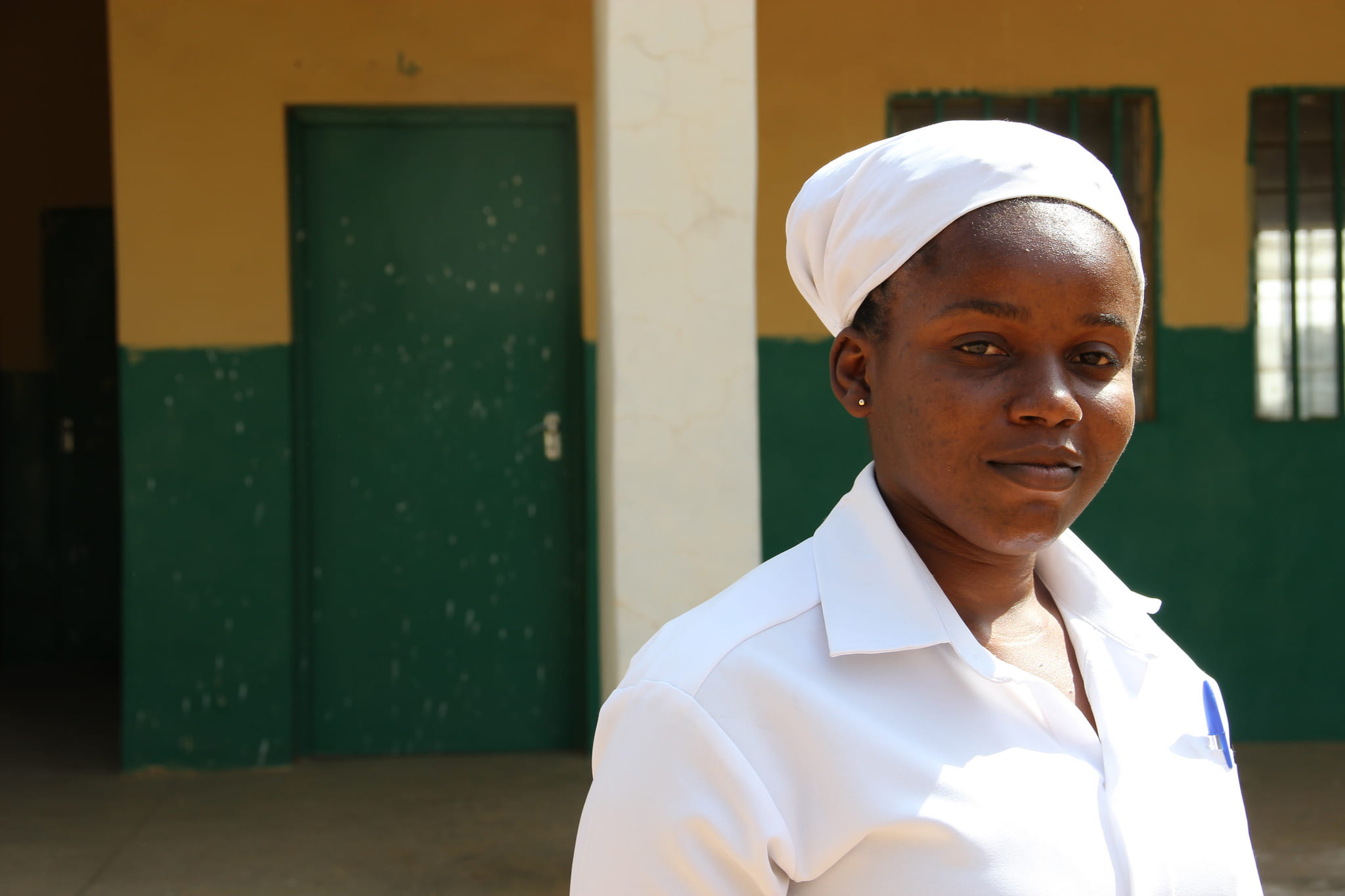
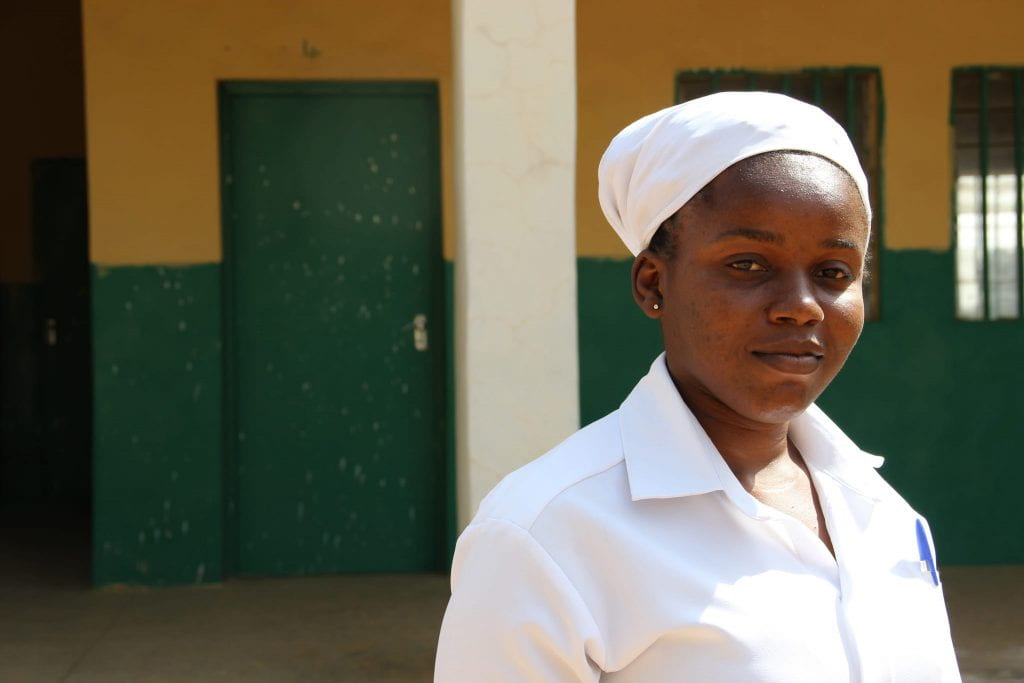
by Grace Ndanu
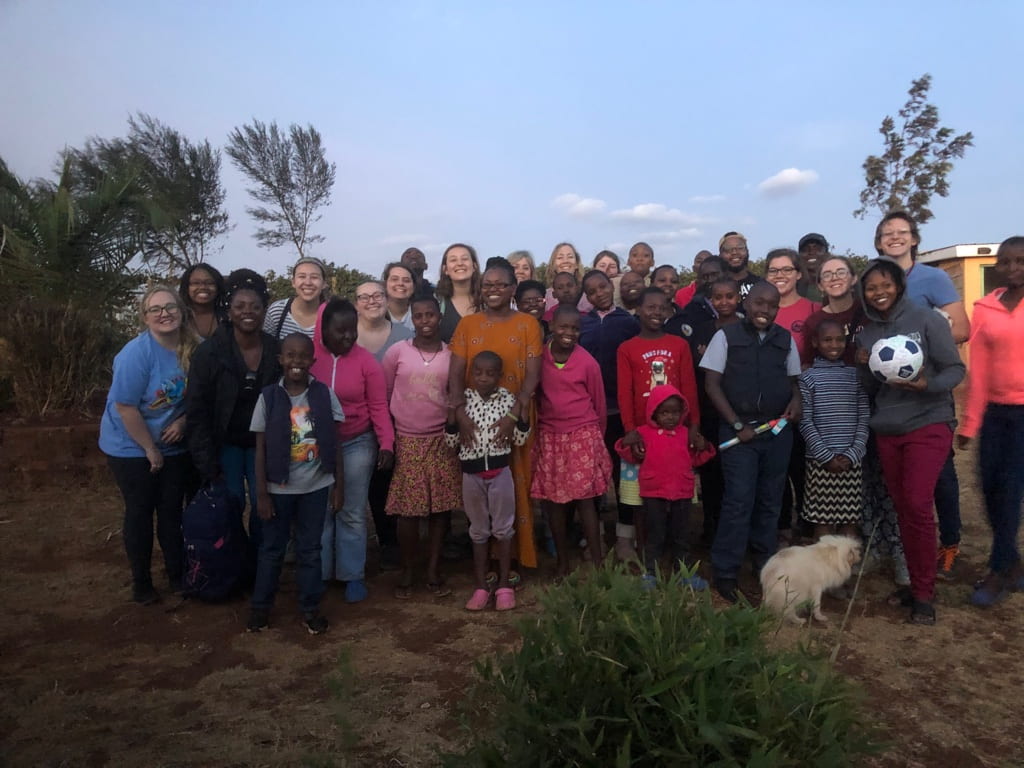
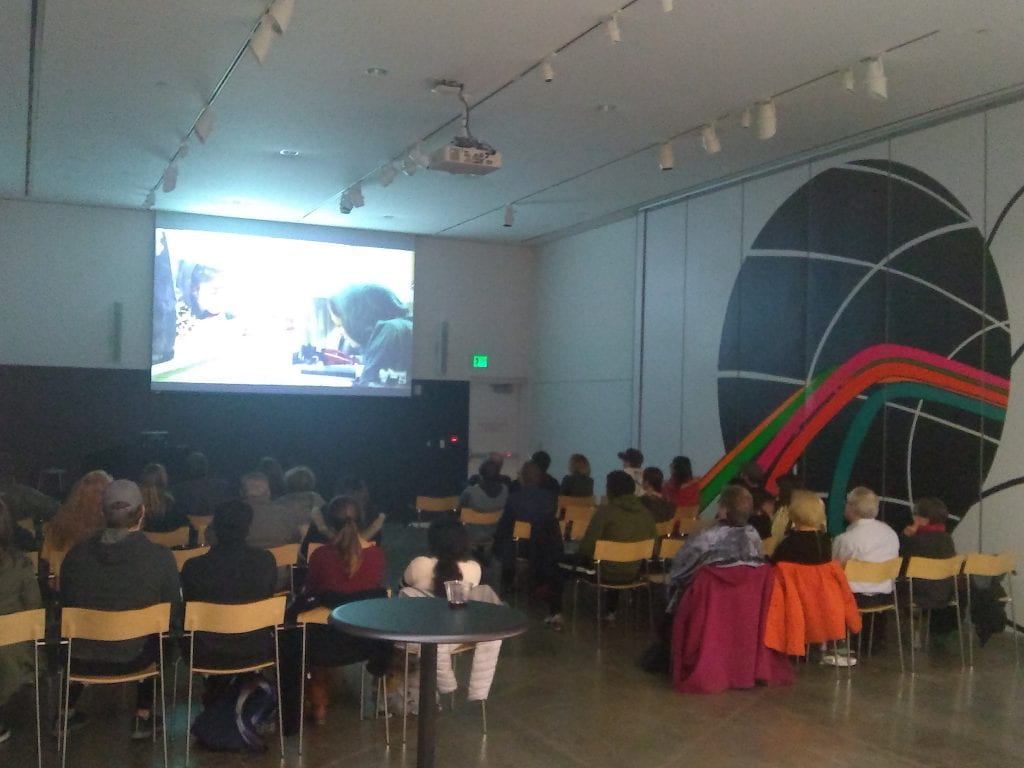
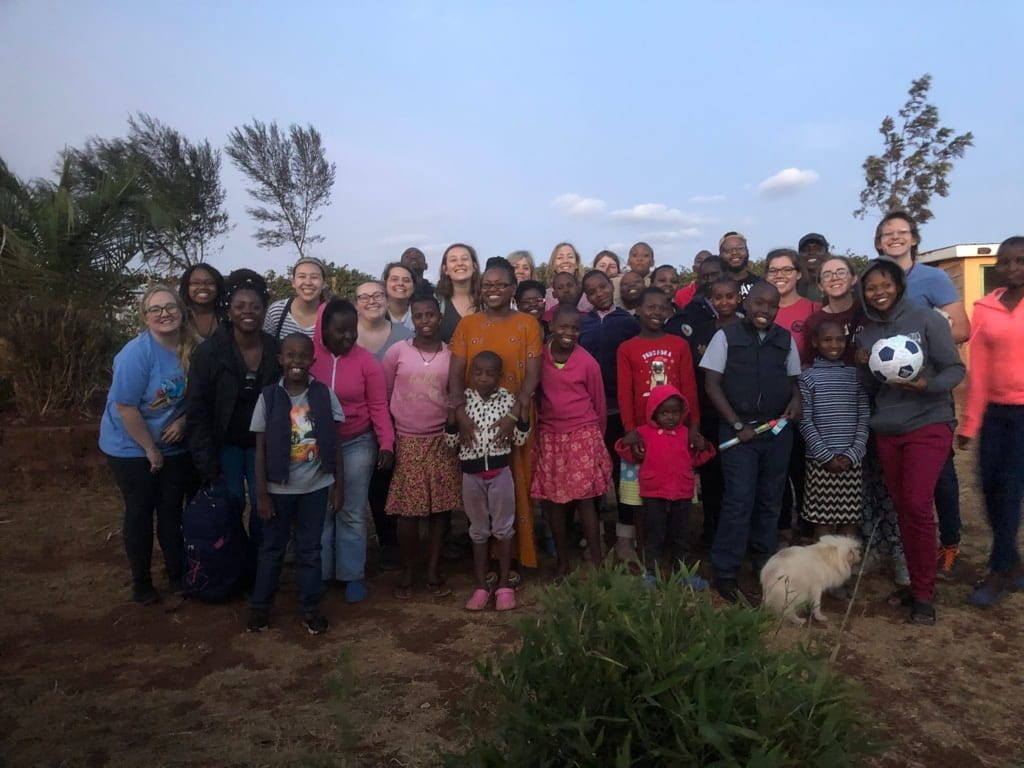
Over spring break 2019, UAB students traveled to Kenya with Dr. Stacy Moak, Professor of Social Work, and Dr. Tina Kempin Reuter, Director of the UAB Institute for Human Rights. They visited CARA Girls Rescue Center where they met Grace, a student and former resident at CARA [she is behind the lady in the orange dress]. Below is Grace’s narrative which includes sexual violence.

As humans, we are born to expect much than to face reality. We come to learn that everything has a purpose.
I was born in 1998 and raised by a single mother till 28th November 2004, where I got a daddy who I thought was loving and caring. Instead, he became a monster. Before my sister who was born in 22nd November 2005, the man started beating me for no reason and not just a child beat, it was a criminal beat whereby he used an electric wire to beat me up. As a child, I expected my mom to get in between and talk to her husband about the matter. My expectations became a fantasy and the beating became a habit. In 2006 in grade 4, I was supposed to go for tuition on weekends, but instead, I was forced to stay with my little sister at home so that my mom can go for work or church meeting. When I refused I was given a thorough beat and asked why I didn’t love my baby sister.
Sometimes the man volunteered to stay with the baby but insisted I remain so that I will help him with the baby. His agenda was opposite and he started molesting me. He started touching my private parts and when he knew it was time for mom to come back, he beat me up so that I should not say. As this was going on, we had a male neighbor who was doing the same as what my dad was doing but didn’t beat me. Until one Sunday, I refused to go to church and now I was left with the neighbor in the compound where he got a chance to rape me and asked me to keep quiet. Later in the evening, I decided to open up to my mom and she said that I was lying. She talked with my dad about the issue and they decided to ask the neighbor. Definitely, he denied. From this point, my parents started calling me a liar. This made my dad more comfortable in continuing what he was doing to me that is threatening me and sexually harassing me. This was still going on and my little sister grew up knowing I was a bad girl. It came to a point where anything happened to her she would say it is me.

On 22 April 2008, I got a baby brother and now I felt my life was at the peak. I didn’t want to live anymore and attempted three suicides. God remained faithful and kept me alive. It was on the second term of my grade 6 and I was transferred from a private to a public school which was 8km away from home. I was forced to walk all the way and come back home remember no lunch for me. In 2009, it was time for my sister to join [to go to] school. She was brought to the school I was which made my life more and more difficult because I carried the girl at my back every morning to school. My going to school late and tired became a habit and whenever I raised the issue, I was beaten and threatened that I will not join high school. I faced rejection, hatred, insult, and isolation. My brother and sister were growing knowing am the baddest person on earth. I went to a different church from the family so that I can come back home and do the house chores at this time. I was not allowed to stay with my siblings become it was believed I had no good intentions towards them.
In 2010, a church friend of my mom noticed she hasn’t seen me for a while and decided to visit us at home. She asked me if am fine and my response was positive but she was not convinced. She decided to pay my school fees and she ordered that I go back to my previous school. My dad was not happy and started accusing me of witchcraft, asking ‘why it is only me and not any other person.’ At this point, I decided to run from home – hoping after five years of tears and pain, I will come to my rescue. I didn’t know where to go but I started my journey in February on a Tuesday. I boarded a bus to a place called Kiserian and another one to Nairobi. I had no money but I reached Nairobi. I stayed in Nairobi for three days without food, just loitering and later I decided to call my mom with a stranger’s phone and she came to my rescue. The following Monday I was taken to school. I tried being strong by working hard but my life was miserable until I was through with my primary school. I promised myself that I will not live any longer and attempted another two suicides; I found myself alive.
I was enrolled in high school in 2011 which made me happy but inside I was dying. I knew the battle isn’t over yet because, during the holidays, I would go home. [In Kenya, most high schools are boarding schools.] My first holiday that was in April, I went home and this gave my dad a chance to rape me. He threatened me with a knife that if I said he will kill me. After four weeks, I went back to school. While in school, I started developing ulcers and depression. I started falling sick each day and this forced me to go home. While my mother was nursing me, I opened up to her about what dad was doing. [I thought she would defend me but] It came out the opposite and she defended her husband. She told me that I was lying. Later that evening she told the man what I told her during the day. The man denied and told my mom that I am cursed and that she should let me get married because I was a grown up at 13 years. I got well and went back to school. I got more depressed and started fainting. One of the teachers realized that nothing was going well with me. She decided to call me and ask me [about] the problem. I opened up to her. She went ahead and explained the matter to the principal. The principal made an arrangement of visiting a counselor and a doctor at the Nairobi Women’s Hospital. I started the medication together with the counseling sessions which was of great help.

The principal did not only helped me get well. She also [helped me] find a good home for me at the Cara Girls Rescue Center. The center took good care of me and they also counselled me. After some weeks, I had no one to pay my school fees there. I was transferred to AIC girls where I would get a sponsor and continue with my studies. After I got someone to support me, I went back to Cara Girls Rescue Center where I am till date. Being suffered for eight good years–my all childhood life has been a hell. There was no love, no care, and no mercy even from my own mother. I promised myself that I will never allow any child or anyone go through what I went through. Through this, I have always admired to be a Gender and Development CEO. I am working towards the goal. I am in my second year of studying in Gender, Women, and Development Studies. I have joined Egerton University Human Rights Club and an organization, Family Health Options Kenya, which deals with sexual health. It involves educating peers about sex and what they should do when their rights are violated. In the future, I am planning to do a Masters in Gender, Peace, and Security. I must ensure children especially the ones living with their stepparents to have full access of their mental peace, and the young girls and women who can’t raise their voices. I aspire to give people light and hope and reasons to enjoy their lives. I have realised I never enjoyed life. I just lived because it was a must but now it is time to live in reality. This is what am supposed to do: make people live the reality life, the life they deserve and deal with the ones that come in between their peace, joy, happiness and their rights.
I believe I am an agent for change. I must bring a change AND WE WILL RULE THE WORLD.
If you would like for girls like Grace to stay in school, please consider donating to our LadyPad project, during the UAB Giving Day Campaign, by using this link https://www.uab.edu/givingday/?cfpage=project&project_id=27174