Even though 1 in 6 people around the world experience disabilities, they are often among the forgotten groups within our society. While people with disabilities today are living under better conditions than their ancestors, there is still a lot of progress needed to be had to ensure that people with disabilities can lead a life of dignity and independence, free from the stigma and failures of society’s ableist mindset. In this two-part blog, we will focus specifically on children with disabilities within the American education system, but before that, it is necessary to frame the historical context surrounding the American education system, and how disability in America has been treated as a whole. As a result, part one of this series will focus on setting the historical context, exploring the American Education System as well as the treatment of people with disabilities throughout American history. The second part of this series will focus on exploring the contemporary issues faced by children with disabilities and their families within the American Education System and learn about a human rights framework for disability rights.
History of America’s Education System
The Unequal Distribution of Knowledge
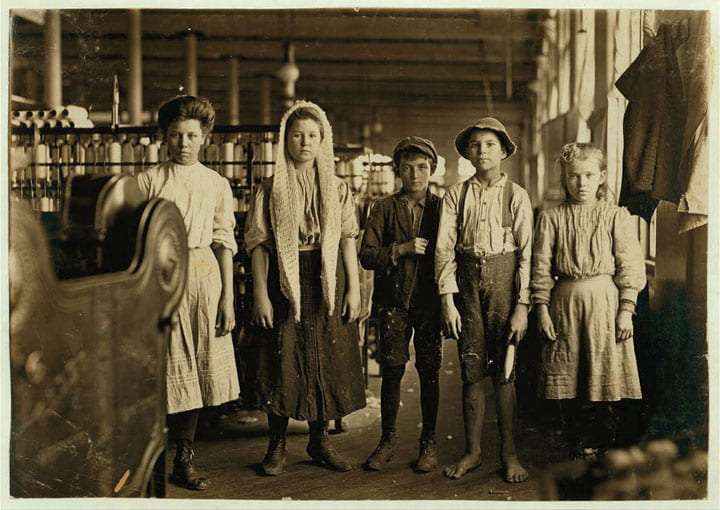

Since the founding of this country is rooted in capitalism, patriarchy, and white supremacy, many groups of people have been historically denied access to education. Traditionally, children from poor backgrounds were expected to help their families on the farm or work in their family businesses to make ends meet. As the industrial revolution took hold, child labor transferred from the farms to the factories, and many industries, such as the textile industry preferred to employ children to exploit their minuscule features. The petite features of the children came into use when they were needed to get into tight spots, or when operating machinery that required smaller extremities. Child labor in America was not outlawed until 1938, meaning that many children from poor families were illiterate and disadvantaged in comparison with children from wealthier families, who could afford to educate their children instead.
In addition to the absence of child labor laws, the patriarchal structure of American society deemed it more important for boys and men to be educated than their female counterparts. While poor families were denied access to education on the whole, even among wealthier families, the education of boys was prioritized over educating women. Women were expected to be homemakers and child-bearers in the private sphere, and the public sphere was reserved for their male counterparts. Many women were denied access to education, were not permitted to participate in politics and were limited to feminine jobs (such as teaching, nursing, and domestic work) when they did participate economically in the larger society. It was not until the 19th century that women were given more flexibility in their pursuit of higher education. Of course, not all women shared the same experiences, and white women were better able to receive education than women from other races, and as expressed earlier, wealthier women had more opportunities to educate themselves than did women living in poverty.
Furthermore, the foundations of white supremacy upon which America was built denied people of color access to education. Education provides the key to empowerment, and the status quo did not want to empower those they deemed to be inferior. Due to the hierarchical nature of this supremacist mindset, people from different groups were “dealt with” in different manners. For immigrants, access to education depended on their country of origin. Some immigrants, such as those from Asian countries, were barred from receiving education in America until the 1880s and were instead used for hard labor, like constructing railroads. European immigrants, on the other hand, were well-received by many in America, (with the exception of the Irish), and were granted many of the rights shared by American citizens at the time. There was however, a difference in treatment between the Old immigrants, (which were members from wealthier backgrounds with skills and education levels from the Southern and Eastern parts of Europe that came to America in the early 1800s), and the New immigrants (who were mostly impoverished, unskilled laborers from Western and Northern Europe who migrated to America in the late 1800s).
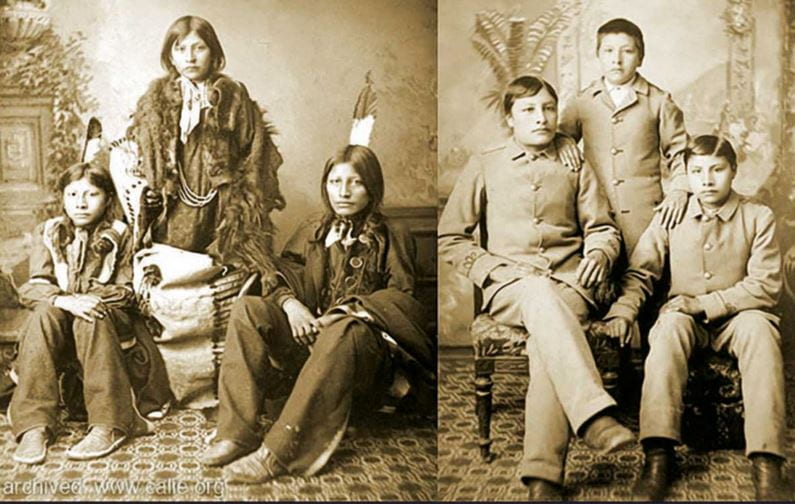
In addition to immigrants, the indigenous population of America also received access to education with a different approach. In an attempt to force them to forget their rich cultural histories and erase the cultural differences between the indigenous population and the larger (White) American society, children from different tribes were kidnapped and forced into boarding schools where they would learn to be assimilated into the American culture. Indigenous children were punished for speaking their language, engaging in their cultural practices, or even wearing cultural clothing (whether it was casually or for cultural practices). This is one of the reasons that today when people appropriate Native American culture (and attire), it can be very insulting, as they were punished for practicing their culture and wearing their traditional clothing.

Furthermore, during the enslavement of African Americans, who were deemed to be on the lowest level on this racial hierarchy, access to literacy was denied to them and outlawed, making it punishable by law for African Americans to be literate. This law was another way in which racist leaders of the time maintained control over the enslaved population. Following this period, there were many racist laws and social barriers to education for African Americans over time, and it was not until the famous passage of the ruling in Brown v. Board of Education that African Americans were given the right to equal education. With all that being said, there is still an ongoing struggle to bring equity, inclusion, and diversity into the American education system.
There can be a whole blog dedicated to the housing market, its impacts on funding for the local schools, and how this influences the level of education the children within those districts experience. As mentioned in previous blogs on similar topics, this funding practice tied to the housing market is, yet another way racism has seeped into American institutions. Transforming the American Education system into a more inclusive one will be a difficult fight ahead, as cries against teachings with an anti-racist approach are molding the current curriculum within the education system today.
The Historical Struggle to Secure the Right to Education for People with Disabilities
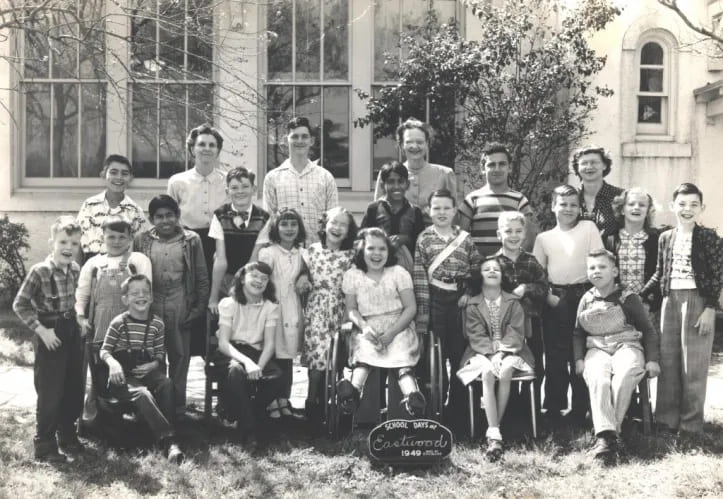
This exclusive approach to education also historically denied access to disabled individuals as well. American society has been structured with an ableist mindset, and people with disabilities have been stigmatized and marginalized by the larger society. In the past, many states prevented children with disabilities from attending school, choosing to place them in state institutions instead. Some wealthier families with disabled children could afford to home-school them, but the rest of the children with disabilities within society were not given that opportunity.
Even after education was required for all children, many states refused to provide accommodations for their students with disabilities, and the responsibility of securing access and mobility was placed on the children and their families, rather than the state. Judith Heumann, a well-known disability rights activist, was denied entry to her elementary school during the 1950s because the school district deemed her a “fire hazard” for being mobility impaired and having to use a wheelchair. It was not until the passage of the Education for All Handicapped Children Act (EHC; later known as the Individuals with Disabilities Act or IDEA) in 1975 that educational rights were protected for groups in need, including children with disabilities. While education access was protected under this law, the passage of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in 1990 was needed to ensure that people with disabilities are protected from discrimination in all aspects of society.
The Horrific History of Disability in America
How were People with Disabilities Viewed in the Past, and how has that changed today?

Understanding the historical context behind the American education system is only one part of this conversation. Outlining the lens through which disability is viewed today, and in the past, is necessary to comprehend the treatment of children with disabilities within the American education system. Today, people with disabilities are viewed in four ways. For one, following the traditional views of disability, most people with disabilities are simply ignored by society, both as a population, as well as systemically. You can see this is the case by simply looking at some of the ableist framings of our infrastructure. Needless to say, being an invisible group within society comes with its own challenges.
Another common way society approaches people with disabilities is to view them as the “super-crip” (which is extremely insulting) and look at their achievements as “inspirational.” People who believe this highlight people with disabilities in a supernatural sense, similar to how many African Americans were portrayed as supernatural beings with superhuman strength and abilities. This troupe was not helpful to the African American community then, and it is not helpful to people with disabilities today. Some may argue that this troupe seems to be a positive outlook of the group, but upon closer inspection, it is important to recognize the stress and burden of success this places on people with disabilities to feel accepted by society. It also encourages the mindset that these people who achieve extraordinary things are superhuman and that their achievements are highlighted because there is a general conception that this is abnormal for the group. Additionally, for a person with disabilities, it can be insulting and demeaning to hear the phrase, “if a person with a disability can achieve this, so can you!”
Another tactless way in which people with disabilities are regarded, as inferior to the rest of the population. Many able-bodied individuals either view them as a burden to society or simply objects to be pitied. This can have the impact of treating people with disabilities as second-class citizens and making them feel as if they are lacking in some way or another. Those who show pity toward people with disabilities may have good intentions, but their actions treat people with disabilities as victims of fate, rather than with dignity and humanity.
Finally, some people within society treat people with disabilities as if they have undergone a tragic event (whatever led to their disability), and people require “saving” or “treatment” to be “cured” of their ailments. This too is not the case. People with disabilities adapt to living their lives with their disabilities, and they don’t require anyone to “save” them from their disabilities. This is extremely insulting and rude to even think that, and it has the same connotations as would a “white-savior complex” within the context of race. The underlying belief in both of these situations is that the person doing the “saving” believes that the person that needs to be “saved” cannot do this for themselves and that they require the help of the “savior”.
While it is important to understand the contemporary views of people with disabilities, it is equally relevant to familiarize ourselves with the ways in which people with disabilities have been treated in America in the past. Until the 19th century, people with disabilities were separated from participating with the rest of the larger society. During colonial times in America, people with disabilities were treated in a similar light as the Salem witches, either burned or hanged. Others viewed disability as a sign of God’s disapproval of the colonists, and people with disabilities were treated as though they were possessed. Still, others felt that people with disabilities were a disgrace to their family and their community, and many were shunned from their homes. The larger society lumped criminals, poor people, mentally ill people, and people with disabilities under the same roof, labeling them as outsiders. This practice evolved into the many horror stories that we may be familiar with today regarding asylums and their treatment of their patients. An important note: as it is with other American institutions, racism, and sexism disproportionately impact the lives of people of color and women within these institutions, and this translates into how they are perceived and treated by the larger society as well. This remains true for people with disabilities with identities that are not aligned with the patriarchal, white society.
The mistreatment and abuse of people with disabilities within asylums
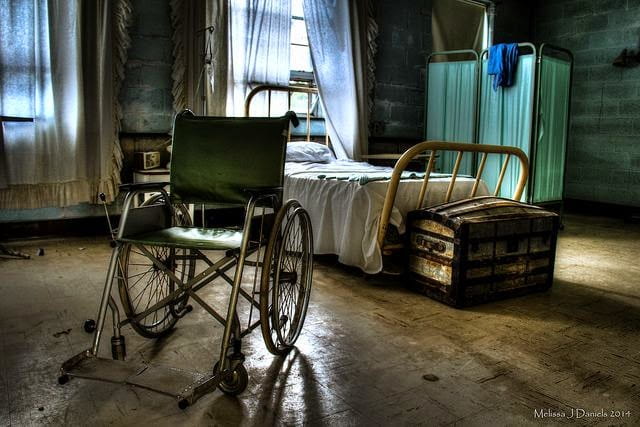

People with disabilities, along with other vulnerable groups that were stigmatized by society, were pushed into asylums. These were large “hospitals” stocked with medical equipment and personnel in which the goal was to provide care and treatment for the patients that resided within these asylums. The reason I placed hospitals in quotations is that many of these asylums were simply places to house all the people society did not want. These patients were experimented on, abused, neglected, and had almost no rights to defend themselves. Some patients that were from wealthy families were able to be treated at home, but others that came from meager backgrounds were not as fortunate. Many of the staff working within these institutions were unsympathetic towards their patients, feeling burdened by their very existence. Many people (within the institution and outside in the larger society) believed that people with mental illness and people with disabilities were “acting out” on purpose, to make life harder for those “upstanding” citizens of society. Many of the patients were misdiagnosed, and the institutions went from trying to care for the patients to “cure” the patients of their disabilities. The stigmatization of these groups within the asylums meant that their needs and wants were ignored. In addition to that, because it did not require a professional recommendation from a medical practitioner to admit patients into the asylums, many people were wrongly admitted to these institutions (because of personal grudges or disapproval of their behavior) for years without the right to defend and protect themselves.
Of course, it is not wise to lump every institution together and generalize about their treatment of their patients. While some were genuinely trying to take care of their wards and research ways to help “cure” them, others were less sympathetic to the plights of people with disabilities, both visible and invisible. For one, similar to the issues that American prisons face today, asylums were overcrowded, understaffed, and underfunded. This meant that each individual residing within the institutions was not given the personal care they required, and instead, they were all lumped into groups to receive generalized treatments. This was problematic in so many ways, but the most obvious is that disability takes many shapes and forms, and each individual had different needs that had to be met. Approaching a group of people with disabilities with generalized treatments meant that the doctors and nurses never took time to understand the details of each person’s disability, much less how best to approach them. As a matter of fact, because many believed disabilities to be a spiritual problem (a person being possessed by the devil), early “treatments” for mental illnesses and disabilities came in the form of exorcisms. When medical professionals finally were able to understand that this was a bodily illness, not a spiritual one, they then proceeded to conduct various experiments on the patients without having any knowledge of how to treat their patients. This is where the tortures began.

Medical personnel proposed many treatments to “cure” people with disabilities, including inhumane procedures that involved drilling holes into the patient’s skull in an attempt to bleed out the disease in question. While it is easy to judge in retrospect, in the beginning, many of the doctors truly believed that they were “curing” their patients with the various treatments they provided them, even as many recognized the inhumane nature of their treatments.
Other various treatments were administered to the patients, which can be defined as abusive and torturous today. Many women with disabilities were abused sexually, both by other patients and their caregivers. In addition to these incidents, many states (through the support of the law) practiced forced sterilization of disabled individuals in these institutions. The justification for this practice was expressed as cleansing humanity of these various illnesses and disabilities. Inspired by the American practice of eugenics, Nazi Germany expanded upon this practice to include everyone that did not fit their description of the “Aryan” race. To this day, America has not acknowledged this practice, and forced sterilization continues to be legal in the United States because of a Supreme Court ruling in 1927. The case in question, Buck v. Bell maintained that the sterilization of Carrie Buck (a woman who was raped and accused of “feeblemindedness”) was not in violation of the Constitution. This ruling permitted the forced sterilization of thousands of people with disabilities and other traits deemed “unwanted” by the general public. While the Supreme Court has outlawed forced sterilization as a form of punishment, it has never overturned its ruling made in Buck v. Bell. As a result, this practice is technically still supported within the legal framework.
With very little funding, the living conditions within the institutions also proved to be dangerous. The asylum itself was built to be uncomfortable because there was a belief that comfortable living would encourage patients to stay there forever. This meant that there was poor insulation, keeping the buildings cold. Due to the shortage of staff, many patients were restrained or locked up, while others were neglected altogether. These conditions, along with the “treatments” they received, exacerbated the patients’ conditions and were detrimental to their mental and physical health. Finally, as a result of society’s exclusion of this vulnerable population, many people outside of the institutions were not aware of what was taking place within. The patients inside these asylums were all but forgotten, invisible to the rest of society.
Deinstitutionalization

In an attempt to expose these terrible conditions to the larger society, journalists and activists spread accounts about the conditions within the asylums. Many were able to do this by investigating these institutions firsthand, and images (and videos) of the ill-treatment of the patients began circulating. As people started learning about the horrific conditions in which their loved ones were being kept in, the asylums faced a lot of backlashes. Amid all the backlash, in 1946, President Truman passed the National Mental Health Act to begin research on neurological issues. It would not be until 1955, however, that things changed drastically for those suffering from mental illnesses. Thorazine, a psychoactive medication that was introduced as a way to treat mental illness, and the population within the institutions peaked around this time. In the 1960s, there was an attempt to take a community-based approach to treat mental health, but it lacked the funding to progress in any substantial way. In 1981, Ronald Reagan takes a drastic step to stop government funding to help with mental health, forcing institutions to close their doors and leaving the patients on the streets.
This dramatic change provided no cushion for the patients to fall on, and much experienced homelessness as a result. With nowhere to go and no help from the government, many people with disabilities lost their lives because of this policy shift. These individuals never received any compensation for their ill-treatment, nor were they given any transitional housing or aid to help restart their lives. Of those that did not end up dead, many people with disabilities were imprisoned for causing “public disturbances.” Unfortunately, this practice continues to exist today, especially impacting people of color, and people living in poverty disproportionately. Of course, the imprisonment of people suffering from physical and mental disabilities exacerbated their conditions, and the lack of care and treatment resulted in many deaths. With nowhere to go, and no rights to protect this vulnerable population, people with disabilities continued to suffer due to systemic failures.
The movement for disability rights

Eventually, following the lead set by the Civil Rights Movement and many other movements such as the Women’s Rights movement, and the sexual revolution that fought for the rights of the LGBTQ+ community, people with disabilities came together to stand against discrimination toward them from the larger society, and fight for their rights to exist and prosper like any other groups. People with disabilities wanted to challenge the practice of institutionalization and employed many of the tactics that were used during the Civil Rights Movement. They staged sit-ins in governmental buildings like the FBI building, challenged the mobility norms of society by blocking busses (that denied accessibility to people with disabilities) from moving, and they protested on the streets, able-bodied allies and people with disabilities alike, fighting for their rights.
People with disabilities were also exhausted with the ableist society they lived in and began to challenge the many barriers within society that kept them from living as independent individuals. They did not need someone to hold the doors for them; they wanted the doors to remain open automatically long enough for them to pass through. They wanted accessible sidewalks on which they could move their wheelchairs, walkers, and other walking devices (if applied) safely, and independently, without having to depend on others to take care of them. People with disabilities and their caregivers began to challenge the largely held view by society that people with disabilities were a burden to society. They argued that societal barriers made them dependent on others and implementing disability-friendly solutions can provide the community with the independence to live their lives freely.
In 1973, with the passage of the Rehabilitation Act, specifically, Section 504, people with disabilities, for the first time, were protected by law from being discriminated against. This act recognized that the many issues faced by people with disabilities, such as unemployment, transportation, and accessibility issues, were not the fault of the person with the disability, but rather, a result of society’s shortcomings in failing to provide accessible services to the group. While this was a major win for this community, this law only applied to those who accepted federal funding, meaning that the private sector, and even many of the public sector, could still discriminate against people with disabilities. Following the passage of this act, many people with disabilities were instrumental in ensuring its enforcement. Many of the sit-ins referred to above happened at this time, as an attempt to keep governmental offices accountable. Protestors would block the entrances into the government buildings, or stay in the buildings past close time, refusing to leave until the necessary changes were agreed to be made to the buildings (such as including ramps to the building or elevators inside the buildings) to meet the Section 504 requirements. This continued until Ronald Reagan issued a task force to stop the regulatory attempts made by supporters of Section 504, and the protections secured by the IDEA, an act that protected the educational rights of children with disabilities. Over the following years, his decision resulted in hundreds of frustrated parents and people with disabilities alike questioning the justification for stopping the regulatory actions of Section 504. This backlash, accompanied by the tireless leaders of the community meeting with White House officials, ended in Reagan reversing his crackdown on Section 504, allowing regulations to continue on businesses that refused to incorporate practices outlined in Section 504.
Additionally, following the passage of the Fair Housing Act in 1968, people with disabilities, along with other protected groups such as race, gender (and sex), and religion, were protected from discrimination in housing. The first passage of the act initially only included race, religion, national origin, and color, as the protected groups. It was not until 1974 when sex (and gender) were added to this list, and not until 1988 when the disability community was added. Still, this act was especially important for people with disabilities because it required home builders to provide reasonable accommodations necessary for the inhabitants to live comfortably and move around the housing unit.
Following these many small victories came the biggest one of them all, the passage of the Americans with Disabilities Act in 1990 (ADA). This law was the first general law protecting people with disabilities from discrimination in all aspects of society, including in housing, employment, healthcare, transportation, and many other social services that impacted the lives of this protected group. The passage of the ADA focused on four main themes: full participation, equal opportunity, independent living, and economic self-sufficiency. Full participation focuses on the ability of people with disabilities to participate in all aspects of their lives, including having access to transportation, entering and exit buildings without issues, being able to vote on inaccessible sites, and enjoying life without social barriers that prevent them from being able to do so. Equal opportunity centers on being able to be employed without facing discrimination due to their disability and being able to take advantage of other such opportunities free of discrimination. Independent living brings attention to the ableist framework that society is structured in and recognizes the need for a more disability-friendly society, with access to handrails, ramps, curb cuts, and other options such as disability-friendly online sites (that for example, speak the menu out for you if you are a person with visual imparities) to raise the living standards for people with disabilities. The basis of this pillar is to empower people with disabilities with tools they can use for themselves in order to live independent life. Finally, the economic self-sufficiency piece mainly concentrates on the economic security of people with disabilities. This includes access and accommodations to receive higher education, better employment opportunities (including training, transportation access, and mobility within the workspace), and other such necessities to promote economic self-sufficiency within the disability community.

Many communities across the United States are brainstorming innovative ways to be more inclusive, but we are far from being a fully inclusive society. People with disabilities remain among the invisible groups within society, not because their advocates are not loud enough, but because their cries are being ignored by lawmakers and their local representatives. Globally, the United Nations established the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities(CRPD) in 2006, working to shift the mindset of people’s views on disability as a whole, as well as protect and promote the rights of individuals with disabilities by empowering them to fully participate in society with the dignity and humanity they deserve.
While this blog mainly focused on the historical context of the American Education System and the perception of people with disabilities in the past and today, the next blog will focus more on the treatment of children with disabilities within the American education system today, the many challenges they continue to face, how the pandemic has impacted their learning and development, and the human rights framework necessary for disability rights to do what we can to be more inclusive and less ableist as a society.