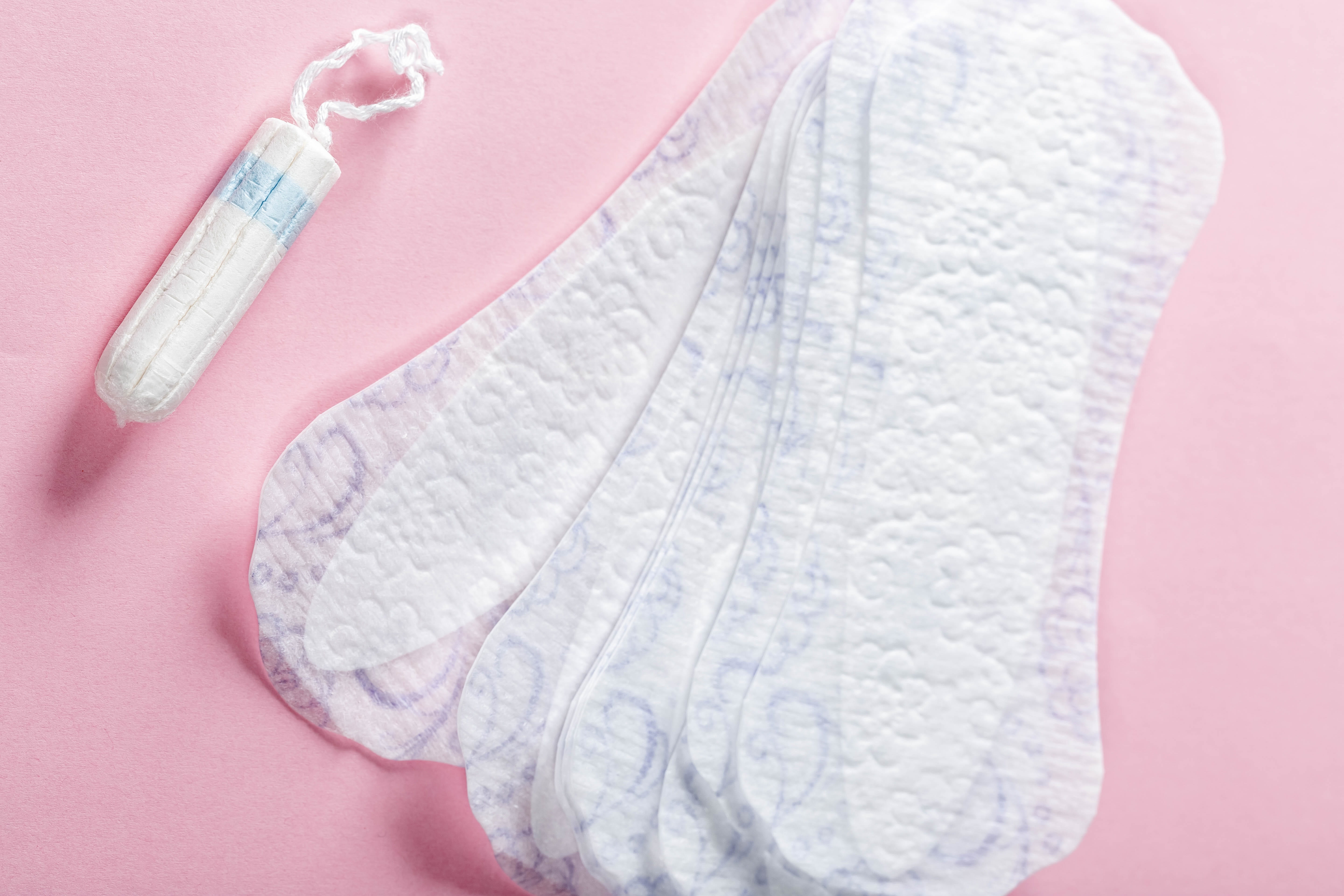
Menstruation is one of many topics that can be difficult and uncomfortable to talk about but is absolutely necessary, as many people do not have the resources they need to manage menstruation within reach. The WHO-UNICEF Joint Monitoring System defines menstrual hygiene management as being when people who experience periods “are able to use sanitary materials to absorb menstrual blood, change and dispose of these materials in privacy as needed, and have access to soap and water to keep clean.” The struggle for accessible menstrual hygiene management can be found in all parts of the world and is even true of some places you would not necessarily expect. One such place is in prisons, where women often have severely insufficient access to products like sanitary pads and tampons. This problem needs to be addressed, as menstrual hygiene products are a necessity. They are not merely items of luxury and should never be treated as a privilege.
However, things are slowly but surely improving. The First Step Act that was enacted in December of 2018 requires the Federal Bureau of Prisons to provide pads and tampons at no cost to the prisoners. While this is a good step forward, it only applies to federal facilities and does not help in state or local ones. Further change continues to be imperative.
Examples of the Problem
Betty Ann Whaley, who was released from the Rose M. Singer Center on Rikers Island in June of 2016, told the New York Times that pads were available “seven out of ten times,” and tampons were even less accessible. It is important to remember that even a nine out of ten times availability would be a serious problem, given the impact it can have on one’s health when menstruating without the means to deal with it.
Even when pads are available, they are often very thin, requiring them to be changed frequently. This leads menstruation to still be difficult to manage, as women in prison often only have access to a small number of pads each month. Chandra Bozelko, who spent some time at York Correctional Institute in Niantic, Connecticut, wrote about her experience with menstrual hygiene management for the Guardian in 2015. Each two-person cell was given five pads each week, giving each woman about ten pads per month. If a woman’s period lasts for five days, she would only have two pads for each of those days. This would not be enough, even if the pads were of high quality.
Topeka K. Sam developed blood clots while she was in prison, meaning she needed sanitary pads that were more absorbent than those available in the commissary. In order to get the menstrual hygiene materials that she needed, she was forced to prove that they were a necessity. She put one of her used pads into a bag and a male staff member determined that she truly needed different pads. Five months had passed by the time she had access to resource she needed.
In some cases, there are even monetary barriers that prevent women from being able to properly manage their menstrual hygiene. Prior to the establishment of the First Step Act, federal prison commissaries charged $5.55 for two tampons and $1.35 for two panty-liners. This is a far greater amount of money than either of these products are worth. For example, you can buy an 18-count box of tampons for $9.19 at Walmart.
Menstrual Hygiene Management in Prisons Is an International Concern
Menstrual hygiene materials are also often difficult to access outside of the United States. In the Bom Pastor women’s prison in Recife, Brazil, Human Rights Watch (HRW) found a few different factors that make proper menstrual hygiene and healthcare difficult. As of March of 2017, tampons had not been distributed to the women since 2015. Water was only available three times each day, which is a barrier to strong menstrual health. There is a risk of infection if there is a lack in adequate soap and water for keeping clean. The prison system of Brazil also only employed 37 gynecologists in 2017, which means there is less than one for every 900 women in the system. HRW also found that 630 women had been placed in a cell that was only built to hold 270. This absence in any privacy and presence of practically no space makes even the act of replacing sanitary products difficult.
According to one study, prisons in Zambia leave inmates responsible for many of their basic- necessities such as menstrual hygiene products and soap. One woman living in a Zambian prison stated, “If others don’t bring them for us, we have nothing. There are lots of people with no relatives here. They have nothing.” The water that is available is often unclean, so they have inadequate ability to keep clean as well. These prisons also have the same overcrowding problem as the Bom Pastor prison, being more than 300% over capacity.

Impacting Health
Ignoring menstruation is not an option. Not only would that be extremely uncomfortable, but it is also a health and safety issue. Lacking access to necessary menstrual hygiene management materials can have an impact on both the mental and physical health of women living in prisons. In terms of physical health, women who are trying to deal with menstruation while incarcerated might develop health problems such as bacterial infections from trying to use other materials in place of regular menstrual hygiene products.
In terms of mental health, being denied the things one needs to deal with menstruation is a dehumanizing experience. At this point in time, talking about menstrual hygiene feels awkward and uncomfortable for many people. This fact does not change among incarcerated populations. When you add experiences like that of Topeka K. Sam, having to prove that she needed the resources she was asking for, the situation becomes even more difficult.
Why Does It Matter?
Truly accessible menstrual hygiene management resources are undoubtedly a human rights issue. According to Article 25 of the United Nations’ Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), all people have the right to a standard of living that sufficiently supports their well-being and health. The harm that can be done to one’s physical and mental health when they lack the menstrual hygiene products they need gets in the way of this right.
Potential Solutions
How do we improve menstrual hygiene management in prisons?
The people who are most aware and likely care the most about this issue are people who have been disenfranchised, as only two states allow people convicted of felonies to keep their voting rights, and only 15 states automatically restore their voting rights after they have served their sentence. Additionally, many people would not have the resources they would need to advocate for change, no matter how strong their drive or greatness of their ideas. It would be helpful in trying to solve the problem if we could figure out a way to empower people who have direct experiences with it.
Prisons could potentially switch from providing disposable menstrual hygiene products to reusable ones, like Thinx or Lunapads. While the initial change would be relatively expensive, it would save them more money in the long run, as they would not have to constantly buy more sanitary pads and tampons. This option could significantly improve menstrual hygiene management in prisons, and, as a bonus, it would also be much better for the environment.
Improving this issue is an important step in ensuring that people who have been incarcerated are still treated with dignity and respect as human beings. People are people, no matter what they have done in the past. There is no reason to treat anyone as less than human or prevent them from having access to their fundamental human rights.
If you have an interest in learning more about the need for improved access to hygiene management, check out this post on MHM!