Disclaimer: The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this blog post are the author’s only and do not necessarily reflect the official position of UAB or the Institute for Human Rights.

On June 24, 2022, the U.S. Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade, the landmark case that allowed women access to abortion. The majority opinion, supported by the Court’s 6 conservative justices, reads (p. 79 of the Opinion of the Court):
“The Constitution does not prohibit the citizens of each State from regulating or prohibiting abortion. Roe and Casey arrogated that authority. We now overrule those decisions and return that authority to the people and their elected representatives.”
Obviously, what’s happening is directly related to human rights. Interestingly, both the “pro-life” movement, arguing in favor of restricting abortion access, and the “pro-choice” position, contending it’s a woman’s right to choose what’s happening to her body, use human rights language to justify their positions.
The question about abortion is, fundamentally, a question about the “right to life.” But whose right to life are we talking about? If you listen to anti-abortion activists, it’s about the life and rights of the unborn. If you follow the women’s rights argument, it’s about the life and rights of women and girls. What rights do women have according to human rights and what rights belong to unborn children, fetuses, embryos, and fertilized eggs? For the sake of this article, I will use “the unborn” to refer to the different statuses of gestation, recognizing that different gestation stages might have different legal implications regarding the termination of pregnancy. I also use the terms “women” or “woman” to refer to pregnant people, acknowledging that not all people who become pregnant identify as women. I chose to do so in line with language used in court decisions (domestic and international), legal and policy documents, and literature, which mostly use the term “women” when discussing abortion and reproductive rights. I also aim to disconnect my argument from the moral opinions of abortion and focus solely on what human rights law and policy have to say on the issue.
Let’s take a closer look.
Women’s rights and abortion
According to the UN, women’s rights include the rights to “equality, to dignity, autonomy, information and bodily integrity and respect for private life and the highest attainable standard of health, including sexual and reproductive health, without discrimination; as well as the right to freedom from torture and cruel, inhuman and degrading treatment.” This means that a girl or woman has the right to make her own decisions over her body, including in matters relating to her reproductive health, which lies at the very core of a woman’s right to equality, privacy, and physical and psychological integrity. Women’s rights have been well established internationally through a variety of documents and treaties, including the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women, the Sustainable Development Goals, and some of the basic human rights documents acknowledging the equality of men and women (e.g., Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), to which the U.S. is a state party). Domestically, women’s rights are enshrined, among others, in the 19th Amendment to the Constitution giving women the right to vote, Title IX protections, and in court cases such as Roe v. Wade.
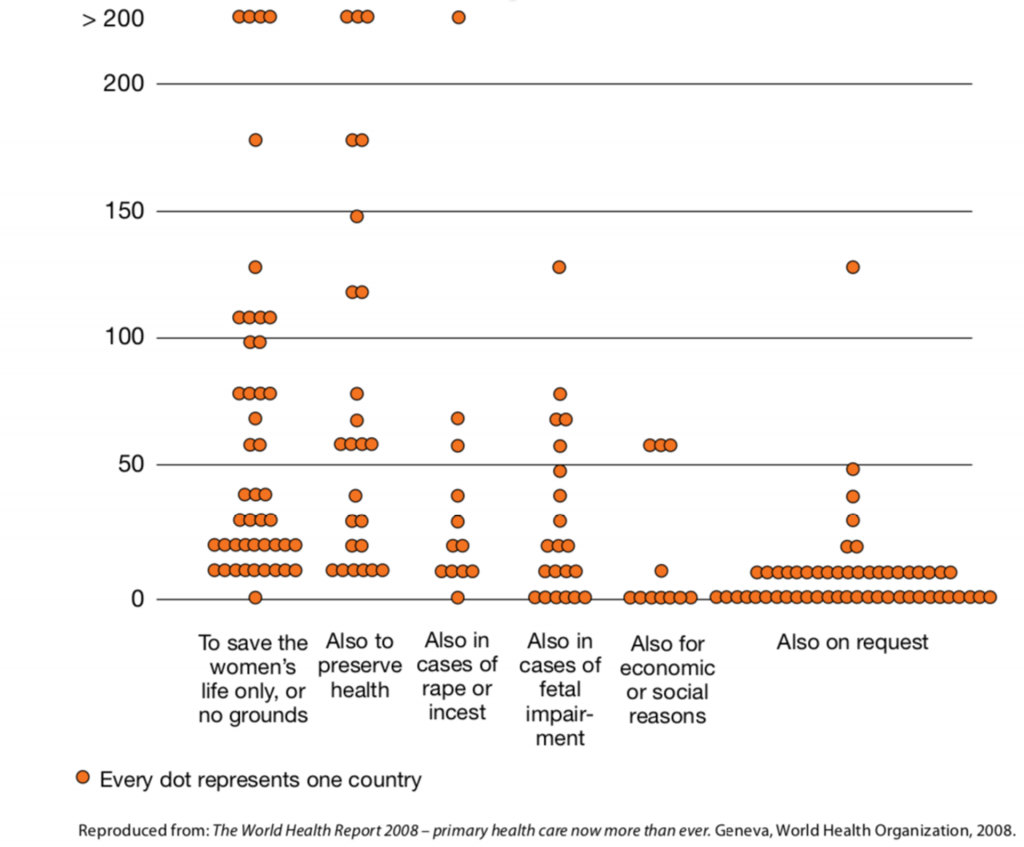
According to the WHO, unsafe abortion is the third leading cause of maternal mortality and morbidity. Unsafe abortion is defined as a procedure for terminating an unwanted pregnancy either by persons lacking the necessary skills or in an environment lacking minimal medical standards or both. Every year, about 25 million or 45% of all abortions worldwide are performed in a hazardous environment and lead to close to 50,000 deaths and temporary or permanent disability of 5 million additional women. There is a high discrepancy in unsafe abortion rates depending on the legal environment guiding termination of pregnancy: in countries where abortion is completely banned or only allowed to save a woman’s life, over 75% of abortions were unsafe as opposed to 10% of unsafe abortions in countries where abortion is legal.
Many studies in the U.S. and around the world have shown that legal restrictions on abortions do not result in fewer abortions or increases in birth rates. Equally, countries legalizing abortions do not experience higher abortion numbers or increased abortion rates. What does happen when abortion is criminalized is an increase in unsafe abortions, which leads to higher maternal mortality and affects everyday life for women. Unmarried and economically disadvantaged women are especially affected by abortion bans, thereby further marginalizing them and putting them at risk of injury and death. In places where abortion is legal and can be performed on a woman’s request, and where safe services are available, unsafe abortion and abortion-related mortality are reduced
The figure below shows the impact of abortion bans on unsafe abortions:
The recent Supreme Court decision will have severe consequences on a woman’s right to life, physical and mental integrity, health, privacy, and inhuman and degrading treatment in states like Alabama that restrict access to abortion or outlaw it in any case. As the three dissenting Justices point out (p. 2 of the Dissent):
“[The Court] says that from the very moment of fertilization, a woman has no rights to speak of.”
Based on above evidence it is likely that the rate of unsafe abortions and deaths of women in the U.S. will increase.
Rights of the unborn
With the unborn, the question is not so much about life, but about personhood. There is no agreed definition of when personhood begins. Across history and different cultures and religions, it has been argued that fetuses acquire personhood at conception, at various stages of pregnancy, at birth, or even after birth following the completion of traditional rituals. Philosophers, scientists, religious leaders, and legal scholars tend to disagree widely on this subject, as does the general public. Particularly influential was Pope Pius IX’s declaration in 1869 that ensoulment occurs at conception as opposed to at “quickening”(when the mother detects the child moving for the first time), which was the Catholic teaching before that point. This laid the groundwork for restrictive legislation on abortion and contraception that still exists in some countries today.
The question of when personhood begins also found its way into major human rights documents. The 1948 Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the most widely recognized human rights document, states in Article 1:
“[a]ll human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights.” (emphasis by author)
making it seemingly clear that human rights, including the right to life, begin at birth. The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), the legally binding human rights treaty based on the UDHR, however, states in Article 6 that
“[e]very human being has the inherent right to life. This right shall be protected by law. No one shall be arbitrarily deprived of his life.”
Similar wording is used in the European Convention on Human Rights (“[e]very person has the right to life” (Article 2)) and in the African Charter for Human and Peoples’ Rights (“every human being shall be entitled to respect for his life” (Article 4). The word “born” is no longer mentioned in these cases.
Somewhat ambiguous is the Convention on the Rights of the Child: It states in its Preamble that “the child… needs… appropriate legal protection before as well as after birth.” However, this is later qualified by Article 24 (health), Article 6 (life), and Article 3 (best interest of the child), which puts the rights of a pregnant girl over that of its fetus. For explanation, preambles can only be used for contextual interpretation of a treaty and do not develop legal effect like articles do.
The only general international human rights instrument that explicitly extends the right to life to the unborn is the American Convention on Human Rights. It states in Article 4: “Every person has the right to have his life respected. This right shall be protected by law and, in general, from the moment of conception. No one shall be arbitrarily deprived of his life.”
This first look makes it, therefore, seem unclear what international human rights law actually has to say about the right of the unborn. Discussions over the wording of Article 6 (right to life) of the ICCPR in 1957 shed some light on the most common arguments both in favor and against a right to life for the unborn: to protect human life at maximum capacity, the right to life starts at conception, which is what Belgium, Brazil, El Salvador, Mexico, and Morocco argued for during the negotiation of the article. The majority of states, however, rejected this interpretation on the grounds that it would be scientifically impossible to determine the exact moment of most conceptions. In addition, some states argued that such an interpretation of the right to life at conception would impede on fundamental women’s rights, especially a woman’s right to life, health, and physical and psychological integrity. Most developed countries liberalized abortion laws between 1950 and 1985, citing women’s rights, equality, health, and safety, thereby embracing the idea that personhood is not established until birth.

How do we solve this apparent tension between women’s rights and rights of the unborn?
To answer this question, we need to dig a little bit deeper and look at the interpretations of the right to life by international lawyers, case law, and reports issued by international human rights bodies. A clearer picture emerges when doing so: the right to life of born persons and fundamental principles of equality and non-discrimination requires that rights of pregnant women supersede interests of protecting the life in formation.
The precedence of the rights of women over the rights of the unborn was reaffirmed most recently and very prominently by the Human Rights Committee, a body of independent experts monitoring the implementation of the ICCPR, the most globally recognized and authoritative human rights treaty on the issue (the U.S. is a state party). After intense debate on the issue of the right to life of the unborn, women’s rights, and abortion, the Committee agreed that:
Although States parties may adopt measures designed to regulate voluntary terminations of pregnancy, such measures must not result in violation of the right to life of a pregnant woman or girl, or her other rights under the Covenant. Thus, restrictions on the ability of women or girls to seek abortion must not, inter alia, jeopardize their lives, subject them to physical or mental pain or suffering which violates article 7, discriminate against them or arbitrarily interfere with their privacy. States parties must provide safe, legal and effective access to abortion where the life and health of the pregnant woman or girl is at risk, or where carrying a pregnancy to term would cause the pregnant woman or girl substantial pain or suffering, most notably where the pregnancy is the result of rape or incest or is not viable. In addition, States parties may not regulate pregnancy or abortion in all other cases in a manner that runs contrary to their duty to ensure that women and girls do not have to undertake unsafe abortions, and they should revise their abortion laws accordingly. For example, they should not take measures such as criminalizing pregnancies by unmarried women or apply criminal sanctions against women and girls undergoing abortion or against medical service providers assisting them in doing so, since taking such measures compel women and girls to resort to unsafe abortion. States parties should not introduce new barriers and should remove existing barriers that deny effective access by women and girls to safe and legal abortion, including barriers caused as a result of the exercise of conscientious objection by individual medical providers. States parties should also effectively protect the lives of women and girls against the mental and physical health risks associated with unsafe abortions. In particular, they should ensure access for women and men, and, especially, girls and boys, to quality and evidence-based information and education about sexual and reproductive health and to a wide range of affordable contraceptive methods, and prevent the stigmatization of women and girls seeking abortion. States parties should ensure the availability of, and effective access to, quality prenatal and post-abortion health care for women and girls, in all circumstances, and on a confidential basis. (footnotes omitted)
To make it a little easier on you, let me summarize: overall, this is a strong affirmation of abortion as essential in ensuring the life of women and girls because of the above-mentioned impact on maternal mortality and morbidity. Unambiguously, the Human Rights Committee confirmed that:
- Safe, legal, and effective access to abortion is a human right protected under the ICCPR.
- Preventable deaths of women and girls constitute a violation of the right to life.
- Restriction on access to abortion can amount to torture, cruel and inhuman treatment, discrimination, and violation of women’s privacy.
- The right to life under the ICCPR begins at birth.
In addition, the Committee imposed strong obligations on states to protect women’s and girls’ right to life, including:
- To ensure effective access to safe, legal abortion in cases in which the life or health (mental or physical) of the woman or girl is in danger, the pregnancy is a result of rape or incest, or the pregnancy is not viable.
- To remove barriers that deny effective access to safe abortions and to protect the lives of women and girls against the physical and mental threats of unsafe abortion.
- To discontinue the criminalization of pregnancies by unmarried women or of women undergoing an abortion or medical service providers assisting them in doing so.
- To offer access to sexual and reproductive health education, contraception, and healthcare for women during pregnancy and post-abortion.
- To revise their abortion laws to take above points into account.
This is affirmed by various other human rights mechanisms, such as the Committee on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women, which stated that “[u]nder international law, analyses of major international human rights treaties on the right to life confirm that it does not extend to foetuses.” In addition, different UN Committees and experts have argued that criminalization and lack of access to abortion is a violation of the right to life, a form of gender-based violence, a form of torture or cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment, a violation of the right to privacy, a breach of the principle of non-discrimination, and even a form of femicide. Consensus also exists on the need to legalize termination of pregnancy for children under the age of 18. All in all, these reports, decisions, and statements, among others[1],reaffirm the calls for decriminalization of abortion and legalization of abortion in cases in which the life or physical/mental health of the pregnant woman is threatened or in cases of rape, incest, or fatal or severe fetal impairment. Similarly, regional human rights courts have been reluctant to assign personhood to the unborn and even the Inter-American Court for Human Rights decided the protection of the right to life for the unborn should not be considered absolute.
So where does this leave us?
It seems that in the current political discourse, we assume a symmetrical balance between the right to life of two entities: the woman and the unborn. From the above considerations, it is pretty clear that in human rights law, this is not the case. In fact, the protection of the unborn in international human rights law is very thin, to say the least. By contrast, the right to life, health, physical and mental integrity, non-discrimination, and equality of women is well-established and comparatively clear cut. Interventions on behalf of future persons may not violate the rights of the born person, namely the pregnant woman in whose womb the gestation occurs. The rights of a born person trump the rights of the unborn person.
[1]See, among others, additional Human Rights Committee decisions (e.g., Whelan v. Ireland, Mellet v. Ireland, and VDA v. Argentina), CEDAW decisions (e.g,L.C. v. Peruand K.L. v. Peru), CEDAW General Comment 35 (gender-based violence), General Comment 22 (calling on states to decriminalize abortion and guarantee women equal rights, non-discrimination, and autonomy), reports by the Committee on Torture linking deaths of girls and women from unsafe abortion to right to life, or the 2016 and 2017 reports by the Special Rapporteur Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment.