One of the most famous blunders made by former U.S. President George W. Bush was, “Africa is a nation that suffers from terrible disease.” President Bush, like many others, misconstrued the fact that Africa is not a country, but a continent.
Africa consists of 54 different countries with a vast array of cultures, languages, religions, politics, agriculture, and cuisine. Many people assume that in Africa, people speak “African” or do not understand other languages; however, this is quite incorrect. In Africa, there are over 2,000 languages such as Arabic, English, French, Portuguese, and Swahili. Surprisingly the most spoken language is Arabic, with over 170 million speakers. Furthermore, English is the official language in 24 of the nations. “About 25 percent of the languages spoken in African countries aren’t recognized anywhere else in the world, which is a testament to its diversity and fullness.”
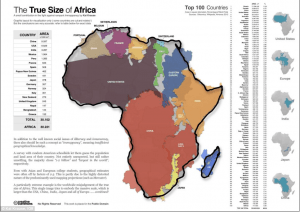
There are approximately 200 independent countries in the world and a quarter of them are in Africa. In fact, Africa has a population of over one billion people and is the second largest continent in the world. To demonstrate the immensity of Africa, the USA, China, India, Europe, and Japan could all fit inside its geographic border.
People often view the countries in Africa as poor. While 218 million individuals live in extreme poverty, 1 in 3 Africans are considered middle class. Additionally, not all people in Africa live in “huts”. About 43% of individuals in Africa live in urban areas. In fact, there are more than 50 cities with a population of over a million people. Also, approximately 70% of Africa’s population is under the age of 30. So, when you combine this young demographic with diversified urban centers, you generate the possibility of innovation throughout the continent. Furthermore, their economy is expanding – out of the 10 fastest growing economies, 6 are in Africa. It is not possible to apply one concept to the entirety of Africa. Yes, some countries are poor, especially in sub-Saharan Africa; however, there are countries such as Nigeria, South Africa, and Egypt that are fairly wealthy. Nigeria exports the majority of the world’s oil, has a GDP of over $594 billion, and is projected to be one of the world’s largest economies in just a couple of years. While South Africa is a well-known tourist location, it also has the 18th largest stock exchange in the world. Egypt is one of the wealthiest countries in Africa.
In terms of landscape, Africa is quite diversified. While the Saharan desert covers one-third of the continent, there are also rainforests, mountains, and lakes. Africa’s largest vegetation zones do not comprise of deserts or rainforests, but, in fact, savannas which are tropical grasslands. There is a myriad of ecosystems in Africa. For example, the Sahara desert is the world’s largest hot desert and has over 300 species of wildlife such as the cheetah, ostrich, and hyrax. On the flip side, the Congo and the Nile are the world’s deepest and longest rivers, respectively. Africa is also home to numerous wetlands, specifically in the Botswana which includes saline lakes, freshwater forests, and massive floodplains. There are also tropical forests in Central and West Africa such as the Congo rainforest.

Western media tends to only portray the negative aspects of Africa – violence, revolution, and wars. However, there is so much more to Africa than the negatives because it is not all danger and violence. For example, Zambia is quite peaceful and has had six presidents since becoming independent in 1964. Furthermore, it has never had a civil war. In Liberia, the former President was named by Time as “one of the top 10 female leaders in the world”. Additionally, she earned a Nobel Peace Prize for her work in women’s rights. Western countries tend to show Africans as powerless and reliant on Western aid to survive. In fact, many ads in the West embody this stereotype by depicting Africans as sad, lonely, and dirty children that need money. However, this is nothing further from the truth. It is thought that Western countries are the ones who help out Africans and are responsible for their well-being. But the truth is that African people who live outside of Africa send more money to their families than all of the aid combined from the Western countries. That is not to say that Western countries should not offer assistance when it is needed, but they must change their minds about what it means to live in Africa. Africa is not helpless, there are many projects created by African people. A Somalian woman, Hawa Abdi, implemented a health clinic, which has now developed into a “school, refugee camp, and hospital for over 90,000 women and children made homeless in the war”. Another example would be the Akon Lighting Africa project, which provides electricity the usage of solar energy to those in Africa.
There are also many assumptions about Africa being a place that is technologically backward. They see it as a place without phones, social media, internet, etc. However, Africa is quite the contrary by becoming “the world’s second most connected region by mobile subscriptions with over 754 million connections”. Interestingly enough, people in Kenya are 4 times more likely to have a cell phone than have access to a toilet. Moreover, at least 80% of African people have access to a mobile device. There are also many innovative advances for renewable energy such as hydroelectric power and solar panels. A lot of African countries are ahead of Western countries when it comes to sustainable energy. Kenya alone gets 50% of their energy from hydroelectricity, while in the UK and US, only 11% of their energy comes from renewable sources. In terms of creativity, Africa has numerous resourceful inventions such as traffic-regulating robots, a biomedical smart jacket that can diagnose pneumonia, and a device that fuses live neurons into a silicon chip.
There is no way to identify Africa as simply one thing. Africa is diverse in areas such as people, language, economy, landscape, technology, and innovations.
George Kimble captivated these sentiments best when he said, “The darkest thing about Africa has always been our ignorance of it.”