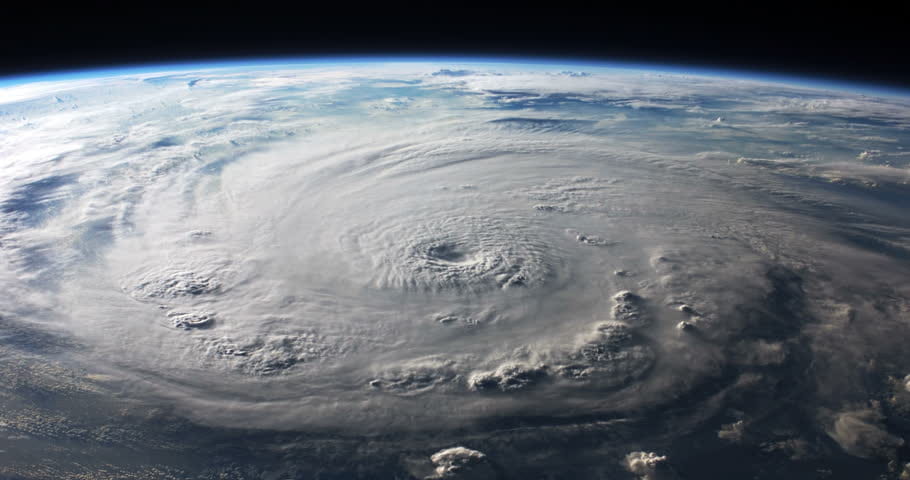
Hurricanes have been a natural disaster that Americans have been aware of for quite a while. They are, however, getting to be more frequent, and unfortunately more intense. They have devastated communities like New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina, the Caribbeans after Hurricane Sandy, and even Puerto Rico five years ago as a result of Hurricane Maria. Well, how do Hurricanes happen in the first place, why are they so damaging, and what is contributing to their intensity and frequency today? Hurricanes generally form over oceanic waters, when the warmth from the ocean water, paired with vertical winds, and the cool, moist air coming from surrounding areas come together in a dangerous mix. The warm water and the moisture in the air combine with the cool air, sucking in the air, and releasing it into the moisture, which then forms rain clouds and thunderstorms, with high winds that perpetuate the cycle. This impressive natural disaster is a powerful one, with wind speeds reaching over 70 mph, and can conduct enough electricity to power the world a few hundred times over.
The El Niño and La Niña

While hurricanes are powerful by themselves, certain occurrences in the environment can impact their severity and frequency. Among these factors are the phenomenon known as El Niño and La Niña, where the normal patterns of the climate are disrupted, impacting trade routes, regional weather systems, and the ecosystem as a whole. These phenomena also impact the hurricane seasons, including where they may impact, and how intense they may be. Under the El Niño conditions, hurricanes are experienced largely in the central and eastern Pacific regions, while during the La Niña, effects are felt in the Atlantic region near Florida and Puerto Rico. Typically, La Niña conditions may mean the possibility of more hurricanes, because the winds during the La Niña are more stable, (as opposed to the sudden changes in wind direction or severity), leaving the storm in better conditions to expand and develop.
Economically speaking, these developments can also impact international trade. Some hurricane seasons are so deadly, many trade routes near the path of the hurricanes are filled with docking spaces for vessels to take shelter during storms. Many companies are taking massive risks moving products during these storms, as their goods can get destroyed by the storm, or get lost in the sea due to changing winds and intensity of the storm. This could prove costly for both businesses and consumers, especially adding to the stress of the already existing supply chain crisis.
Hurricanes and the Danger to Human Lives
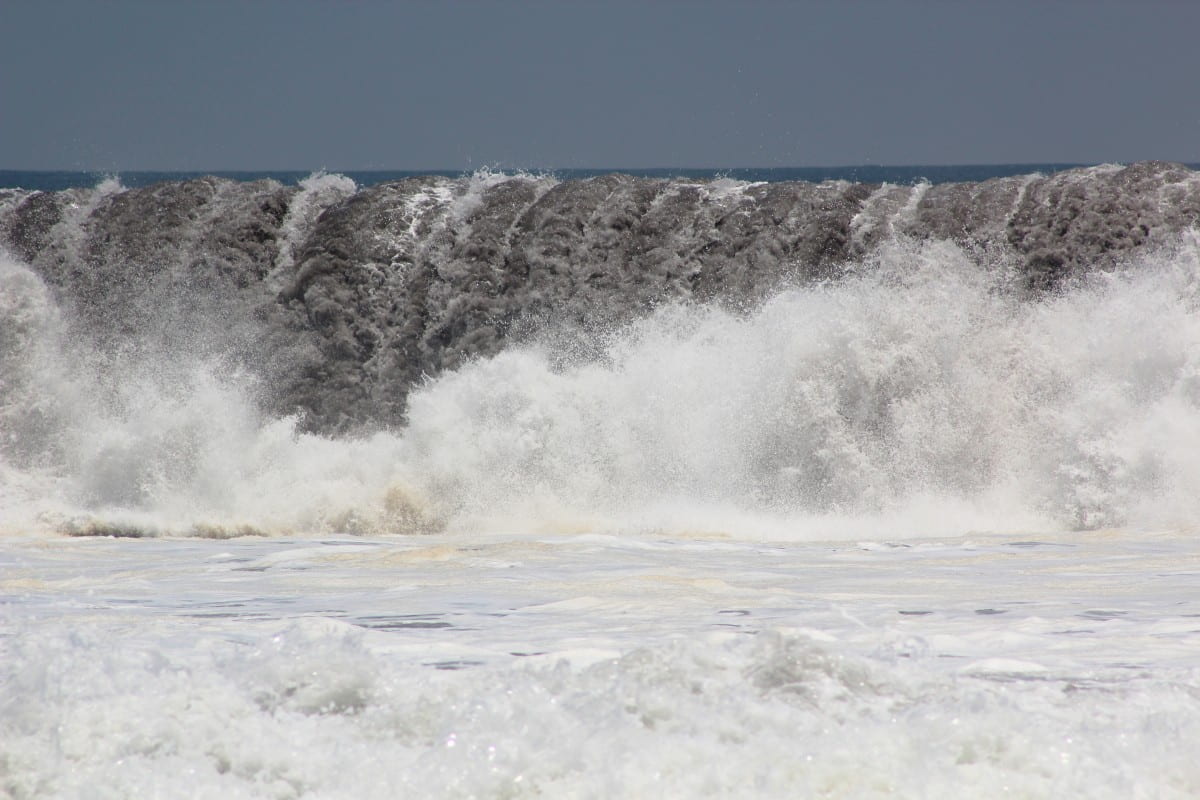

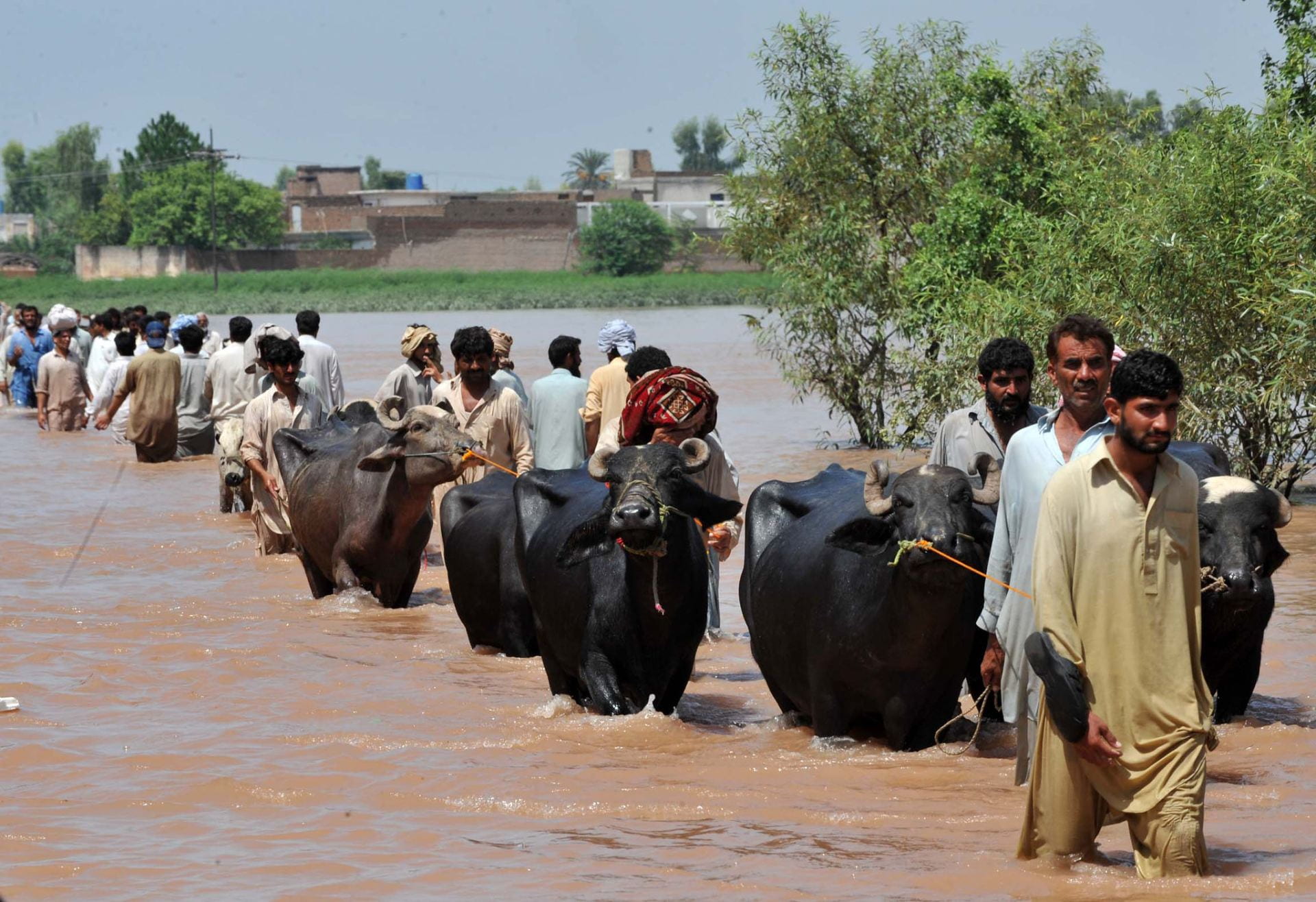
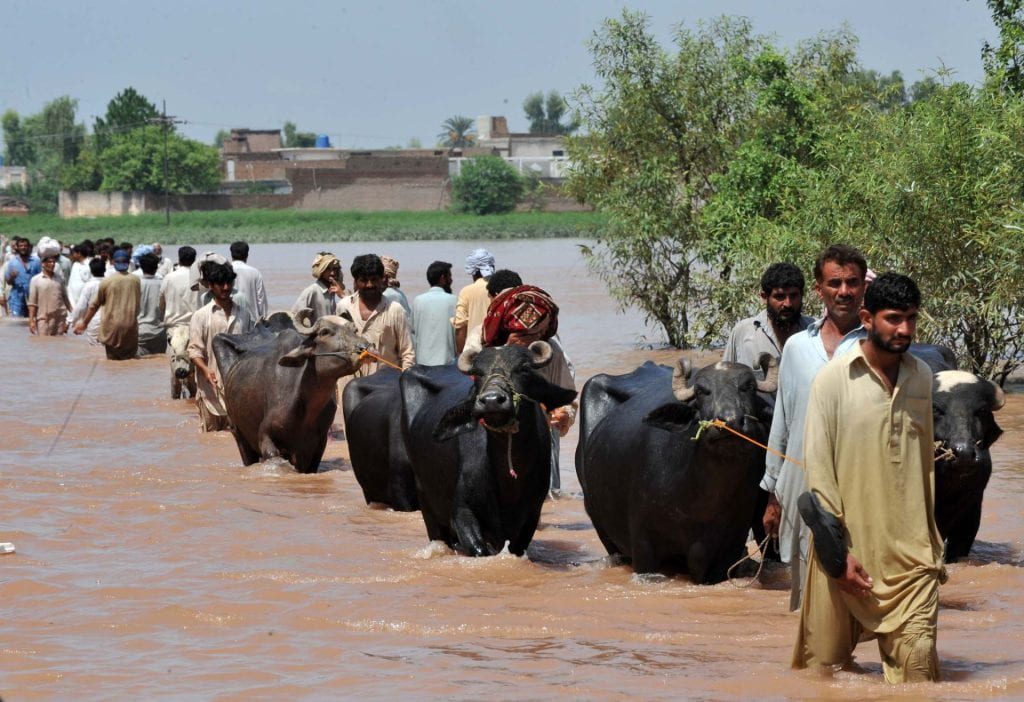
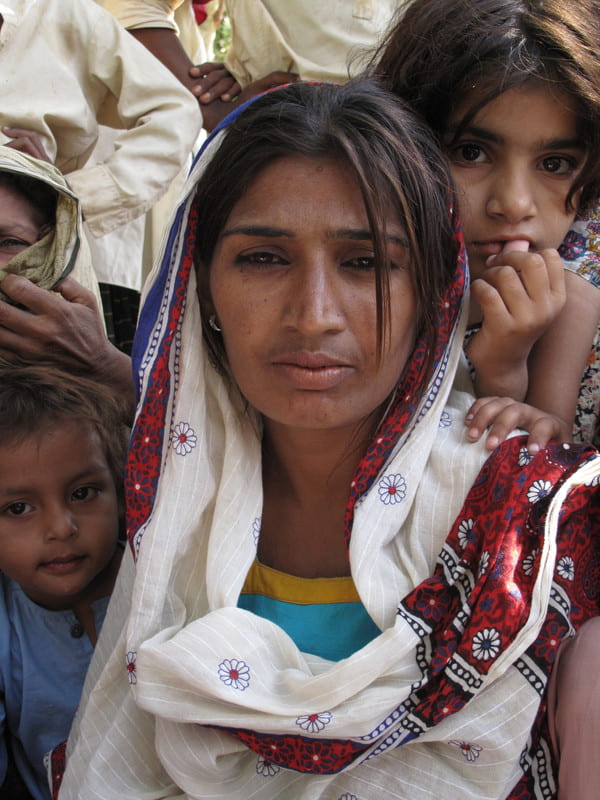
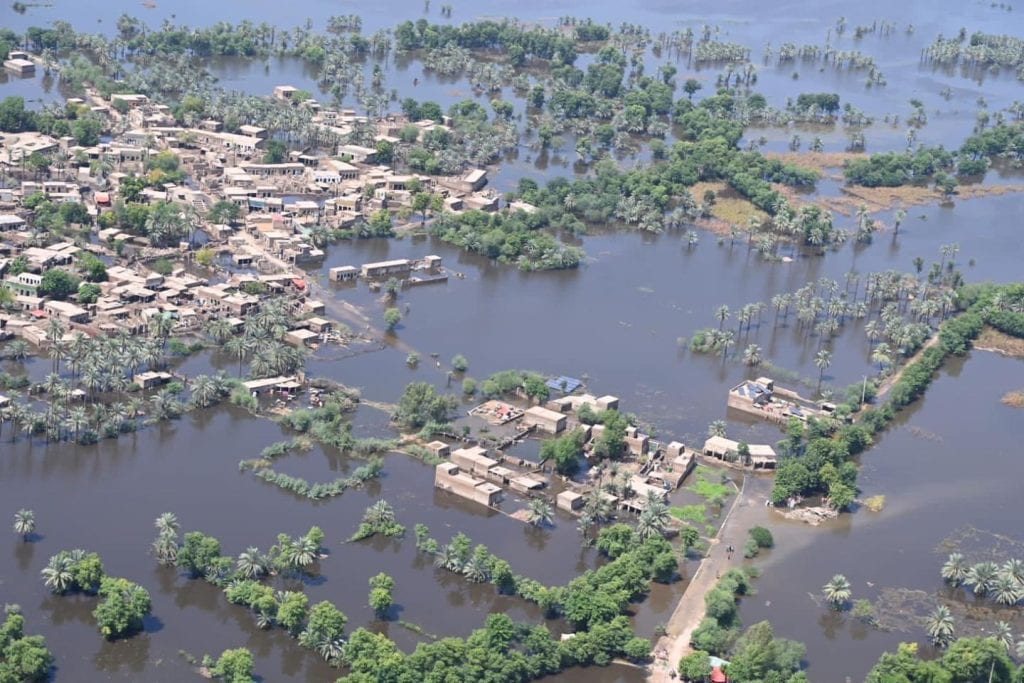
As intimidating and incredible as hurricanes sound, they also come with many health hazards and massively disrupt the way of life for the communities impacted by them. For one, hurricanes bring with them massive storms and high winds, oftentimes killing many people from their impact. If people manage to shelter from the storms, the resulting floods from the heavy rains can claim homes, properties, pets, and lives, as people struggle to literally, stay afloat. Even as this goes on, the community’s infrastructure is attacked, including roads, bridges, the power grid, and the water supply, as well as institutions such as banks, hospitals, and universities, to name a few.
Many of these institutions and infrastructure are essential for survival, meaning that people may remain stranded or stuck in a part of the region deemed dangerous simply because they no longer have access to travel across the roads and bridges the storm claimed. This also means that people of the impacted communities have to deal with the wet, cold temperatures while not having access to power or heat. Having no access to banks and hospitals means that you may not be able to withdraw much-needed funds or go to the hospital because it’s flooded or their equipment can no longer be used. Add onto this the issue of water supply, then suddenly the impact of the storm produces a failing society. These are issues that may take weeks or months even, to fix and get back to “normal” conditions.
Hurricanes are especially damaging because they bring in strong storm surges, which are walls of ocean water pushed onto shore because of the high winds, both of which are powerful enough to knock buildings over and destroy the standing infrastructures. Hurricanes can also cause storm waters, which are runoffs with contaminants that are picked up by the storm along the way, and which can include sediments, debris, fertilizers, fuels, and even sewage from nearby sewage infrastructures that have been damaged.
This can be dangerous to use and consume, and many official statements are posted following hurricanes urging people not to consume these waters, and the best practices to employ to decontaminate the waters before use. Hurricanes simply existing are majorly impacting people’s right to movement, freedom, safety, life, clean water, and so many more basic necessities. However, there is also an added layer of racism in this mix, mainly in areas of how hurricanes from different regions are responded to, the consequences of climate change, and how this continues to expand the developmental gap between nations of the Global North and the Global South.
Hurricanes, Climate Change, and Double Standards?
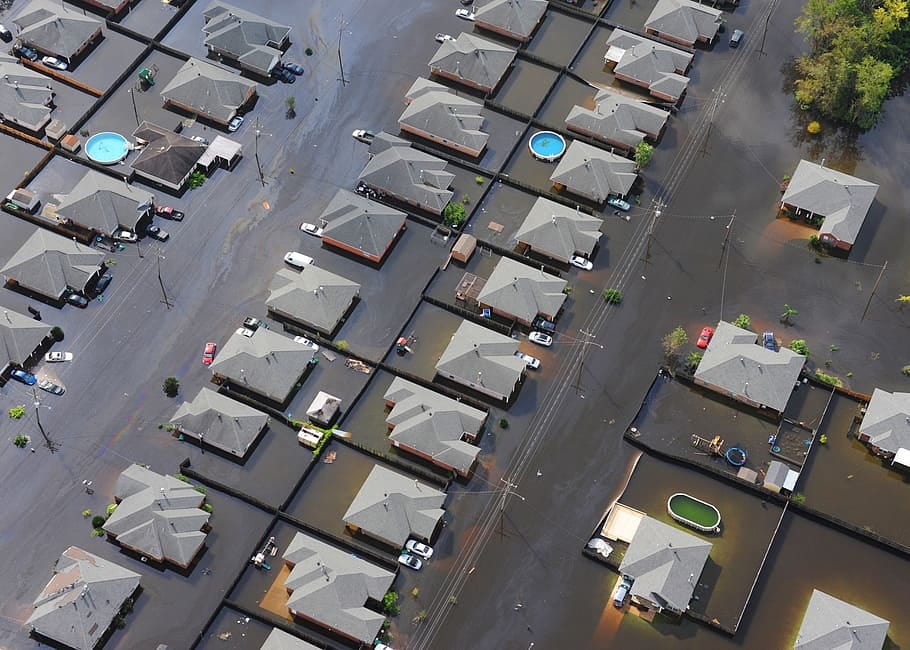

Unfortunately, the growing severity of the storms means that the communities impacted by them are having to not only brace against the storms but build their infrastructures to withstand the next round of storms. With the frequency of storms increasing, this also means that instead of a once-in-a-lifetime storm, these communities are experiencing storms of similar intensities every few years. Hurricanes form under conditions of warm water mixing with moisture and vertical winds, so the rising ocean temperatures (resulting from global warming) are naturally going to lead to conditions where hurricanes are more probable.
Among other things, climate change can impact not only intensify the storms, and the resulting consequences from them, that these communities deal with on a seasonal basis but also lead to the rising sea and ocean levels that will submerge many communities under water within the near future if climate change is left unaddressed. This will also contribute to the many other issues that will come out of climate change’s intensity, including the increasing number of climate refugees, the expanding food shortages, and the many conflicts that experts say will break out as a result of boundary disputes.
To make matters worse, although the storms do not discriminate where they make landfall, the responses to the storms have been different depending on the storm’s target. This was very clear in how the media and many Americans reacted to the two hurricanes that hit Florida and Puerto Rico within less than a couple of weeks of each other. Despite both regions being part of the United States, (Puerto Rico is a U.S. territory), Florida received more assistance and coverage when Hurricane Ian made landfall than Puerto Rico did following Hurricane Fiona. Fiona’s destruction was in addition to Puerto Rico’s recent recovery from Hurricane Maria’s impacts only five years ago. The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), which is the government’s response to natural disasters, awarded Puerto Rico $456 million following the destruction of Hurricane Fiona. This may seem like a lot, but FEMA awarded $1.2 billion to Florida in response to Hurricane Ian’s impacts.
Although the efforts of FEMA in response to Hurricane Fiona are considered by many to be an improvement from their responses during the aftermath of Hurricane Maria five years ago, the island of Puerto Rico continues to struggle with poor infrastructure and dwindling supplies. While it is fantastic that such support was given to Floridians struggling with the aftermath of Hurricane Ian, many of whom are people in the elderly age demographic, Puerto Ricans are terrified that their struggles will be brushed aside to make room for Florida’s recovery from Hurricane Ian. President Biden has promised that this will not be the case, and on his visit to Puerto Rico in early October, has even promised additional funds for their recovery endeavors. This funding, however, (a proposal of $60 million), is still nowhere near the required funds to rebuild an entire society for the second time within a decade.
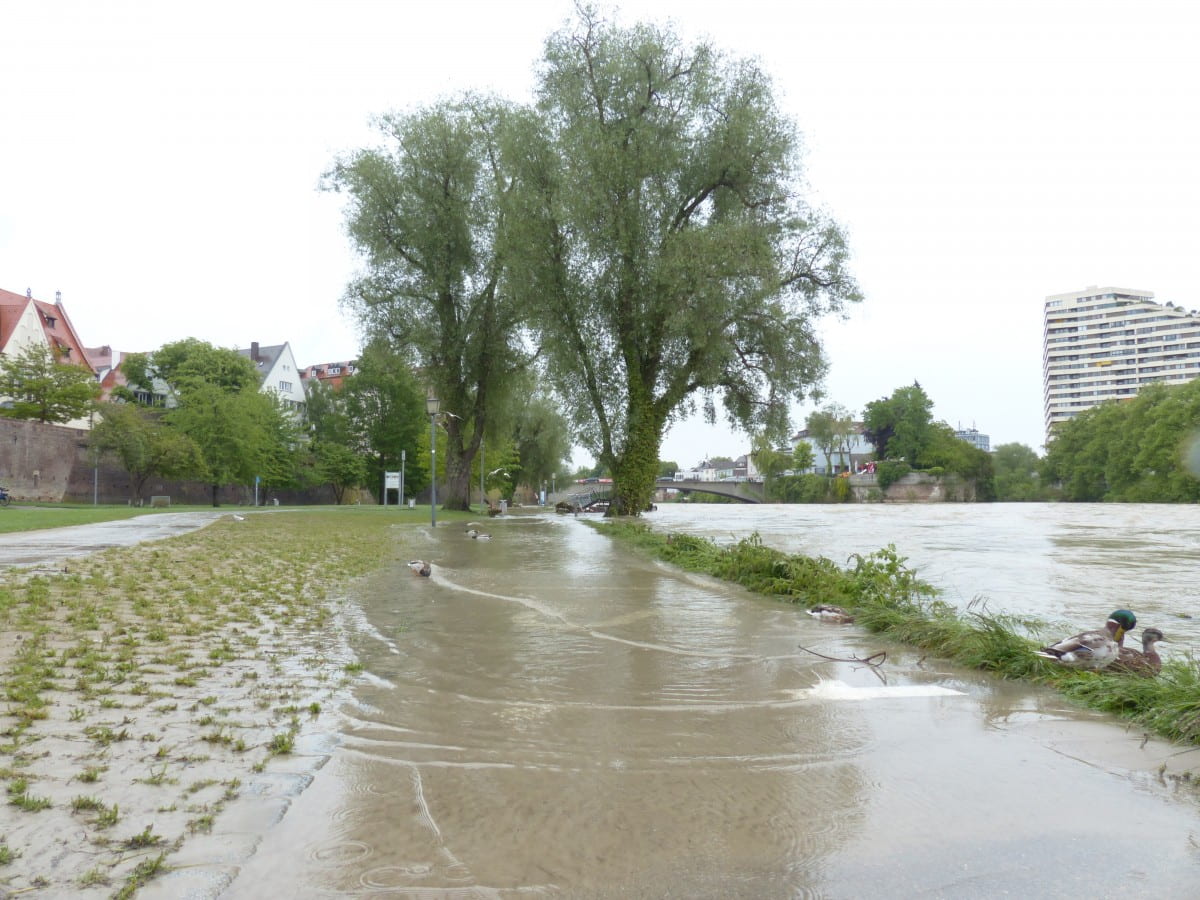

Additionally, although climate change is a global phenomenon, many of the communities impacted by it are those who are already experiencing marginalization, and this adds another layer to the climate crisis. There have been cries about how climate change is anthropogenic, (meaning it is an impact of human activities), and how the industrialized West has been contributing to climate change for centuries while the developing nations are experiencing the consequences of the activities of the industrialized West. This inequitable reality not only transfers the consequences of the West’s actions but also, the increase in climate awareness and environmental consciousness are used as arguments to prevent developing nations from using the same type of infrastructures required to compete with the economies of the industrialized West effectively and efficiently.
While this sentiment is definitely understandable, the push should be toward shifting policies to develop green infrastructures and help these nations transform their energy to incorporate renewable resources instead of chastising them for trying to develop their societies using the same techniques used by the West that brought the world to this stage in the first place. Blaming the developing nations while the industrialized ones continue to pollute is both hypocritical, and further destabilizes the economies of the developing nations, perpetuating the cycle of exploitation and the following lack of accountability that was founded and perfected during colonial times. When addressing climate change issues, these are some nuances to keep in mind; if climate policies are passed without considering the inequalities between how climate change impacts the developing nations differently than the industrialized nations, the wealth and inequality gap will continue to increase between the Global South and Global North.
Finally, with the increasing severity of hurricanes and the rising sea levels due to climate change, many cities around the world would be underwater as soon as 2030. These cities include Venice, Italy; Kolkata, India; Basra, Iraq; Bangkok, Thailand; Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam; and even several cities in the US, including Miami, Florida, and New Orleans, Louisiana. This will take with it the homes of the people who live there, and the immense history that can be found in these places today. It will instead plunge many people into food insecurity, forcing many to become climate refugees and increasing hostilities between the members of these communities and their inland counterparts to fight for survival.
So, What Can Be Done?

With the increasing severity of hurricanes, added to the ongoing climate crisis, many people around the world are experiencing both the worst and unfortunately the mildest (when compared to future possibilities of the climate crisis) impacts from these natural disasters. One of the many things that can be done on a global level is to continue to pressure every nation to convert their energy systems to support renewable resources and shift away from the fossil fuels that continue to exacerbate the climate crisis. This includes shifting away from oil, coal, and carbon, to incorporating solar, wind, and hydro-powered energy systems. Countries can implement green infrastructure and slowly attempt to return the environment to pre-pollution levels, (which may take hundreds of years to accomplish if started now).
At the domestic level, climate protections can be added, expanding the overall number of protected lands, and making acts such as deforestation and pollution illegal. Additionally, industries that impact the environment can be regulated for their business practices and their carbon footprints, and industries that use water systems can be further regulated for their practices of waste disposal, making sure the waterways are not polluted by their use of the resources. Furthermore, great effort needs to be taken to ensure that communities most impacted by climate change are included in conversations about policies and aid. Finally, on a more personal level, becoming more knowledgeable about the climate, and educating yourself and others to be more environmentally conscious can help shift the societal mind frame, resulting in the push for better policies addressing climate change as a whole.