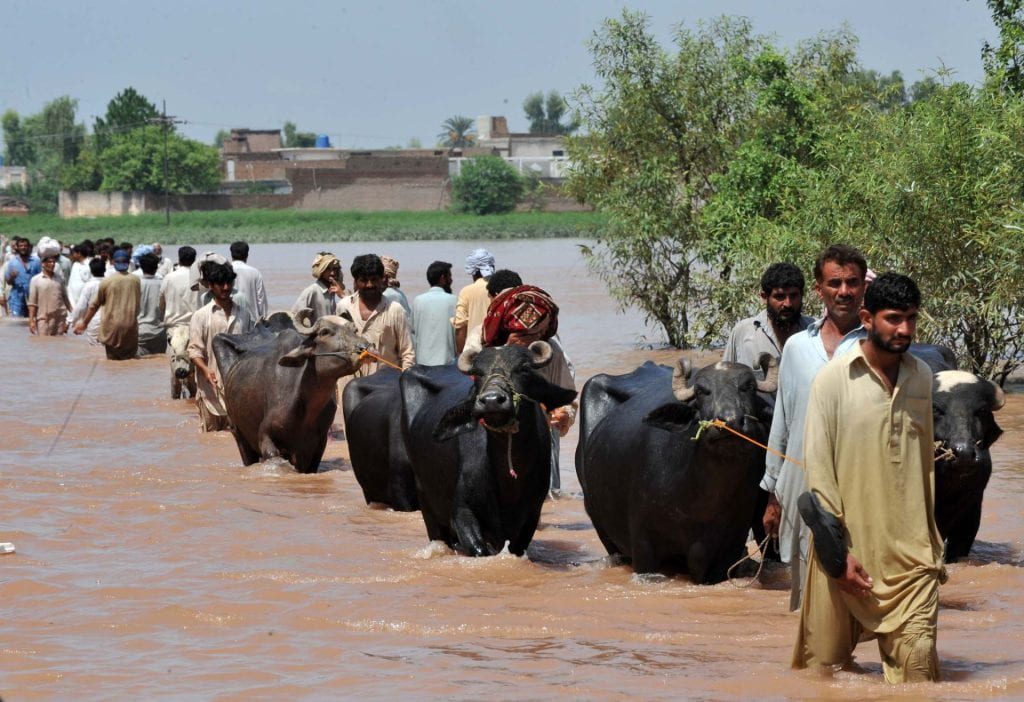
One third of Pakistan is underwater following disaster-level floods that have ravaged the country since mid June of 2022. The flooding is a humanitarian crisis of epic proportions, bringing climate change and environmental justice into the focus of conversations about why the floods are so devastating. The record-breaking monsoon rains have affected 33 million citizens, leaving millions displaced and threatening the economy by washing away the fall harvest and essential farmland. Pakistan’s most vulnerable are struggling to access the scarce aid that is available, including the 19 million children affected by the floods. It is an unprecedented, once in a century crisis event exacerbated by climate change, poor infrastructure, and the damages of the recent economic crisis prior to the flooding.

Direct Impact of the Floods: Hunger, Disease and Displacement.
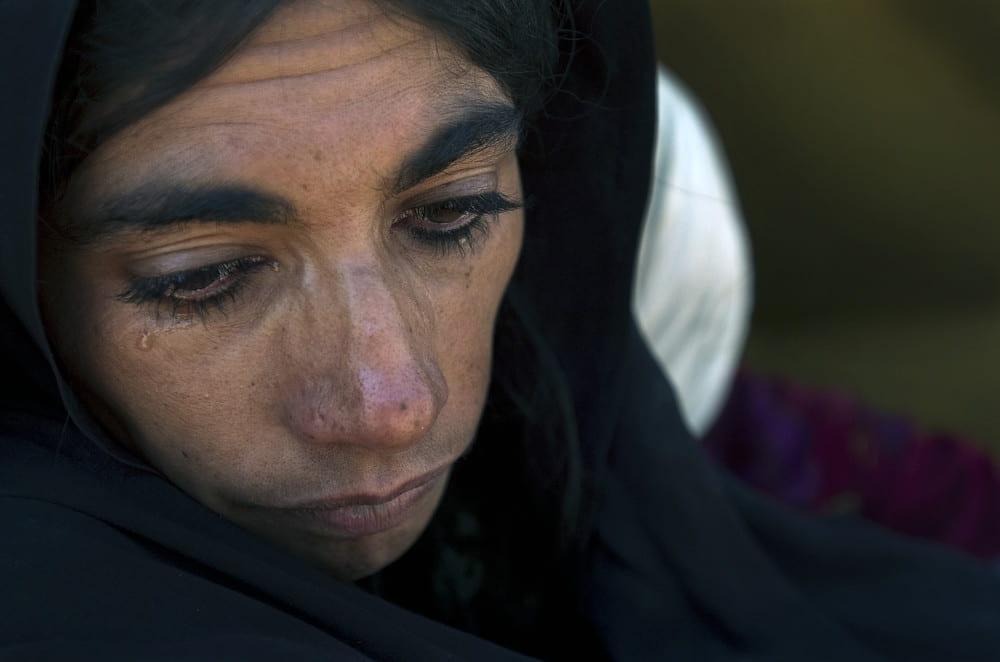
The monsoon rains have killed over a thousand people, roughly 400 of which are children. However, hunger, thirst, disease, and shortages of essential supplies threaten the lives of even more; millions of Pakistani people have been displaced over the course of the floods since June. The United Nations Refugee Agency has estimated that 6.4 million people are in need of immediate support.
Any discussion of rebuilding has been shelved in submerged regions as the flood waters may not recede for months, leaving the thousands of kilometers of roads, tens of thousands of schools, hundreds of thousands of homes, thousands of essential healthcare facilities destroyed by floodwater, and prior residents stranded or displaced. In addition to the initial death toll from the floods, the Pakistani people are facing immediate dangers of water borne disease, lack of access to food, water and shelter, and risks of violence; especially for women, children, and minority groups.
The country’s health system has faced substantial blows, both from loss of structures and supplies caused by the flood and the overwhelming need of those affected. Dehydration, dysentery, cholera, malaria, and dengue fever are ravaging make-shift camps as the flood waters become stagnant and clean water and sanitary supplies become harder to come by. Sindh Province, the second-most populated province in Pakistan, and one of the hardest-hit by the floods, has seen over 300 deaths from water borne-diseases since July. Early disease surveillance by the WHO has revealed that tens of thousands of cases of flood water-caused diseases are already present amongst those within reach of relief efforts. Countless villages remain stranded as roads and highways are underwater, so the true number of deaths, displaced persons, diseased, and persons otherwise impacted by these crises are expected to climb as more recovery efforts continue to search the flooded regions.
Without international aid and intervention, an epidemic of disease caused by the floods will cause a second wave of deaths in Pakistan, of which the elderly, children, and pregnant women will be the largest groups facing losses. International aid, medical and humanitarian organizations have joined the Pakistani government and are regularly dropping medical supplies, malaria nets, food and provisional shelters, but the need continues to grow as more people find their way to temporary camps and the rate of disease climbs.
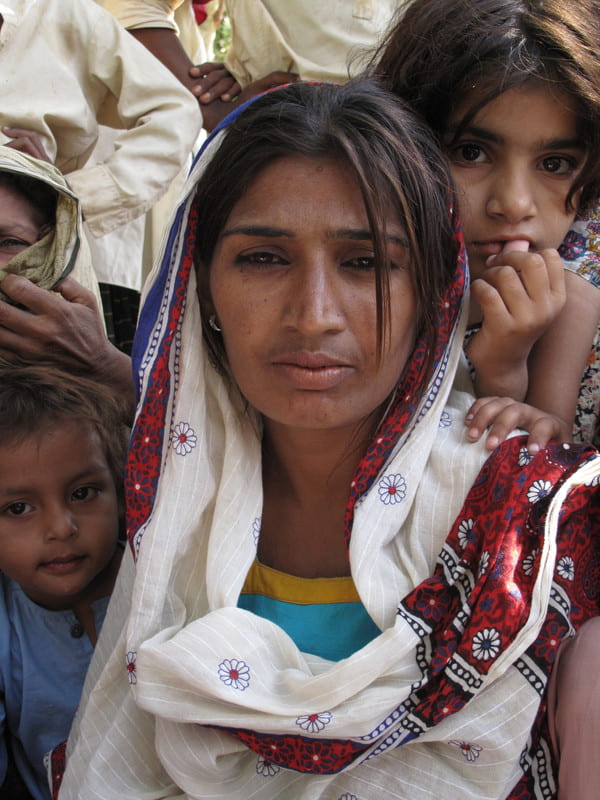

Human Rights & The Most Vulnerable
A nation’s most vulnerable populations are often the ones who suffer the worst effects for the longest time after a natural disaster like these floods. For Pakistan, those vulnerable groups are women, children, the Khwaja Sira (transgender) community, those living in extreme poverty, religious minorities, and other marginalized groups. Typically, socially disadvantaged groups are living in regions with lesser infrastructure, facing the initial worst impacts of natural disasters, but marginalized status often leads to upwards battles to access humanitarian aid after the disaster as well. There are estimated to be 650,000 pregnant women displaced in Pakistan right now, in urgent need of maternal health care and safe, sterile facilities to give birth in, with many taking perilous journeys in hopes of reaching a hospital or safe places to give birth.
CARE, an international human rights and social justice organization, spoke on this concern. Pakistan Country Director for CARE, Adil Sheraz said, “With entire villages washed away, families broken up and many people sleeping under the sky, the usual social structures that keep people safe have fallen away, and this can be very dangerous for women and girls.”
Following the 2010 floods in Pakistan, denial of aid and violence against minorities became a prevalent issue and large protests against law enforcement arose due to their failure to protect vulnerable groups. Preventative measures against recurrence of these issues have been few and far between since 2010, and international human rights communities are on high alert for rising reports of discrimination in relief distribution and crimes against minorities. Reports of sexual violence have already increased following the floods.
In addition to some of the most vulnerable Pakistanis are roughly 800,000 Afghani refugees who have been hosted by Pakistan in Sindh and Balochistan; two provinces faced with the worst of the flooding and submersion. Pakistan has a deep history of offering asylum and refuge for those fleeing across the border from conflict in Afghanistan, and is home to 1.4 million Afghani refugees currently in 2022. Following the August 2021 withdrawal of US troops from Afghanistan, the Islamic Emirate government (also known as the Taliban), Pakistan became an even more essential haven for the influx of refugees fleeing a violent authoritarian regime. In the wake of this natural disaster, the loss of $30 billion dollars worth of infrastructure, homes and supplies, and facing an economic crisis, Afghani people with hopes of finding refuge in Pakistan must now find new routes to safety.
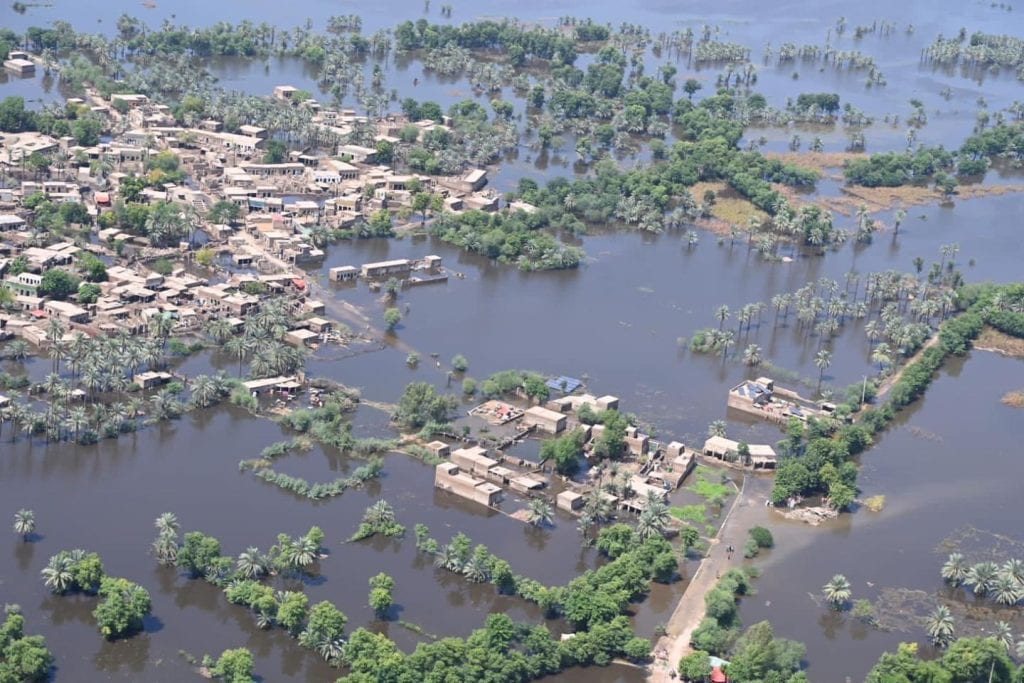

Environmental Justice & Climate Change
Though Pakistan faces annual flooding of the Indus river from heavy rains in monsoon season, record breaking rains preceded by an extended heatwave contributed to an unrivaled degree of flooding this summer. Heatwaves brought temperatures around 50° Celsius (122° Fahrenheit) to India and Pakistan between March and May of this year. Monsoon rains followed the spring heatwaves, and in the regions of Sindh and Balochistan rainfall reached 500% above average. The 2022 floods will leave a significant economic, infrastructural, and humanitarian impact on the country of roughly 220 million people. The reason for the dramatic influx in severity is complex, but simple at its core: climate change.
Pakistan is facing an unfair share of the consequences of climate change; while it was responsible for only .3% of global CO2 emissions in 2020, it is likely that this year’s heatwaves and floods will be on the less severe end of what is to come. The United Nations has deemed Pakistan a “climate change hotspot”, stating that people in South Asia are 15 times more likely to die from climate impacts. As the global temperature rises and geohazards become more extreme, disaster-prone regions like Pakistan will face more and more devastation. The best prognosis for the region comes with prevention efforts like strengthening anti-disaster infrastructures. As the global north is responsible for 92% of excess emissions contributing to global warming and climate change, Pakistan, the United Nations, and other international agencies are calling for countries like the United States to make increased contributions to relief funds and infrastructure development overseas.
United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres, while visiting Pakistan in September 2022, said, “…the fact is that we are already living in a world where climate change is acting in such a devastating way. So, there must be massive support to what usually is called adaptation, which means to build resilient infrastructure and to support resilient communities and to create conditions for those that are in the hotspots of climate change. Pakistan is one of the hotspots of climate change. For those countries to be able to prepare for the next disaster and to be able to resist the next disaster, this needs a huge investment and this investment needs to be provided.”
Relief & Aid
Pakistan has faced an overwhelming series of calamities since the start of this year, and the impacts from these disasters are greatly exacerbated by food shortages and an economic crisis prior to the start of the disasters in March. There are millions of people in need of aid, and every bit of support helps. If you are unable to financially contribute, please consider sharing this or other articles about this crisis to increase international attention on those who need our help.
For donations of money, time, or other resources, we have compiled some reputable aid agencies below:
- Pakistan’s Red Crescent Society is providing clean drinking water, medical treatments, temporary housing, and other essential aid across flood-hit regions. Donate or get involved with their flood response efforts here.
- The United Nations Refugee Agency has provided millions of dollars in aid to Pakistan, and you can contribute here to support their continued relief efforts.
- The International Medical Corps are on the ground in Pakistan, providing medical care and responses to both the floods and gender-based violence across the country. Find out more & how you can donate here.
- Muslim Aid has reached over 29,000 people in three affected districts of Pakistan, providing hygiene kits, shelter, and essentials to those in need. Contribute to their fund here.