Imagine discovering that your internal identity does not align with the way that your body looks or the way that you are perceived by society. Because you recognize this internal dichotomy, the society you know and love treats you as an outcast. You are regarded as less than human. Your family abuses you for pursuing a physical body and social presentation that aligns with your internal identity. Society at large is structured in a way that makes it relatively impossible to get a formal job or make money in a safe way. Transgender people in India experience this every day.
A. Revathi is an activist for the rights of transgender people and other gender and sexual minorities in India. In her book, A Life in Trans Activism, she details many struggles she faced while navigating the economic system of India. Most transgender people in India work in the informal spheres of sex work and street begging, but a lucky few find low-salary jobs at LGBTQ+ Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) or service places.

Because of the prejudices and stereotypes held by many employers within India, transgender people are often discriminated against in the formal sphere. If a man comes in for an interview, and his documentation still has an F sex marker, the employer will know that he is transgender and all prejudices and stereotypes that they hold will then apply to the man searching for a job. The process of changing one’s sex marker on official documents is a complicated and grueling process for transgender people, which makes it almost impossible to go stealth* in one’s workplace. It was this lack of economic mobility that lead Revathi, and many others like her to the streets for sex work.
*Stealth (adj.) – describing a transgender person who presents themself as a cisgender member of the gender they identify as, often to avoid discrimination. For example, a male-to-female (MTF) transwoman presents as a cisgender woman and keeps her trans identity a secret to avoid violence.
In India, self-employed sex work is legal, but many police officers will find other reasons to accuse sex workers of crimes like loitering or stealing, whether the accusations are true or not. The general public tends to accuse them of stealing in order to demonize them or try to get them off the streets, which often leads to violent confrontations with community members and the police. During sex work, Revathi, like many transgender women, was often put into dangerous situations with the public as a result of the deeply rooted stigma surrounding transgender people. She experienced sexual assault, public abuse, and was sometimes not paid for her services. Most transgender sex workers must be very careful to keep their identities as transgender silent because many face violence if they are outed.** On the other hand, when outed, some people receive dehumanization in the form of fetishization which results in more violence and less pay.
**To out someone (v.) – to reveal someone’s sexuality or gender identity without their permission or control, often leading to dangerous situations for them.
Economic Consequences
The few that find jobs, often at LGBTQ+ organizations, are often paid less and treated with disrespect by their colleagues and employers. While reading A Life in Trans Activism, a pattern stuck out to me. I would like to call this something like “The Vicious Cycle of Workplace Inequality.”
- The formal work of a certain group of people is undervalued and/or ridiculed by society.
- The marginalized group then internalizes this as a reflection of their character and feels as though they have “something to prove” while working in the formal sphere.
- They then work harder and accept lower pay than their colleagues.
- Co-workers and employers take advantage of their willingness to work hard for lower salaries and disrespect their work-life boundaries.
- The disrespect becomes a foundational aspect of their workspace, and transgender people feel and live subserviently to society. The cycle repeats.
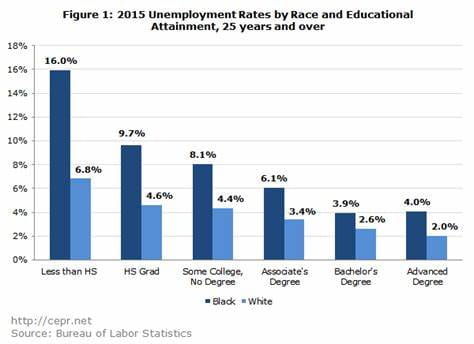
The Vicious Cycle of Workplace Inequality can apply to any group of people whose work is undervalued. We see this in the American workforce with Black employees. There is a widely-held stereotype in America that Black people are “lazy workers” because of their lack of sufficient economic mobility. Employers internalize this and hold Black workers to a higher standard in which they must “prove themselves” as hard workers. It is often the case that Black employees work twice as hard as their White counterparts and are still undervalued by their employers and colleagues. They internalize this as a reflection of themselves and work harder and harder for less and less. This phenomenon is not only manifested in the salary gap between races, but also in the levels of worker burnout and unemployment rates.
A. Revathi experienced the Vicious Cycle herself while working as an openly transgender woman at an LGBTQ+ NGO in India called Sangama. Even while she was head director of multiple subsections of the NGO, she experienced disrespect from the staff she was directing. Here, Revathi reflects on her experience:
“[Sangama staff] were well behaved with [past directors] and respected boundaries. However, with me, they were very different. They would storm into my cabin and argue endlessly with me, often in very rude or offensive language. They demanded prompt promotions, increases in salaries, and crowded my working hours with endless demands and trivial things, which they could have handled themselves.” (Rēvati, 110)
Revathi charitably credits this to her open-door policy and her show of belief that hierarchies in workplaces were solely for accounting purposes, and should not reflect upon the social interactions of the staff. I suspect that the main reason that she has these policies and beliefs is that her work has been consistently undervalued and she has internalized that she will never be seen as “above” anyone else in her workplace. By setting and enforcing certain boundaries with her staff, she would have to acknowledge that she is above them in the workplace. This would break the social contract that says that she is always on the base of the metaphorical pyramid because of her transgender identity.
Government Progress (or lack thereof)

The Indian Supreme Court ruled in 2014 to create a third gender category called “hijra” which would be inclusive of gender nonconforming and transgender individuals. People in this category were legally categorized as an “other backward class” or OBC. Job reservations were made for people of OBCs in an attempt to improve the economic status of transgender people. Read more about this ruling here.
In addition to this ruling, in 2019 the “Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill” was passed, which served as an anti-discrimination bill meant to improve the status of transgender people in education and the workforce. It was faced with backlash from the trans community because it required a person to submit proof of gender reassignment surgery to the government before being able to change their gender marker legally. This type of policy is called trans-medicalism*** and is exclusive and harshly binary. Read more about this bill here.
***Trans-medicalism (n.) – the idea that one must medically transition, in other words: go through gender reassignment surgery, in order to be a valid member of the transgender community.
Although these actions were well-intended, neither the 2014 ruling nor the 2019 bill has been well enforced. They have been inefficient in changing the economic and educational statuses of transgender people. Employers still have room to discriminate against workers. Sex workers are still treated horrifically and inhumanely in the streets. Transgender employees are still disrespected in their workplaces and have low opportunities for economic mobility. One of the problems with these actions is that they are both “top-down” approaches, which start with government implementation and slowly trickle down into cultural changes and real-life improvements for transgender people. Many recommend a “bottom-up” approach, which begins with radical cultural shifts and builds its way up to government implementation. While both are valuable, the “bottom-up” approach is more efficient in creating quicker social change for people genuinely affected by the social issues at hand.









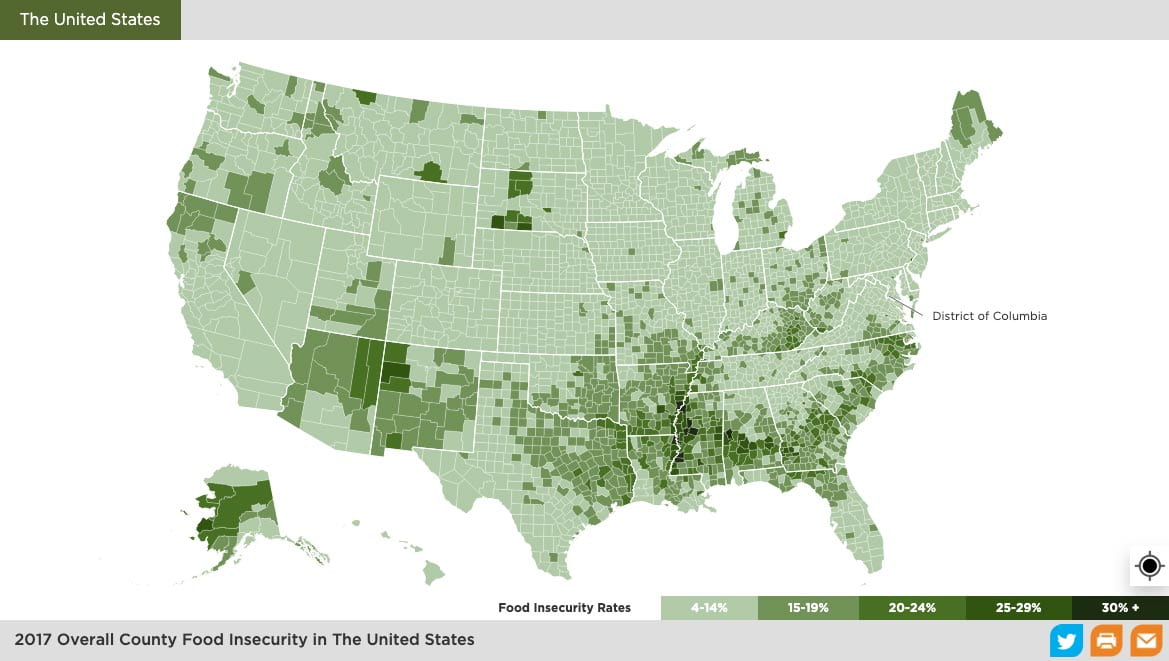
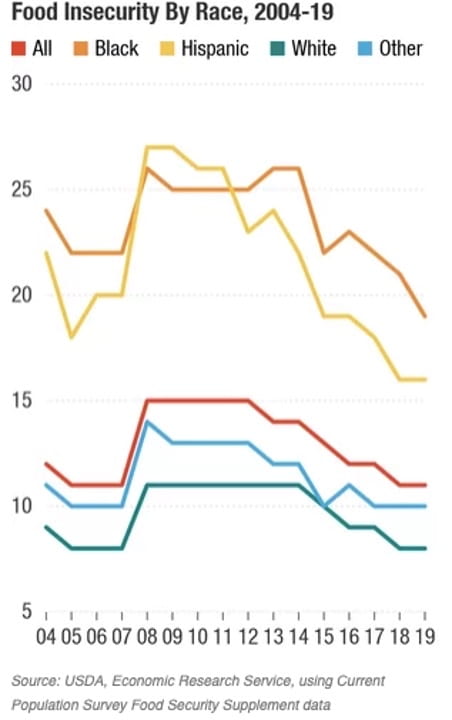 This chart goes on to show the differences between food insecurity rates based on race. Although each demographic has seen a decrease in their food insecurity rate over the last several years, there is still a very large gap between the races, with the biggest difference being between Black and white Americans, who have a difference of roughly 10% between the groups. Even worse, there are countless combined consequences that can hurt already marginalized communities from living in a food apartheid, including an increase in obesity and physical conditions like diabetes due to the lack of access to affordable and healthy food options.
This chart goes on to show the differences between food insecurity rates based on race. Although each demographic has seen a decrease in their food insecurity rate over the last several years, there is still a very large gap between the races, with the biggest difference being between Black and white Americans, who have a difference of roughly 10% between the groups. Even worse, there are countless combined consequences that can hurt already marginalized communities from living in a food apartheid, including an increase in obesity and physical conditions like diabetes due to the lack of access to affordable and healthy food options.