Over the past few weeks, we have been examining, in this environmental series, the various ways in which our over-consumption, coupled with the negligent practices of industry, have led to the deterioration and devastation that climate change has yet to fully unleash upon us. We have observed the intersectionality between fast fashion, human rights violations within the industry, and how the fashion industry perpetuates colonialism and imperialism while simultaneously amplifying the climate crisis. We have also studied in detail the process of oil development, and the very real consequences that carelessness from industry can have on communities and ecosystems alike. We have further focused on the lasting implications of these industries, and how environmental racism and exploitation, both of resources and people, have led to global inequities in quality of life. Now, we shift our focus to the mining industry, which encompasses so many raw materials that are transformed into the products we consume on a regular basis around the world. These products include materials for constructing infrastructure like roads and buildings, raw materials used to build and support the electric grid, and even materials used in today’s newest laptops and smartphones. One can even argue that mining is a vital part of an advanced industrial society.
The Mining Industry

The mining industry can be categorized into many different groups, but some of the most popular categories include, coal and Uranium mining, metal mining and industrial mining. Coal mining, and the mining for Uranium are largely used for energy purposes, such as generating electricity or using the mined Uranium for nuclear power. Metal mining consists of mining for metals such as zinc, gold, copper, iron, silver, and other such precious materials. These metals can be sold for use in technological devices, but, in cases like iron and zinc, can be turned into various products, from tools to jewelry. Finally, industrial mining digs up raw materials for manufacturing and industrial consumption, including raw materials and chemicals used in construction jobs. These three areas of mining alone impact so many aspects of our society, from our energy consumption to our smart gadgets and our stylish accessories, down to the buildings we work out of, and to the homes we live and grow up in. This is just an introduction to just how crucial a part mining plays in our lives, and why it is necessary for us as a world to begin to ween off of this dependency on mining and shift our focus toward sustainability and renewable resources. In order to fully comprehend the need for this shift, we must look closer at some of the mining techniques and the dramatic impacts their operations have on the environment.
Surface Mining Techniques and their Environmental Impacts
Strip Mining
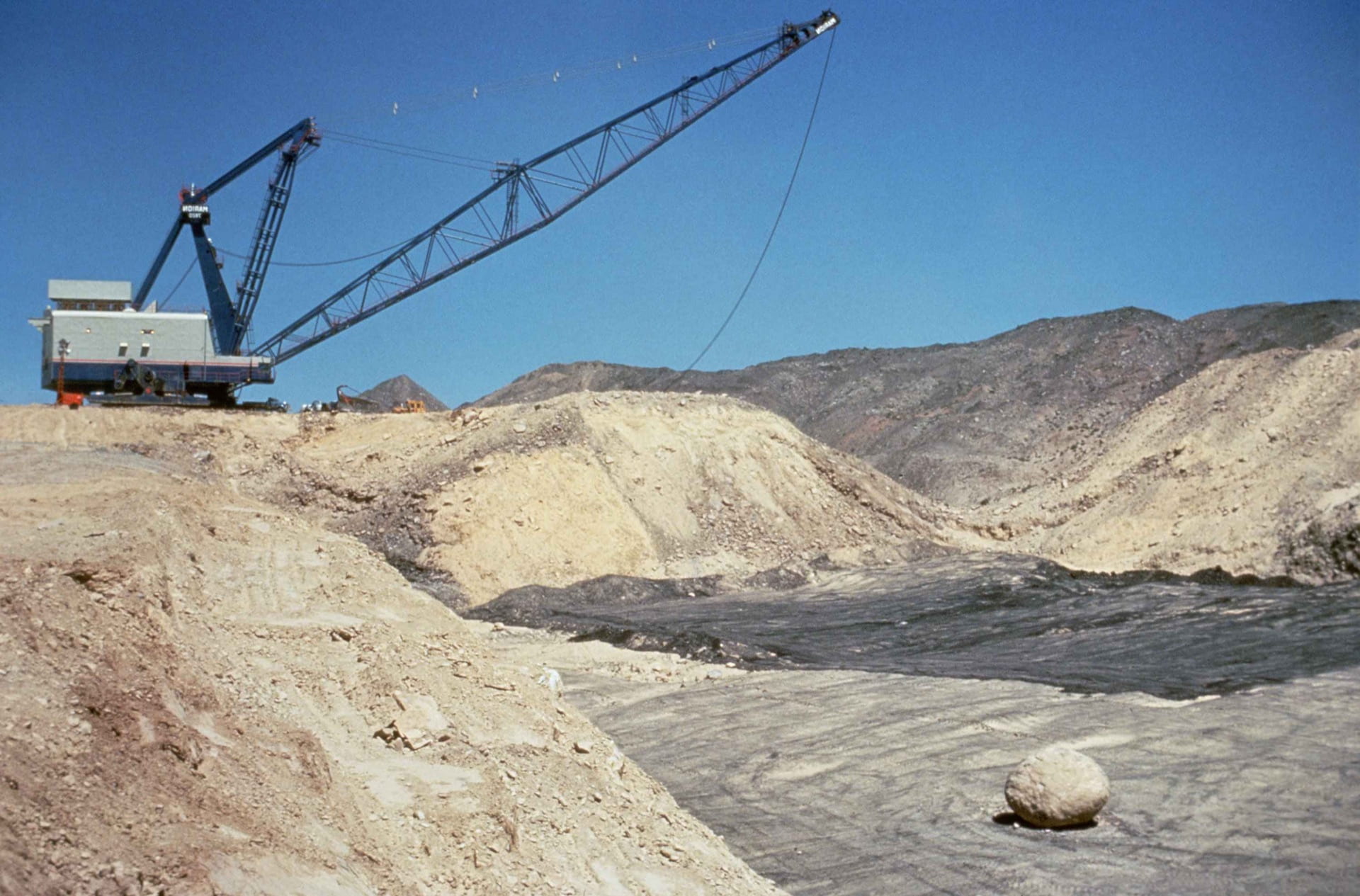

A commonly used surface mining technique, strip mining is used to remove the surface layers of soil until the desired resource is exposed. Especially used for coal extraction, this process includes drilling and blasting portions of the earth to reveal the minable resource. These blasted off pieces of “overburden” are cleared and removed from the site, and chunks of coal, (or other resources), are extracted from the blasted site and loaded up onto trucks that transport them away for use. This method greatly impacts the environment in the surrounding areas. The earth is made up of many layers of minerals. These minerals are made up of decomposed organic matter that have been compressed over time into materials we extract today, such as fossil fuels and sand. One of these layers consist of topsoil, a rich layer of naturally composed, nutrient-rich soil that is crucial to the land’s ability to grow food or herbs. The strip mining method, along with some of the other techniques of mining, leaves the topsoil exposed to the natural elements, and the soil can begin to erode, leaving the land barren and jeopardizing its ability to support life. Strip mining can also pollute nearby sources of water by releasing certain acidic minerals that are dug out of the ground during mining operations and spill into the waterways, react to the water and oxygen, expose the marine life to toxic waters and pollute water sources used for domestic and agricultural consumption. These practices impact the biodiversity of the regions in which they take place, transforming more than just aesthetic beauty for us to enjoy. Biodiversity serves varying purposes, as each organism is part of a larger food chain, and having a rich, vibrant, biodiverse environment comes with its own benefits to the planet and its life forms. Certain keystone species play crucial roles in the survival of an ecosystem, and these mining practices endanger their existence, further deteriorating the conditions of survival for many species living in these areas, including humans.

Open-Pit Mining
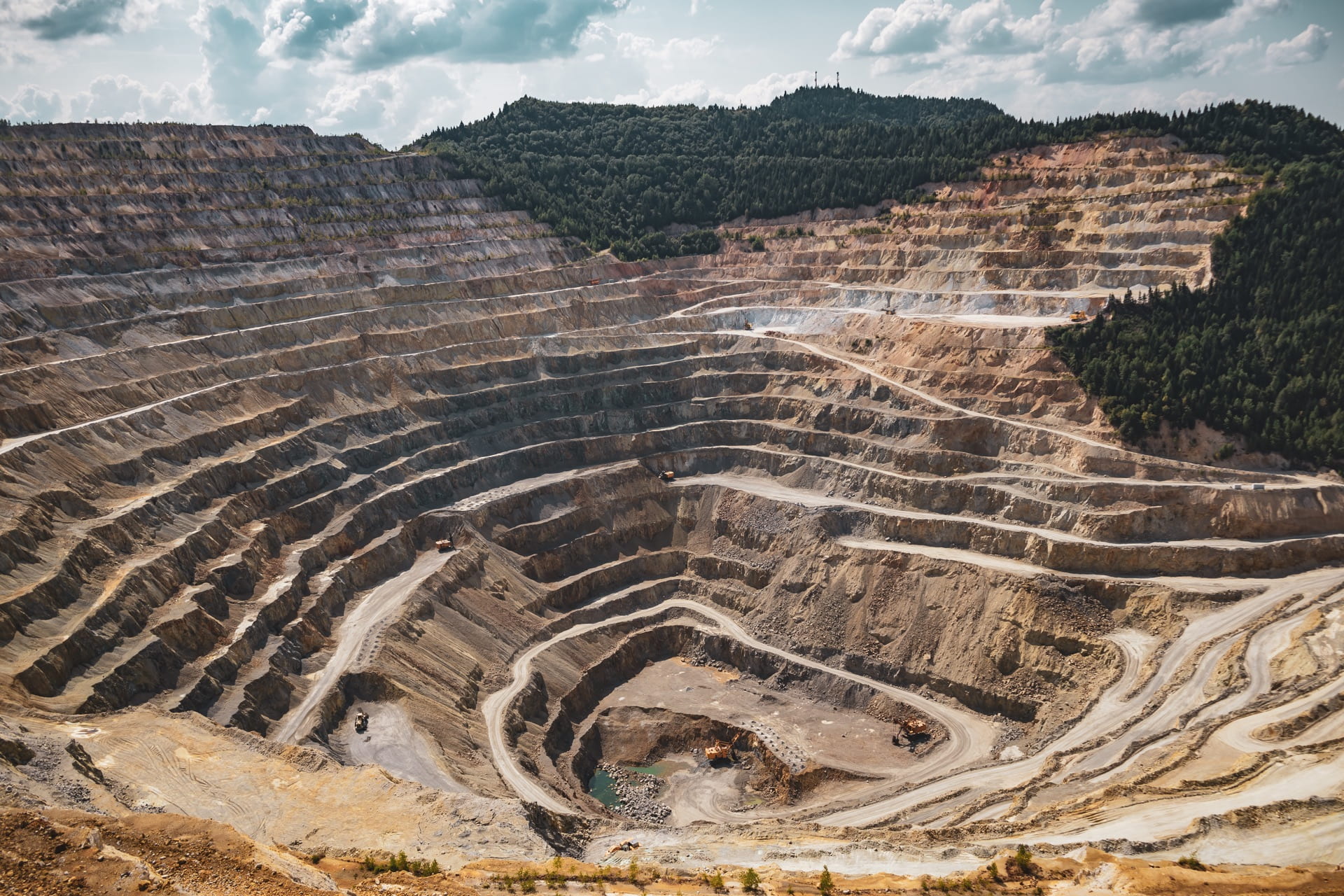

Another surface method of mining is the open-pit mining technique. This process is similar to the strip-mining method, in the sense that it also requires the blasting of mining zones. It does differ however, in that these explosions are used to create large craters, and then machines are used to extract precious materials from these concave, open pits. Materials extracted from this process are also transported away via trucks, similar to the strip-mining method. This method is commonly used for both coal mining, as well as mining metals such as copper, gold, or iron. This method, just like the strip-mining method, causes severe degradation and destruction of the natural environment. Some of these impacts include polluted waterways, air pollution, soil erosion, and a destruction of habitats that support and promote biodiversity. The process of open-pit mining, during the blasting and drilling of the earth, release metals and radioactivity into the dust clouds. Anyone breathing this air is at risk of developing serious respiratory illnesses. In addition to the dust clouds, the emissions released by the heavy machinery also add to the polluted air of which mining workers as well as local residents have to breathe regularly. As if that was not dangerous enough, open-pit mining also causes water pollution, in similar ways to strip-mining. The release of sulfur into the local waterways, and its reaction to the oxygen turns the water acidic, endangering the aquatic life, and poisoning the local communities’ waterways. Similar to other surface mining techniques, the open-pit technique also requires massive amounts of ground water and freshwater for its operations, further threatening the local communities’ access to water.
Mountaintop Removal

One of the most landscape-altering surface mining methods, mountaintop removal is a technique used to mine coal by blasting off the tops of mountains (which are filled with biodiverse forests), tapping directly into the resources they want to mine. Like the other surface mining methods discussed above, this method also has similar environmental impacts to the air, the water, and the area’s biodiversity. The waters are polluted with the toxins released from the mining process, killing off marine life, while entire forests are blasted out of existence. This method of mining is especially harmful for climate change because it permanently alters the topography of an area, releases tons of carbon emissions and other pollutants into the air, while destroying the many trees and plants that could have helped store some of the carbon emissions being released from these operations. This method also leads to soil erosion which can cause an increase in natural disasters such as flooding, forest fires, and landslides, and leave the land barren, making it difficult for local residents to grow crops on it.
These surface mining techniques are some of many methods that are used to extract minerals and valuable resources out of the earth. We discussed in detail the process of oil and natural gas extraction, using drilling and fracking techniques, and many of us are also familiar with the underground coal mines and tunnels that go on for miles beneath the surface. Those extraction methods come with their own risks and hazards to both the environment and its people. While we will not be covering those mining methods in this blog, we will be focusing more on the mining industry more generally, and its impact on human lives.
Human Rights Violations in the Mining Industry
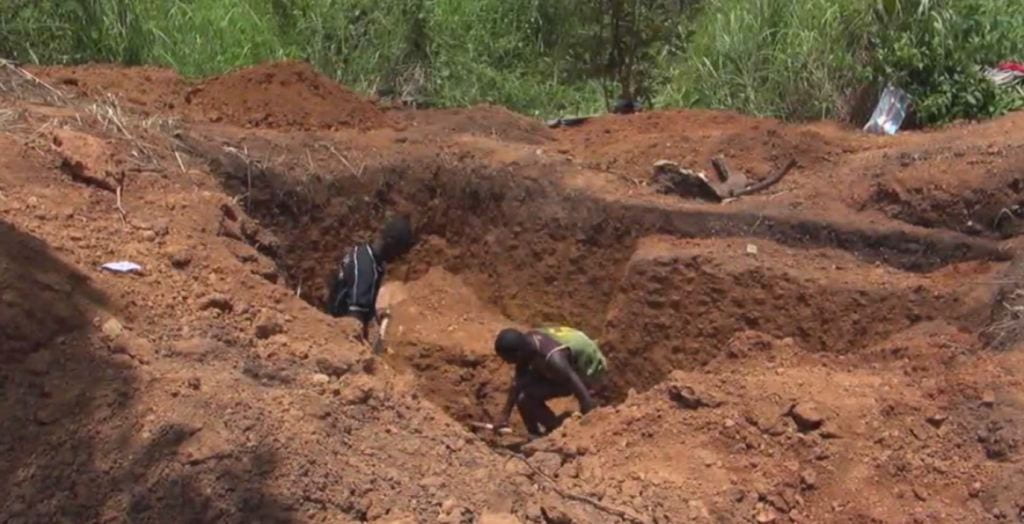

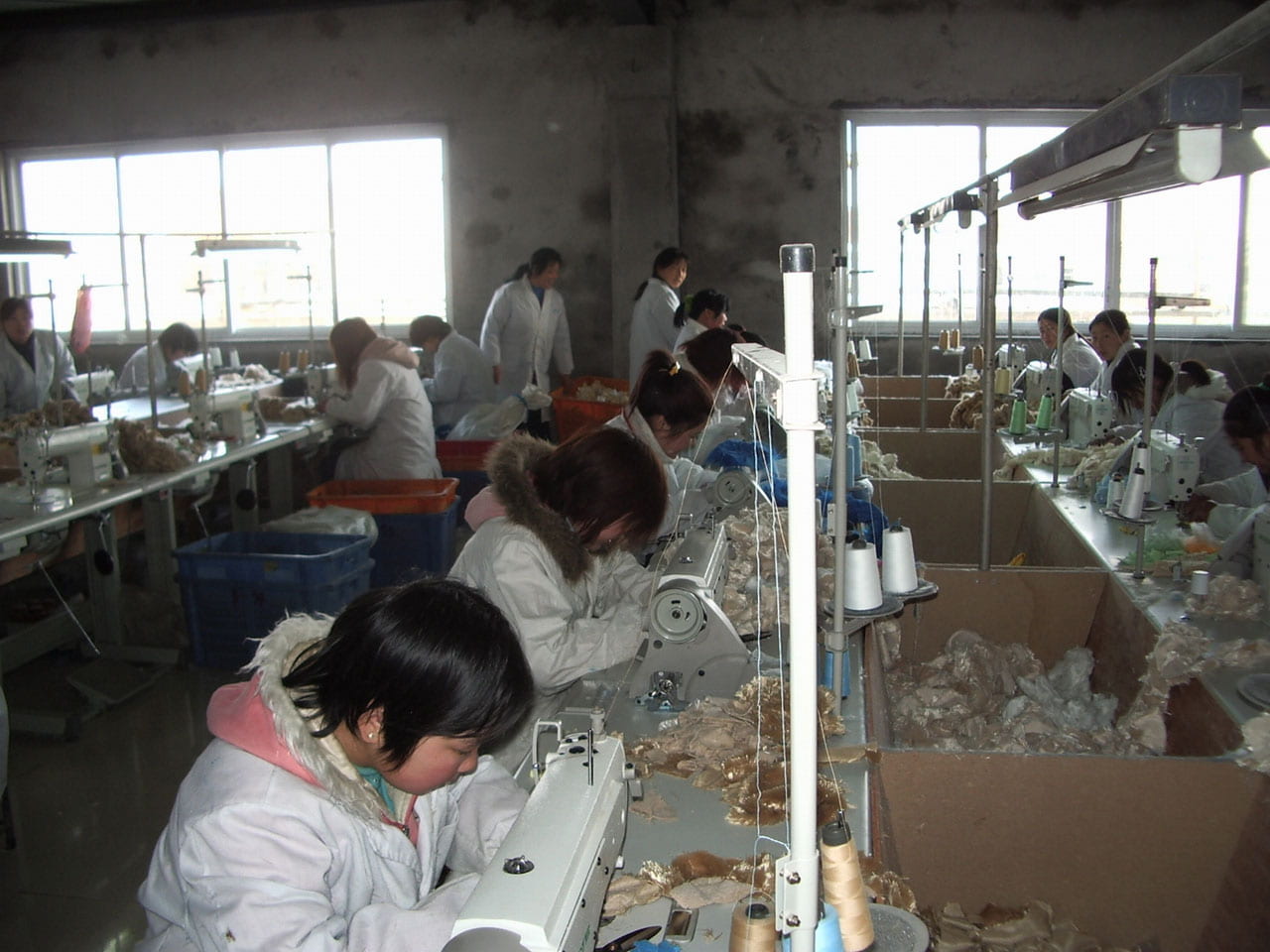
One of the most horrendous violations of human lives comes from the mining industry’s use of child labor in their mines, especially in poorer nations of the global south. While this certainly has to do with issues of environmental racism and avaricious profit motives, child labor has also become an increasingly preferred labor force used in multinational industries like fashion, oil, and mining, to name a few. The use of child labor in mining practices denies these children their entire childhood, and instead exposes them to dangerous working conditions that end up impacting their health for the rest of their lives. These children are exposed to toxic chemicals and micro metals and radioactivity released from the blasting process that they end up breathing in. These are especially harmful for developing children, whose growth can be stunted because of constant exposure to toxins like sulfur, mercury, and uranium. They are also required to work in contaminated waters, leading to skin infections and other issues that can impact their hormone levels and their overall growth. In addition to these dangers, children working at these mining sites are also in constant danger of physical harm from heavy machinery and the possibility of landslides due to weakened landscapes caused by the explosions and other disruptive practices.
Due to the profit-centered nature of these multinational industries, children and adults are exposed to some harrowing working conditions to meet the profit margins. These conditions have serious health implications, including lung disease, hearing issues, exposure to radioactive materials, mental health issues, and even back injuries. Respiratory illnesses and risks of developing chronic lung problems such as black lung disease, are very real consequences of breathing in the polluted air around these mining zones. Workers can develop issues with their hearing due to the loud and constant blasts from the mining operations, as well as the noisy machinery used in the mining areas. The blasts themselves, as discussed above, add metals into the air, and release radioactive gas into the surrounding air. Although some miners are given protective gear against these dangerous gases, miners are frequently required to breathe in this polluted air, which has large amounts of radon, a cancer-causing gas, while simply trying to just do their job. Due to the physically straining work that miners are expected to perform, mining can induce incredible amounts of stress. Miners also are required to work long hours, expend a lot of physical energy, and as a result, are more likely to injure themselves on the job. Although miners in the United States and other industrialized nations have workplace protections that shield the miners from obtaining injuries at the job site (or holding their employers accountable should such workplace injury occur), those working in areas without these regulations are more vulnerable to being injured and receiving little to no compensation or assistance through these injuries.

Why Should We Care and What Can Be Done About It?
Upon reflection, the mining industry seems to be damaging to the environment and, because of its harmful practices, a threat to the future of humanity. Even as we continue to extract more and more minerals from the earth, we are slowly running out of resources to mine. Some experts invested in the mining industry argue that the next step is to switch gears and expand our technological advancements to be able to mine asteroids and other elements in space. While this suggestion might address the issue of resource availability, it does not address the fact that these practices, (along with other industries), are adding to the climate crisis. Until anthropogenic actions are not regulated in industry, climate change is going to continue to be an existential threat to this Earth.
On an international level, therefore, regulations need to be passed on mining practices, and the working conditions of miners. Along with these regulations, multinational corporations that fund this industry should be stopped from exploiting vulnerable nations for their cheap labor and loose regulations. Just like with other natural resources, many of the economies of nations that are exploited for their resources and labor are heavily dependent on the sale of these resources. It is important, therefore, to ensure that they can shift their economies into stable ones that depend on renewable resources before abandoning these already vulnerable nations to deal with the consequences of the exploitation of the mining industry. On a more domestic level, the United States needs to transition into a greener, more sustainable economy so that there is no pressure for constant exploitation of these nonrenewable resources such as coal, oil and gas, and other such minerals. Stopping mining practices can allow the earth to heal and grow back some of the biodiversity that has been lost from centuries of exploitative mining practices. In addition to transitioning into a greener society, we should provide some sort of relief for communities that have been impacted by these careless practices and ensure that remediation attempts take place to restore the impacted lands to conditions that existed before the mining practices took place. On a more personal level, we as consumers have some power over the industries we incentivize. This is still true when it comes to stopping some forms of mining, (such as mining for gems), but largely out of our individual hands when it comes to stopping the use of certain resources that are a crucial part of our infrastructure, such as coal. Even with this in mind, one thing that each person can do is educate one another about the various impacts these mining practices have on the environment and on human lives as a whole. Bringing awareness to issues such as this can help alter the public opinions about using such resources, and in turn can lead to a much-needed paradigm shift in our approach to ending climate change.