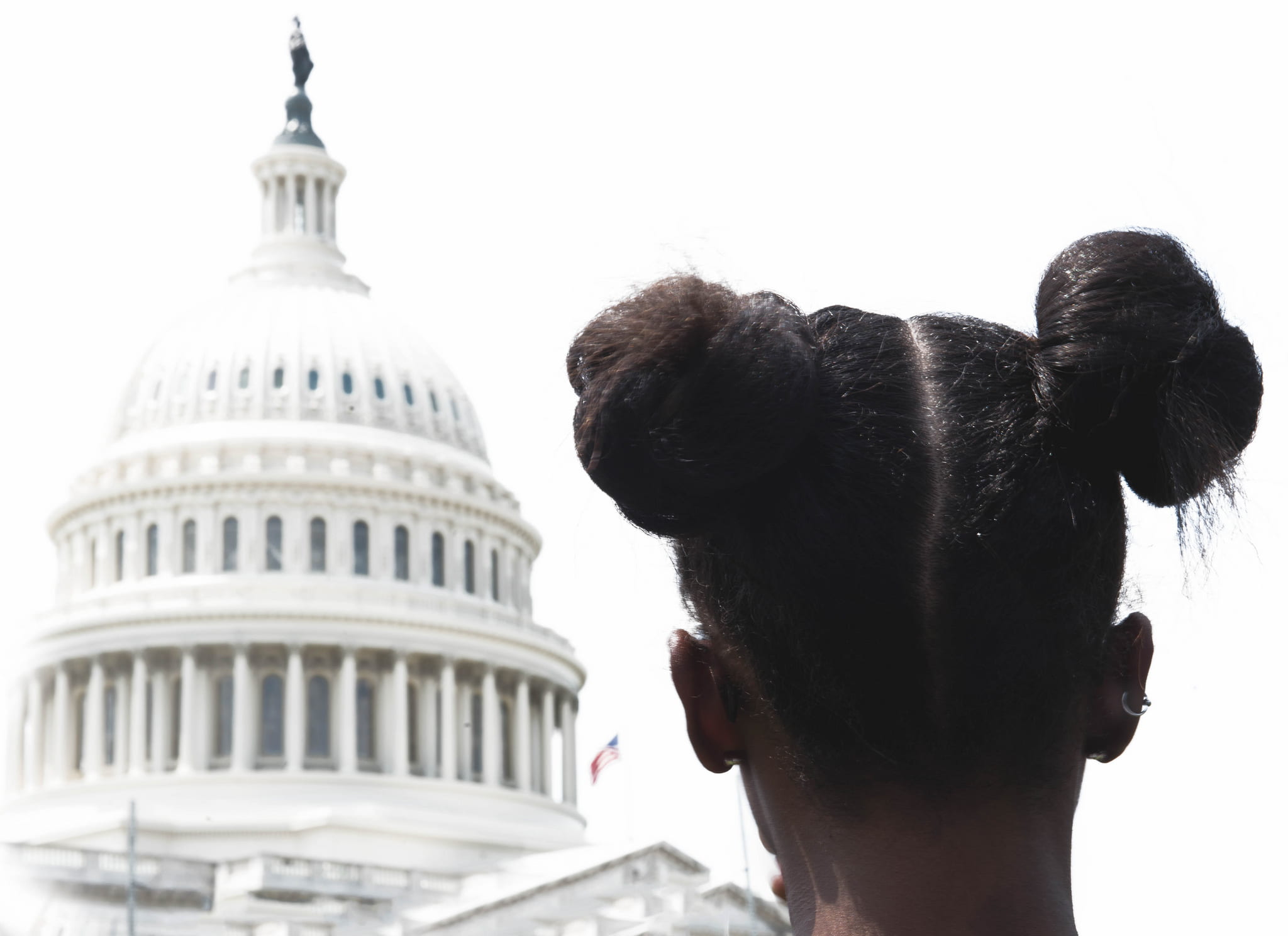
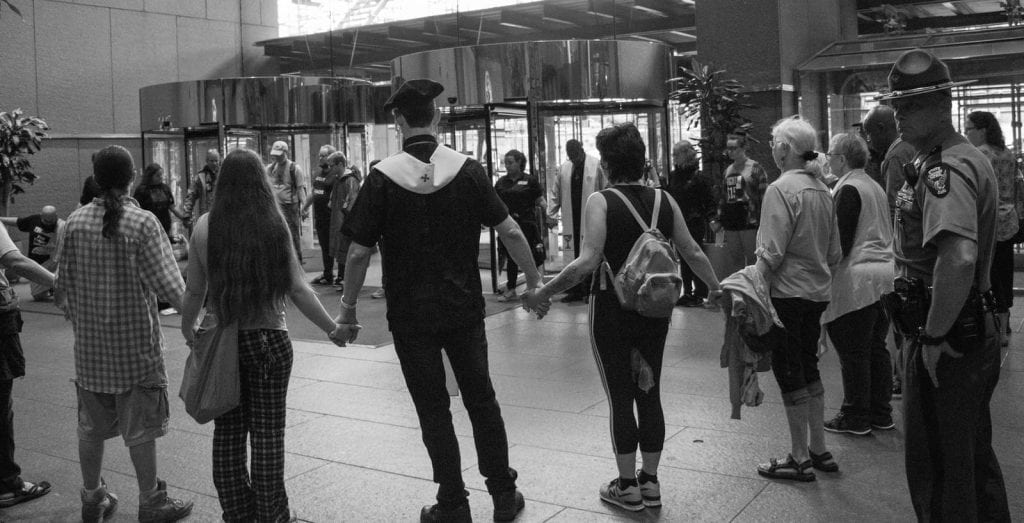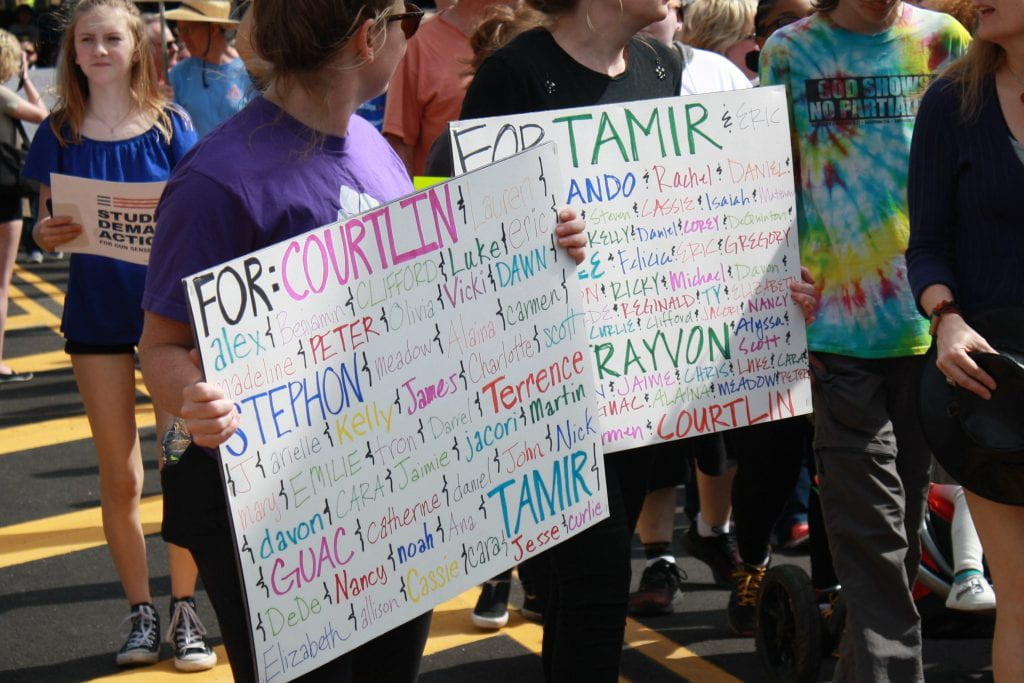I read “The Presumption of Guilt: The new liberal standard turns American due process upside down” the other day. I found this piece presumptuous at worst, and revelatory at best. The WSJ editorial board outlines three core tenets potentially derailing due process in the Kavanaugh appointment, most notably the presumption of his guilt. These core tenets, in the board’s estimation, will defend against a mockery of “the new liberal standard of legal and political due process.” What strikes me most about this piece is the presentation of their core beliefs about the justice system in America: “The core tenet of Anglo-American law is that the burden of proof always rests with the person making the accusation.” What the board revealed is the ever-present reality that populations of color in this country know and experience daily, and this fact is symbolized in the very name of the board’s ideal legal system itself: Anglo-Saxon. The law is not as colorblind or unbiased as the justice system would have us believe. The law is not for the protection of all; it is for the protection of Anglo-Americans. It is a law to the exclusion of everyone else. This blog, using the outlined WSJ tenets as section headers, speaks to the presumption of guilt applied daily to marginalized populations without due process.
Tenet #1: The core tenet of Anglo-American law is that the burden of proof always rests on the person making the accusation. Non-whites do not get the benefit of the doubt, even when video evidence, witness statements, or 911 recordings indicate otherwise. For marginalized persons, few opportunities transpire to make an accusation or offer a defense. Consider any number of non-threatening Sikhs, Muslims, Native Americans, or Blacks who find themselves on the receiving end of the “fear” of a White person for their safety. The accusatory nature of white America against persons of color, especially Blacks, living their lives has become so galvanized that #whileblack is a social media phenomenon.
#WhileBlack spotlights White Americans willingly interfering and causing disruption in the lives of Black people. Whether a politician canvassing a neighborhood or realtor checking on a property or a White grandmother riding home with her Black grandson, White Americans usage of the police as quenchers of irrational fear may result in the death of another unarmed and unassuming citizen. A few months ago, a group of Black women packed their car following their vacation when White residents phoned the police, accusing the women of robbing the AirBnB house where they stayed. Even after pleading their case, the officers did not believe the Black women. A White student at Yale phoned the police on two different Black students on two different occasions because she believed they did not belong on the campus. Colorado campus police detained two Native American students visiting a university when a White parent complained that the boys seemed threatening because they did not say much during the tour. In addition to highlighting the direct and structural violence that non-Whites face over the course of the day, #whileBlack showcases that the mastery of accusation and othering heavily favors the dominant party.
Tenet #2: An accusation isn’t any more or less credible because of the gender, race, religion or ethnicity of who makes it. This tenet suggests that any accusation is worthy of address. Recent history, including accusations against Roy Moore and this current case, tell us that many Americans presume the innocence of white males in the entertainment industry and political arena over white women. Thus, revealing a gender bias. Just ask Bill O’Reilly, Les Moonves, and Louis C.K. Presently the exceptions to this rule are men of color like Aziz Ansari and Bill Cosby.
Accusations of sexual misconduct by women of color are often dismissed or discredited. In 1991, Anita Hill came forward with allegations against Supreme Court nominee Clarence Thomas. When Lupita Nyong’o said Harvey Weinstein sexually harassed her, Weinstein denied the possibility of it, despite more than 40 other women making similar and more explicit claims. This tenet, however, is inaccurate if you are Carolyn Bryant or Donald Trump. Carolyn Bryant lied to a judge and jury in 1955. With that lie, she sentenced Emmett Till, a 14-year-old Black boy from Chicago, to a lynching by Bryant’s husband and other family members. Donald Trump, in 2008, initiated and perpetuated the birther narrative about President Obama. Despite the release of Obama’s birth certificate in 2011, many doubt Obama and believe Trump.
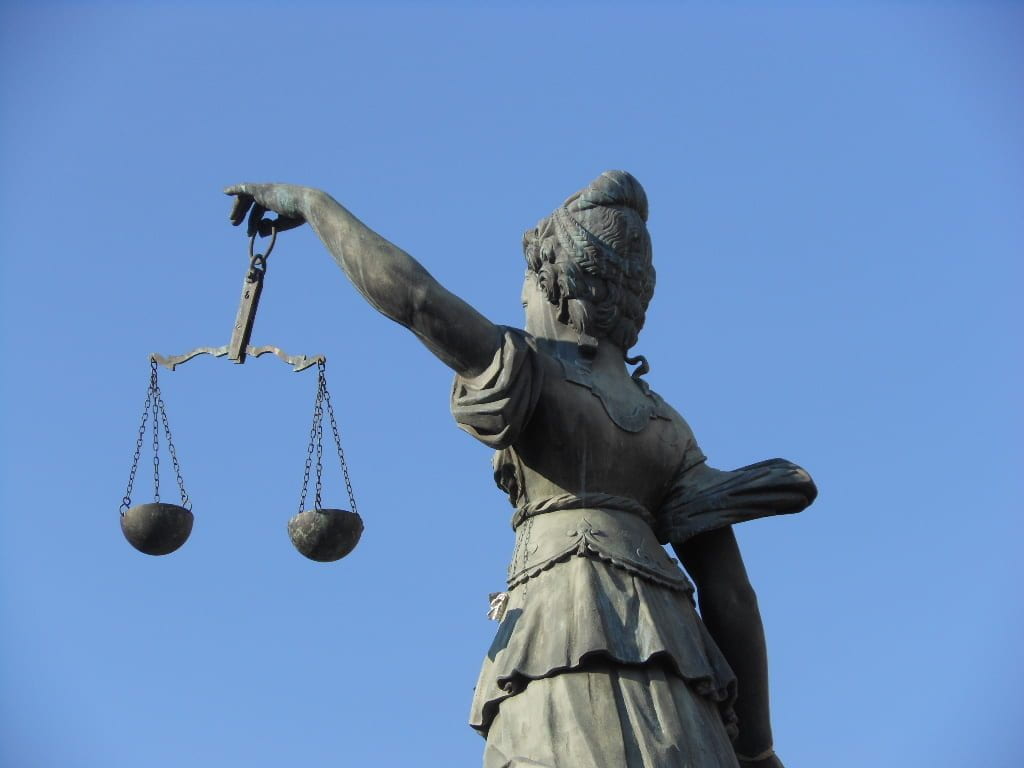

Tenet #3: The right to cross-examine an accuser. This tenet is the crux of due process as exercised under the auspices of a third party, whether a mediator, a judge, or an adjudicator. “The denial of cross-examination is a major reason that campus panels adjudicating sexual-assault claims have become kangaroo courts.” The right to confront an accuser is a component of justice; however, in many cases of sexual assault and violence, there is an invoking of “boys will be boys” and/ or “that’s just what we did in high school and college” to bypass cross-examination and the potential for prosecution altogether. This flippant attitude is primary to the problem. A double standard has always existed when describing the sexual behaviors of men and women.
In conclusion, what is interesting is for all the chatter of due process in this piece, the WSJ editorial board fail to recognize that due process is exactly what the women who have stepped forward desire. Due process allows the accusers the opportunity to tell their sides of the story and Kavanaugh to tell his side. It allows for cross-examination and a committee of his peers to decide if he should find himself rewarded with a lifetime appointment to the Supreme Court. Due process should bring about a more just society and system.
If the failure to administer due process signals “the new liberal standard”, how does it apply to conservative-led initiatives? Republicans control the executive, the legislative, and the judiciary – in effect, the Republican party is the chief executor of due process in all branches of government. Are Americans to infer that government officials have not implemented the due process as standard operating procedure? If there is a failure of due process, the burden of responsibility falls at the feet of the Republicans.
Due process seems like an overarching ideal outworked in the request to receive all the documents concerning his judgeship so proper vetting could take place in preparation for the confirmation hearing. It seems like a logical next step when considering the “committee confidential” emails that should not have been confidential; if there is nothing to hide, given the presumption of innocence and blind trust this society is to have for its leaders. Why is a due process so important in this case and for this person but not for others?
Where are the demands for due process for the children stolen from their parents and held hostage by the government as migrant families seek refuge in a country that once held so much promise? Where are the demands for due process when unarmed men, women, and children are murdered in their schools or on playgrounds, or streets or in their homes? Where are the demands for due process for the thousands of survivors of abuse in the Catholic Church? Where are the cries for due process when individuals commit suicide because they experience bullying because of something they cannot change or choose?
Articles 6-12 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights outline the basic tenets of due process. If Kavanaugh has nothing to hide and believes, as an officer of the court, that the system is just, then he should have no issue facing his accusers, calling a cross-examination, and letting the justice system work. Unless he knows the demands for due process are inequitable because justice is not just.
What is the meaning of “due process” as a component of the justice system, if a potential justice stymies the rights of accusers during his pursuit of a position in the highest court of the land as an executor of the justice system?