On Tuesday April 6th, the Institute for Human Rights at UAB welcomed acclaimed author and activist Brittany Packnett Cunningham to speak. Brittany facilitated a conversation entitled “Pursuing Justice with Love and Power.” The discussion was moderated by IHR graduate assistant Jaylah Cosby and IHR intern Faiza Mawani.
Brittany began with discussing her inspiration for the phrase “love and power.” The phrase was actually borrowed from a lesser known piece of writing by Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. It can be utilized in word format or in a series of emojis: the heart emoji to represent love and the fist emoji to represent power. Love and power are conceived as two opposites. For example, love is perceived as soft whereas power is perceived as intense. However, Brittany emphasizes the importance of the two together. Our power can be informed with our love. This can be seen in a political landscape with loving policies that empower people where they are.
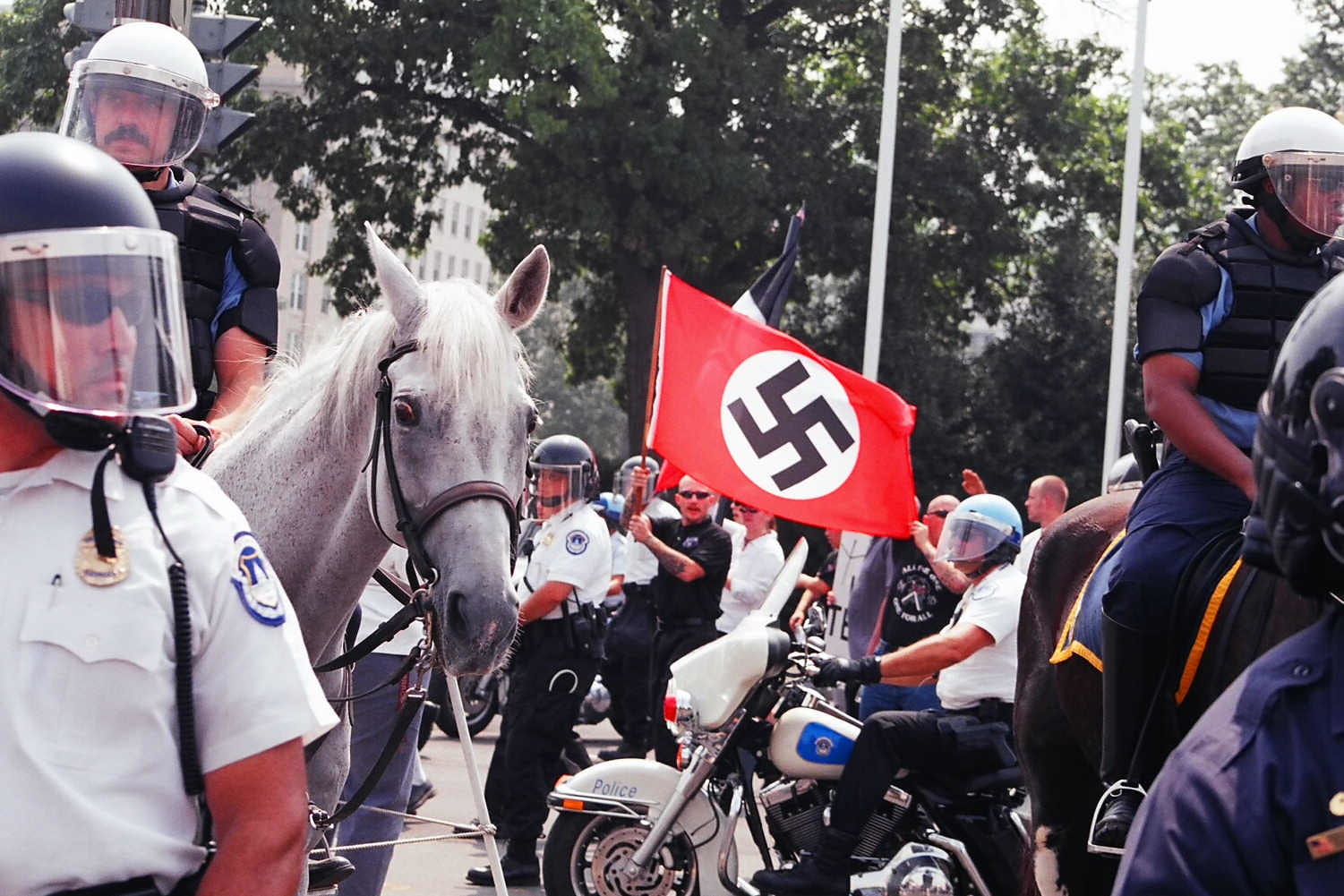
Brittany then pivots the conversation to discuss love and power in the context of community building. Community building begins first by being in and participating in the community. She describes 2014 as a pivotal turning point in American history and in her personal history. With 2014 came the protests in Ferguson where young people protected the American people’s right to protest. Communities showed their love for themselves and for others by standing up to the injustices in local, national, and international communities. Love is the root of protests. Brittany states, “We don’t need to know the people who have died by police violence to love them.” To actualize what love looks like, it is required to be in community with people.
When asked about whether the term “community” can mean an integrated community or a homogenous community, Brittany confirmed that both are necessary in making sense of our racial identity in the world. Affinity spaces allow for safety and comfort in what we know and understand. Finding community in those affinity spaces often provides the opportunity to find community in multicultural spaces. While working towards that multicultural community can be difficult and uncomfortable, that safe space from the homogenous group is still there at the end of the day. In answering this question, Brittany emphasizes the need to push for integrated spaces while also understanding the simultaneous need for affinity spaces.
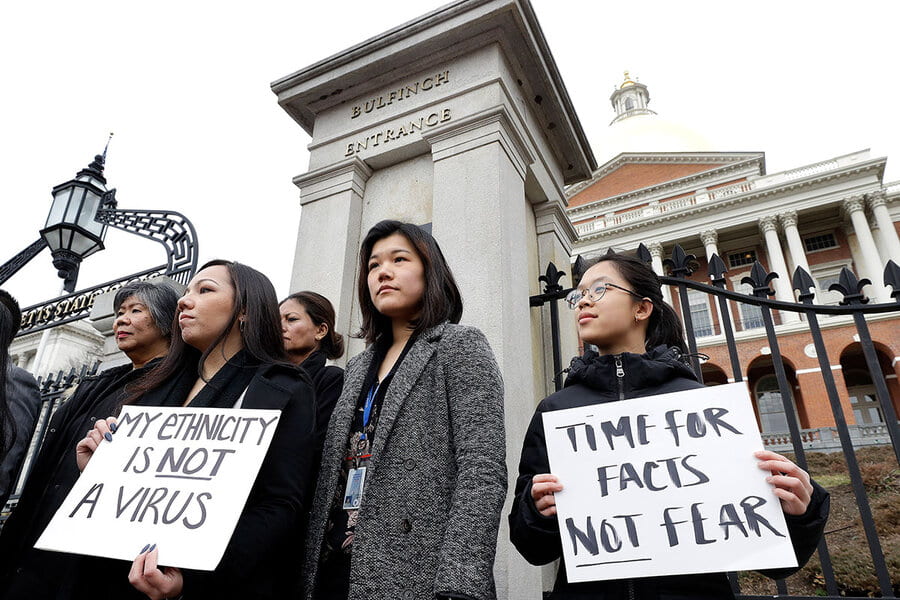
In the time of COVID-19, digitalization has become ever more present in all spaces an advocacy is no exception. Brittany acknowledges how digital spaces have somehow made it easier to work as an activist. She describes digitalization as another tool in the toolbox that works toward justice. It changes the way people can view work, life, and accessibility. However, the digitalization of life and work has also allowed misinformation to flourish. Brittany’s example of the dangers of misinformation is with voter suppression. The most effective form of voter suppression is to convince voters to stay home by encouraging them to believe that their vote doesn’t count. Similarly, Brittany warns against performative digital advocacy. If an Instagram post is being created with the sole purpose of gaining followers, this is an example of performative digital advocacy. Instead, advocacy posts should encourage action and therefore be productive. Most importantly, digital advocacy must amplify the folks most affected by the issue whenever possible.
A question from the audience inspired Brittany to discuss the intersection between religious faith and social justice. In response, Brittany stated, “I identify as political not in spite of my faith but because of it.” Brittany speaks from the perspective of a Christian and highlighted many of the issues modern Christianity has.
The conversation began to orient towards the Derek Chauvin case, which was ongoing at the time of the event, and policing in the United States. Brittany admitted to not watching the trial but looking at the coverage after the fact. Her primary reason for doing so is an understanding that nothing in the Derek Chauvin trial will bring back George Floyd. She highlights the important difference between justice and accountability in this section of the conversation. Justice would be an anonymous, alive, George Floyd sitting with his family and friends and living his life. That will never happen due to the actions of Derek Chauvin. However, Chauvin can be held accountable for his actions. When discussing the trial, Brittany states how she hopes that from the spectacle that is the trial, people are able to understand that police officers should never be expected or allowed to be the judge, jury, and executioner.
Brittany’s perspective on policing in the United States is that it needs to cease to exist how it is. She cites the “abolitionist tradition” of the United States. The people who fought against the abolition of slavery often argued the economics of slavery and the reliance the United States had on it, a similar argument we see occurring now when discussing police systems. Brittany asks the audience that if reimagining what public safety looks life scares you, to ask yourself where you would have stood on the abolition of slavery. “The safest communities,” Brittany states, “are not those with the most cops, both those with the most resources. Period.”
Brittany ended the conversation with advice on how to “get on the train” of activism. She says that the most important things to do are to listen, learn, and act but acknowledges that the temptation in activism is to default to whichever of those three is your are comfortable with, which is often “learn.” Brittany explains that it is easy to fall into the trap of sitting in the corner of your house, reading the literature and listening the people but never exiting to help build the communities and act. Learning is only half of the work. With such a digitalized world, there is an opportunity to learn and listen from the people we are the least like. Brittany advises to write down what gives you a privilege and an advantage in the world and follow the people who do not have your privileges. She also advises to act locally, highlighting the fact that you do not have to travel to another place to be an activist. “Link up with the organizations in your community,” Brittany advises, “and that is how we get to work.”