by Eva Pechtl
This is the beginning of a series I will be writing about Indigenous justice systems. Though Indigenous people span across the world, I will be providing information specifically on policies and relations of the United States in this blog. Indigenous justice methods are compellingly distinct processes. In this opening post, I will first summarize the history of limitations placed on Indigenous justice and then explore traditions and values behind the restorative processes of Indigenous communities.

History of Foreign Limitations on Justice Processes
First, it is important to acknowledge the history of legislation put in place by the federal government that has greatly affected Indigenous justice systems. Constant structural changes imposed by colonizers resulted in wide variations between Indigenous tribal justice systems, meaning some are more similar to the US legal system than others. However, overarching this entire topic is the question of whether Indigenous, federal, or both governments presume jurisdiction over criminal offenses in Indigenous countries.
This question was decided when the federal government essentially ended the exclusive Indigenous jurisdiction over crimes in Indigenous countries. Before exploring Indigenous justice practices, I would like to briefly contextualize the complex and confusing history of Indigenous jurisdiction.
First, the General Crimes Act of 1817 extended federal jurisdiction over crimes committed on Indigenous land in cases where the defendant is non-Indigenous. At this time, the government only cared to interfere with crimes that involved non-Indigenous people. The Major Crimes Act in 1885 granted the federal government jurisdiction over serious crimes where the defendant is Indigenous, regardless of the victim’s identity. It originally listed seven offenses but has been increased to sixteen. After negotiation, tribal courts retained concurrent jurisdiction to prosecute Indigenous people for any conduct listed as a Section 1152 or Section 1153 felony. This means that an Indigenous defendant can be prosecuted by both the tribal justice system and the federal justice system for the same offense. This is because protection against double jeopardy in the Bill of Rights doesn’t apply to Indigenous nations.
Indigenous people gained more power to govern themselves in 1934 with the enactment of the Indian Reorganization Act. While it recognized tribal governments, the act offered money to those mirroring the U.S. Constitution, attempting to Americanize Indigenous societies. Many customs had disappeared, and Indigenous people were intentionally challenged to create self-government among distinct nations.
Next, Congress enacted Public Law 280 in 1953, requiring six states to assume civil and criminal jurisdiction on reservations, meaning the federal government gave up jurisdiction over Indigenous people to those states. This law was opposed by Indigenous nations because it was an unconsensual process that further complicated and failed to recognize tribal self-determination.
The Indian Civil Rights Act in 1968 offered states civil and criminal jurisdiction with the “consent of the tribe” over crimes in any Indigenous country in the state. It limited the sentencing powers of tribal courts but did not require the separation of church and state because of the importance of spirituality in all processes. The Tribal Law and Order Act in 2010 intended to improve tribal safety, slightly increasing tribal sentencing authority to a maximum of 3 years and a $15,000 fine. However, these new privileges were dependent on the imposition of further regulations regarding due process protections in tribal courts.
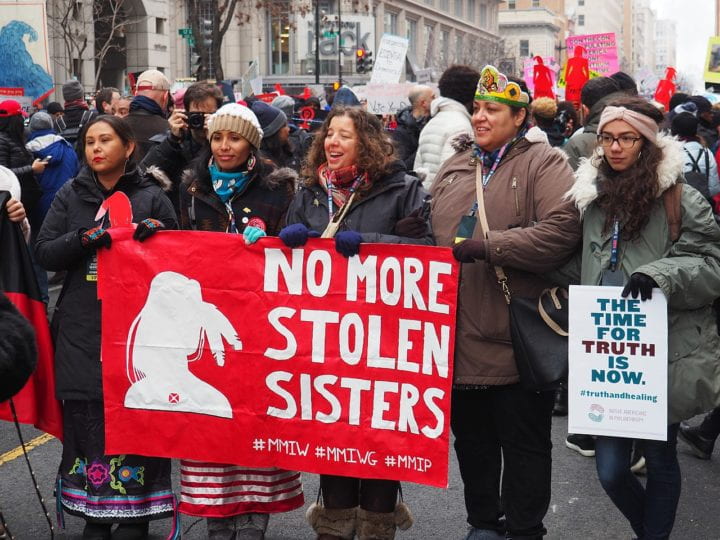
Finally, the Violence Against Women Act (VAWA) in 2013 authorized tribal courts special jurisdiction over non-Indigenous offenders in domestic violence cases. This was a landmark shift from the Supreme Court decision Oliphant v. Suquamish Indian Tribe in 1978, which held that tribal courts have no authority to prosecute non-Indigenous people, even if the victim was Indigenous. The VAWA was amended again in 2022 to expand special tribal jurisdiction to a list of covered crimes, including child and sexual violence, sex trafficking, and assault of Tribal justice workers. Indigenous courts can now prosecute and sentence regardless of the offender’s race for crimes against Indigenous victims that had commonly been ignored.

Because of colonization, Indigenous peoples’ principles have gone unrecognized by America’s Anglo-centric justice system. Consequently, Indigenous nations retain limited power to create a befitting legal structure that administers justice. However, they continue to persevere and have cultivated distinct methods, such as restorative and healing practices.
Harmony and Balance in Restorative Justice
In Indigenous communities, restorative court systems are similar to traditional systems where a council of tribal elders or community leaders will facilitate conversations to resolve interpersonal problems. In this type of resolution, the compliance of the offender is necessary for the families involved. Most importantly, this process attempts to heal the underlying means for a crime, preventing repetitive behavior and aiding the offender’s reintegration into the community. These types of meetings are also known as forums and can be conducted within families and communities.
In various areas of North America, circle sentencing reflects traditional Indigenous peacemaking aspects and has proven to be an effective approach to healing the offender, the victim, and the community. Specific practices vary by tribe, but the idea is to address participants’ feelings about how offenders can begin making up for their actions. Circle sentencing produces better satisfaction and healing, breaking the cycle of crime and allowing people to reconnect with spiritual traditions with the help of their community. In common Indigenous views, justice and spirituality are deeply connected.
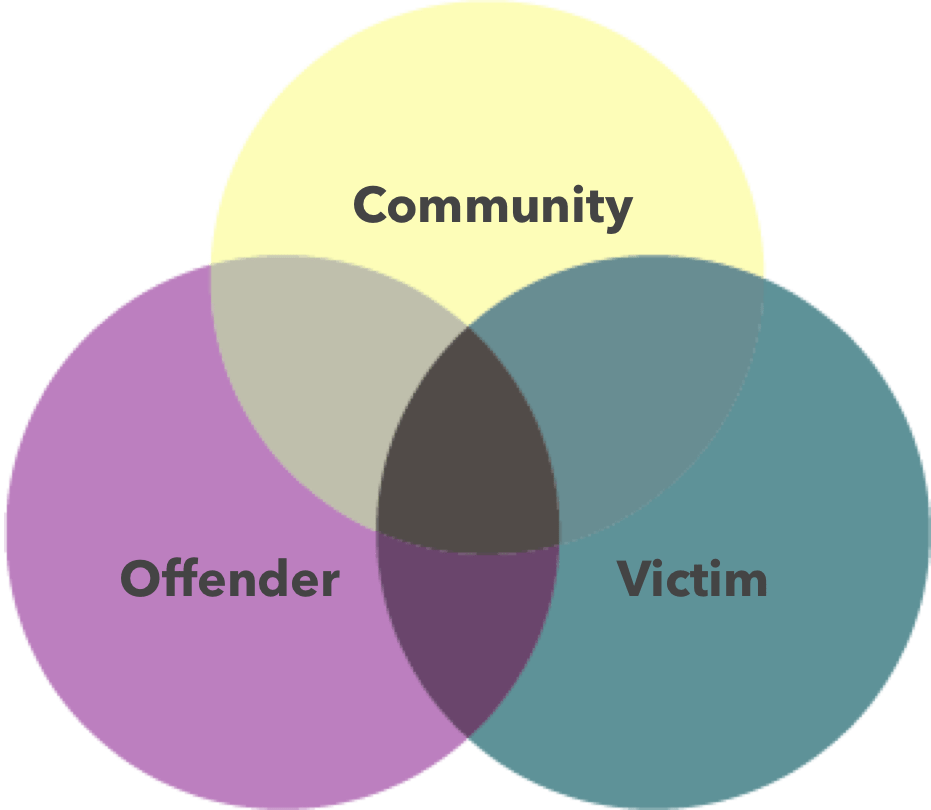
Tribal courts differ from other methods since they use written codes rather than being passed on through tradition. These judicial forums handle a range of legal problems and are led by judges from Indigenous communities. Most defendants or plaintiffs must represent themselves since the Indian Civil Rights Act does not ensure the right to legal counsel if individuals cannot afford an attorney. Tribal courts, interestingly, still tend to use family and community forums to handle interpersonal matters. This allows for alternative resolutions, sentencing, and victim-offender mediation.
Indigenous courts intend to restore harmony and balance to one’s spirit, following the belief that people who are whole do not act harmfully. Judge Joseph Flies-Away from the Hualapai Nation says, “People do the worst things when they have no ties to people” and that “Tribal court systems are a tool to make people connected again.”
Incorporation of Values In Peacekeeping Systems
Indigenous peacekeeping systems promote the resolution of underlying problems and make an effort to keep relationships strong. Indigenous justice represents a holistic approach where communication is fluid rather than rehearsed. They recognize that argument is not an effective approach and that discussion is vital to review a problem in its entirety. Indigenous justice is inclusive of all affected individuals, different from the American justice system, which often excludes participants.
Source: Yahoo Images via Mi’kmaw Spirit
The Navajo Nation’s peacemaking process centers on the individual and helps an offender realize that what they have done is incorrect. Instead of labeling and punishing individuals as criminals to prevent them from repeating the behavior, the Navajo way separates the action from the individual. Retired Chief Justice Robert Yazzie of the Navajo Nation Supreme Court states that the process is related to k’e, meaning to restore one’s dignity and worthiness.
What I find particularly remarkable about these concepts of justice is that, instead of adopting an immediate punitive approach aimed at simply removing the offender, the system focuses on correction and rehabilitation. Offenders are obligated to verbalize their accountability and take responsibility for changing their behavior. Instead of releasing the offender after their time is served, the system supports reparations to the victim(s) and community involving apology and forgiveness. These Indigenous restorative justice approaches are distinct from America’s legal process, which focuses on labeling and punishing the offender. Furthermore, traditional types of justice are able to promote communal healing and support in reintegration rather than hiring professionals to dispute a case with little interest in the community.

Source: Yahoo Images via Policy Options
Indigenous leaders continue struggling to ensure that their justice systems are meaningful to their people. We rarely consider Indigenous justice systems, but maybe we ought to start. Please stay tuned for my next blog in this series, expanding on current struggles imposed on the Indigenous justice system and its people.




















