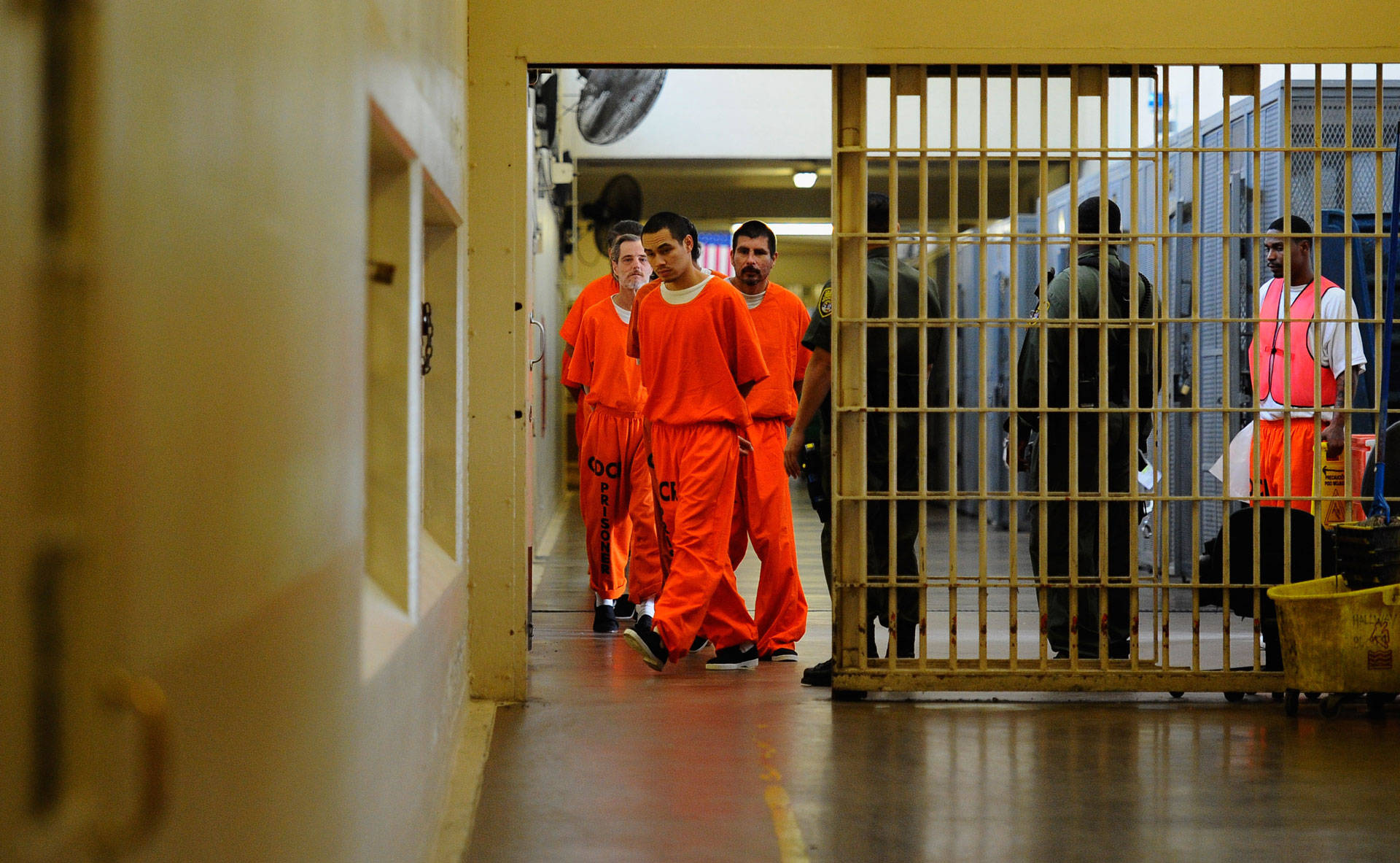
This is a continuation of the conversation about the Alabama Prison Crisis as exposed by Mary Scott Hodgin in her podcast, “Deliberate Indifference.” If you have not read the previous blog post on this topic, “The Ongoing Alabama Prison Crisis: A History”, it is recommended that you do so. Also, if you would like more information and details regarding this topic, please listen to the podcast, “Deliberate Indifference,” by Mary Scott Hodgin. Now, without further ado, let us jump right in from where we left off.
In the previous blog, we focused on the history of prison systems in America, and particularly, some of the legislations and ideologies that laid out the foundation for the correctional institutions we know today. We explored in detail the convict leasing system that helped rebuild the infrastructure of the Antebellum South following their defeat in the Civil War, and the racialized laws and legislations that disproportionately landed Black and Brown people in prison over their White counterparts. The War on Drugs era followed by the Tough on Crime era landed hundreds of nonviolent offenders in prison, serving longer and harsher sentences and life without parole. While our focus in the last blog was more nationwide, it was necessary context to set the stage to better understand the realities that face the Alabama prison systems focused on in this blog.
The objective now is to look deeper into the conditions of the penal system in Alabama, the lawsuits they faced in 2017, and the most recent one in 2020, how the pandemic exacerbated these conditions, the prison strikes that took place within these prisons, and some ways to move forward to bring about actual change – change in the mindset of our fellow Alabama voters, and a shift in the way the prison population is viewed and treated as a whole. We will look at some groups that are trying to do just that, from organizations like Alabama Appleseed and the Offender Alumni Association to religious groups and other educational groups that sponsor programs within the prison system to provide opportunities for higher education to the imprisoned population.
Prison Conditions

While exploring the most recent reports that resulted from the federal investigations of Alabama’s prisons, there were many similarities in the reports. While the problems of understaffing and overcrowding were expressed in detail, (which will be discussed below), there was also extensive observation of the living conditions inside the prisons. What the investigations revealed was shocking, and despite having been advised to address these issues even in the 1970s investigation of Alabama’s prisons, the conditions had not improved. Rather, it had deteriorated even more due to the consequences of staffing and crowding issues.
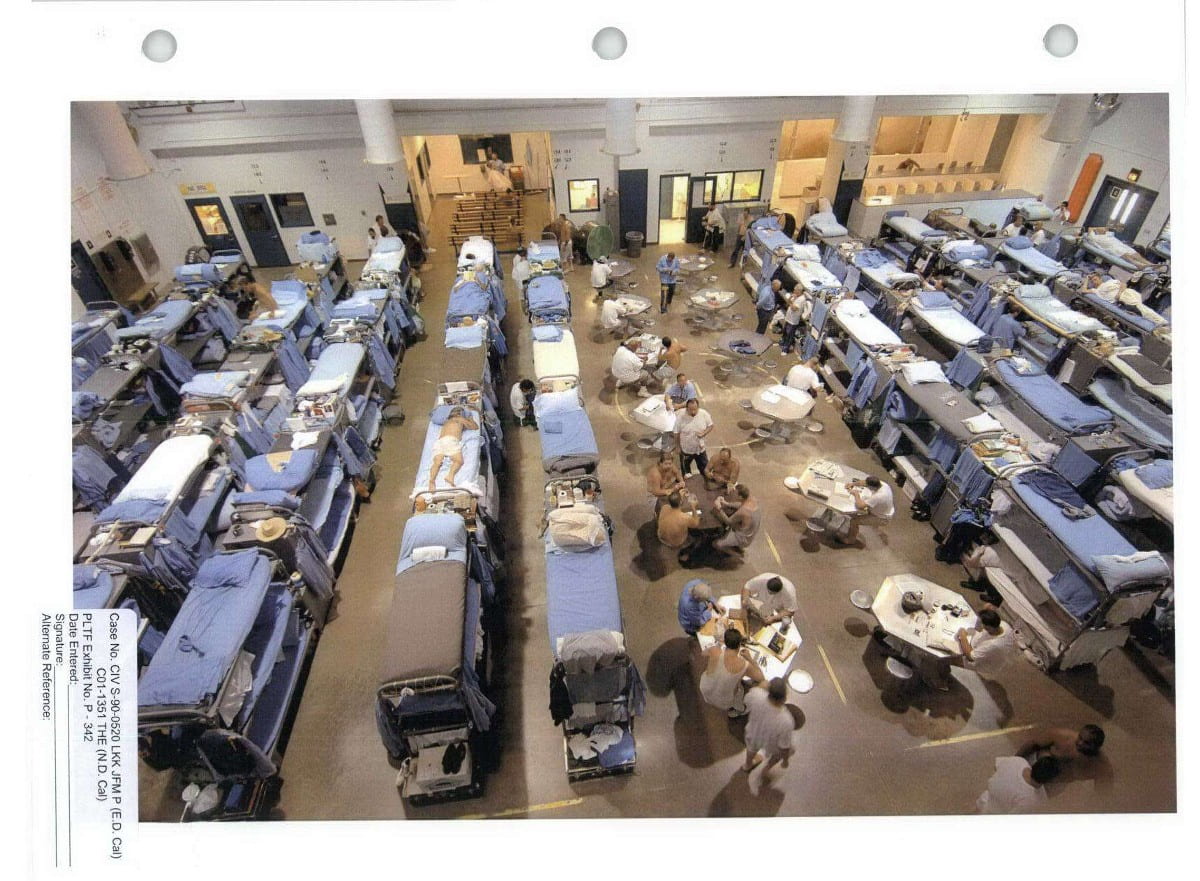
Both reports extensively provide detailed examples of violent outbreaks within the prisons, between prisoners, and even at the hands of prison staff targeting the prisoners. Many such incidents go unreported, and others have even ended in the death of the imprisoned person. One of the things that contribute to this violence is the structure of the prison itself. Many of Alabama’s prisons are fashioned in a dormitory-style of housing units instead of the individual cell units depicted in popular culture. These housing units are essentially enormous halls that are secured on the perimeters, with bunk beds piled into the room as close as they can fit. With little to no privacy, and jampacked in tight spaces, people can get easily agitated, and this can lead to violence. Due to the overcrowding issue, many people are even expected to sleep on the floors, which can be unsanitary and uncomfortable. Due to the continuous staffing issues these prisons face, these large units may go unguarded for long periods of time, sometimes even entire shifts.
This puts both the inmates within the units at risk for violence, and the prison staff who, to the incarcerated individuals, represent the authority from which these conditions are sanctioned. Even still, many officers, due to the understaffing issue, have overlooked contraband possession (such as drugs or cell phones), deciding to pick and choose their battles in an already tense environment. As a result of all these issues, corruption is rampant within the prison walls, and many prison staff, according to narratives from both reports, take advantage of this tense environment to assert dominance over prisoners with increased brutality. People who are incarcerated are not viewed by society as individuals with their own pasts and presents. They are only viewed as “criminals,” remain invisible to society and are dehumanized. Regardless of the crimes that a person commits, they are at the end of the day, still, people, who deserve dignity and basic human decency. As an institution of the state, prisons are legally responsible for providing a safe and secure environment for people who are incarcerated to serve out their sentences as punishment. The American Constitution does not support “cruel and unusual punishments”, and under the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), the rights of imprisoned individuals are fully supported.

2017 Federal Investigation
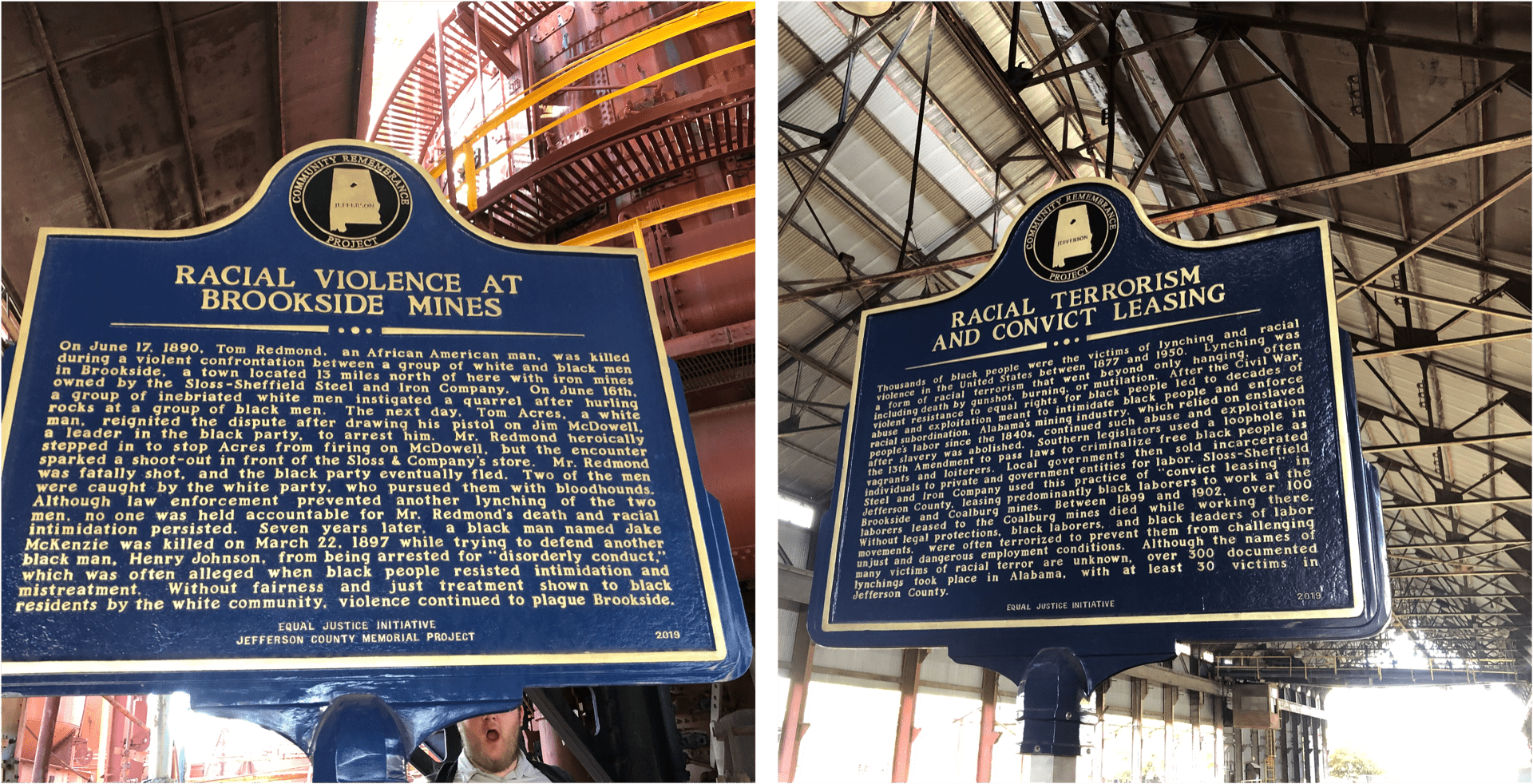
In the previous blog, we focused on how the prison system of Alabama has been under federal investigation nearly 50 years ago in the 1970s. Unfortunately, the conditions outlined in those reports were never fully addressed, and the issues that were highlighted have only been exacerbated over the years. In September 2017, the Department of Justice from the federal government toured one of Alabama’s prisons, Bibb County Correctional Facility, for their official investigation of prison conditions in the Alabama penal system. What they uncovered was outlined later in a report published in 2019, stating over 50 pages worth of evidence against Alabama, and the minimal expectations the federal government laid out for Alabama to achieve, both short-term and long-term.
The report is prefaced by the fact that these concerns were underlined within a week of their investigation. According to the report from the observations made in 2017, the Alabama correctional facilities faced a myriad of issues, including an overcrowded prison population, with dangerously low staffing, issues of contraband entering the prisons, and a host of observations pertaining to violence within the prisons, including physical, mental, and sexual violence. As discussed in the previous blog, these overcrowding issues come from the various legislations that were passed, increasing the lengths of sentences, criminalizing drug abuse and mental health issues (instead of treating them as medical issues requiring rehabilitation and treatment), and incorporating mandatory sentencing minimums and three-strikes laws. Along with identifying the concerns stated above, the report also deemed the penal system’s inadequate protection of its inmate population from harm, violence, and death, a failure. The report discussed at length how, along with unsanitary living conditions, there are dangerous weapons and drugs that are circulating within the prisons, making them unsafe for both the incarcerated people, as well as the officers who work there. This in turn is both caused by and exacerbated by the issues of overcrowding and understaffing within the prison walls. With fewer officers to supervise the dormitory-style prisons in Alabama, incarcerated people are packed together to fend for themselves.
While not all people locked up in prison are violent offenders, studies have shown that desperation, (which is rampant in these prisons), can lead to violence, distrust, and increased criminal behavior within the population. While the study referenced focused on populations outside of prisons, it is safe to assume that these results are only amplified within the prison system. The people within are both desperate and already undergoing punishment, which means that even the threat of punishment is not a deterrence from committing these violent acts. This also means that with fewer officers to supervise the dorms and halls of the prison, the overall violence within the prisons is increased, making it dangerous for the entire prison population.
As explained in both the report by the federal investigation, as well as the podcast by Mary Scott Hodgin, there were at least 11 men that died in 2019 alone due to the increase in violence within the Alabama prisons. To make matters worse, the federal investigation also found that the Alabama prison system’s record-keeping on these incidents and others was inaccurate, finding that there were many incidents that went unreported, and even many deaths misclassified as due to natural causes or medical reasons rather than due to the violence found within the prisons. If you count the total number of deaths within the inmate population in 2019 classified as natural causes or otherwise, the number is as high as 119 deaths.
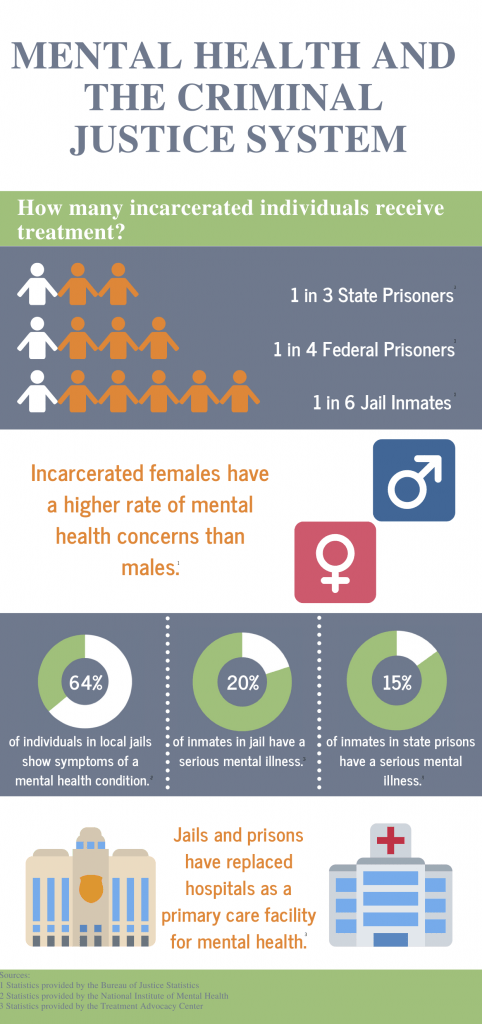
In addition to the misclassifications and incidents not being reported, Hodgin also details in her podcast the inadequate mental health care offered to incarcerated individuals within Alabama’s prisons. This can lead to an escalation of violence, and abuse of drugs, and place incarcerated individuals dealing with mental health issues in dangerous situations. Without the proper medical attention required to treat these individuals with mental health illnesses, prisons can become a charged environment that can exacerbate their conditions, making them more vulnerable to both becoming victims of violence, as well as the perpetrators of the violent acts. Unfortunately, because people with mental health issues are four times more likely to be imprisoned instead of receiving treatment and care, many individuals in prison already enter the system without knowing how to follow social norms. This can put them in danger of being abused by officers and other imprisoned individuals alike, and without proper care, their conditions can become worse, and at times, can end in death, either at their own hands or at the hands of another.
Another major topic of concern addressed in the report is that sexual abuse and sexual violence. Sexual violence is rampant in Alabama’s prisons, and this issue is exacerbated by the understaffing issue present within these facilities. With fewer officers staffed to care for increasing numbers of imprisoned people, there is less monitoring and supervision taking place, creating a breeding ground for violence, both sexual and physical. Much of the sexual abuse either go unnoticed, or unreported by staff members, and while the victims can report these incidents too, many choose not to for fear of retaliation or feelings of shame. Their fear is not unsubstantiated, as many accounts have been provided in which sexual assaults took place in retaliation to the victim’s reporting of a previous sexual assault. In addition to the low staffing numbers, many of the facilities in Alabama are constructed in a dormitory style, meaning that imprisoned individuals are grouped into a big hall rather than individual cells. This can be challenging for clear visibility of each individual inside the prison and their whereabouts. At times, only one or two officers may be in charge of the entire unit, and sometimes, the incarcerated people go unsupervised.
Many incidents of sexual assault occur as a result of “drug debt”, where an incarcerated person owes another incarcerated person money for drugs or other contraband and does not pay. There have even been incidents where family members of people who are incarcerated have been extorted for money, with the threat of sexual violence against their imprisoned family member. Many victims of sexual abuse within the prisons also alleged that these instances occurred after the victims themselves were drugged or held at knifepoint. While much of this goes unnoticed by the prison staff, some reports that do manage to document these incidents have even labeled sexual assault as “homosexual acts” rather than nonconsensual sexual abuse. People who are incarcerated that belong to the LGBTQI+ community are even more vulnerable to sexual violence simply for their identity. Unfortunately, many of the officers in charge of ensuring that the prisons comply with the Prison Rape Elimination Act (PREA), are not even aware of who among their incarcerated population belongs to the LGBTQI+ community. The PREA flags the LGBTQI+ population as being most at risk for sexual crimes, and the PREA managers in the Alabama Department of Corrections are not fully complying with the standards set by the legislation.
After identifying and explaining the various issues the Department of Justice found within Alabama’s prison system, the report argued that these conditions violate the constitutional rights of the incarcerated people, and as such, provided some bare-minimum measures that Alabama should take immediately to avoid a federal takeover of the prisons. These remedies included addressing the issues of overcrowding and understaffing, the rampant violence (both physical and sexual), the access to contraband, and the living conditions within the facilities. In addition to these short-term measures, the report also suggested some long-term measures to implement, including – among a list of other things – better incentives to improve staffing issues, improved systems to track, record, and address issues of violence, and more regulation over prison conditions and treatment of the imprisoned population. Alabama closed down one prison after this report (Draper Correctional Center) and closed a particularly harmful “behavioral modification unit” or “hot bays”, (where incarcerated individuals are held as punishment for violence and drugs within the prison) at Bibb Correctional facility. While these closures were a good place to start, they should be in no way, the only solutions to the long list of problems outlined by the report following the federal investigation. Unfortunately, Alabama, as expressed in the report itself, has been “deliberately indifferent” to these situations, and as a result, experienced yet another investigation in 2020.
2020 Federal Investigation

The 2020 report from the Department of Justice’s investigation into Alabama’s prisons found similar problems echoed in the 2017 investigation they conducted. As mentioned in the 2017 report, the 2020 report also addressed issues of overcrowding of prisoners, stating that all of Alabama’s 13 prisons held thousands of people over the capacity they were designed for, making Alabama’s prisons among the most overcrowded prisons in the nation. This report also referred to the dangers of not having adequate staff members to care for and run these overcrowded facilities, this time focusing on how these staffing and overcrowding issues have led to an increase in officers using excessive force against the incarcerated individuals, further aggravating the violence that exists within the prison walls. This issue of excessive force is further examined in the report, claiming it is a violation of the Eighth Amendment to the Constitution of the United States which outlaws cruel and unusual punishments against imprisoned people.
The 2020 report details the many reasons why officers use excessive force against people who are imprisoned. Unfortunately, many officers have been known to use violence and excessive force to “handle” a situation, even in times when there is no physical threat to the officer, and even when the incarcerated people are complying with the given orders. This has the tendency to escalate the situation, placing both the incarcerated individual and the officers in danger’s way. The report provides various examples of such incidents where the imprisoned people are reported to be complacent with the officers’ instructions, even handcuffed without ways to fight back, but have still been beaten, tortured, and abused inhumanely. These officers filed false incident reports claiming that they did not engage in such actions, and even after investigations of the incidents, the officers did not face any legal consequences or disciplinary actions for their behavior.
At times, excessive force is used by officers as a form of punishment or retribution for disrespecting the officers or reporting them. The 2020 report describes multiple incidents where excessive force was used against incarcerated people simply for not following the specific directions laid out by the officers. One incident includes an imprisoned person being physically abused and forced to eat all the leftover chicken for simply wanting some extra food. Other incidents outline the use of chemical sprays to punish incarcerated people or as a form of retribution for not following verbal orders. Chemicals sprays are used even in times when the imprisoned people do not pose any physical threats to the officers. Finally, many officers also use force to simply assert dominance and inflict pain on their charges, something that not only endangers the people involved (both officer and incarcerated individuals) but also causes the incarcerated individuals to distrust the officers in charge, escalating the tensions between the two groups.
All these incidents are violations of the eighth amendment, and while many of the investigations that these incidents resulted in agreed that there was no justification for the use of excessive force in any of these outlined incidents, the officers faced little to no disciplinary actions for their conduct. The Department of Justice also included this issue in their report, arguing that unsurprisingly, officers either fail to report or inaccurately report incidents where excessive force is used. Many times, excessive use of force is investigated internally and recommended for an I & I investigation (Investigations and Intelligence unit of the Alabama Department of Corrections in charge of investigating misconduct by prison staff). Unfortunately, the report declares that of all the incidents recommended to the I&I unit, only 40% of them are actually reviewed. To make matters worse, many of the cases that are investigated by the I&I unit, where excessive force has been confirmed, are seldom referred to be criminally prosecuted. This means that many of the officers abusing their authority and misbehaving with incarcerated individuals go unpunished for their conduct. Many more of the incidents where excessive force is used go unreported, with only the victim’s bruises to bear witness to the incident. For fear of retaliation, many imprisoned persons go without reporting the abuse they face at the hands of officers. If the victim does not cooperate in the investigation, the incident is deemed “unsubstantiated”, and the investigation is closed.
Following their investigation, the federal government proposed a list of measures that Alabama’s Department of Corrections needs to take in order to fully comply with federal regulations for correctional institutions. These immediate measures included the need for more I&I investigators, a better system for victims of abuse from officers using excessive force to report their incidents anonymously and independent of the prison’s authorities, clear procedures for accountability for officers, and better documentation and investigations of incidents where excessive force is used.
COVID-19 and Its Impact on the Prison Population

In addition to these inhumane conditions the imprisoned population experience that violate the basic human rights of incarcerated people, the outbreak of Covid-19 greatly amplified this issue, and soon, the prisons became a contagious and deadly environment for both the prison staff and their charges. With little to no access to adequate healthcare and deteriorating mental health caused by the conditions of their environment, people who are incarcerated are especially vulnerable to disease outbreaks. On the national level, according to a study conducted in 2020 by the American Medical Association, people incarcerated were five times more likely than people living outside the prison system to be infected by the virus, and the death rates among prison populations were higher than the national average at the time. Making matters worse, due to conditions of overcrowding inside the prisons, the outbreak was especially dangerous, as incarcerated people were unable to adequately quarantine and unable to maintain safe social distance between each other. There was also the probability of prison staff bringing the virus into the prisons from the outside world, and also recirculating the contagion within the prisons back into the larger society. A UAB publication by the School of Public Health declared the prisons a “petri dish for COVID-19”.
To add to this problem, the prisons were notoriously unsanitary, meaning that preventative measures such as maintaining clean spaces and washing hands with anti-bacterial soaps, were impossible to maintain. Furthermore, understaffing issues complicated this situation, as those who were infected were either neglected until conditions were too bad to ignore, or they were provided with inadequate healthcare measures. In Alabama, a unique situation further complicated the negative consequences of the pandemic. A large portion of Alabama’s prison population belongs to the older age groups due to the strict and long sentencing laws of the state, and the fact that the pandemic was considered to be even more dangerous for elderly people further put people incarcerated within Alabama’s prisons in jeopardy. Access to healthcare within the prison system makes this issue life-threatening, and despite the urgency from the American Medical Association to include the prison population in the vulnerable communities list for vaccinations, the Equal Justice Initiative reported that Alabama’s prisons denied its incarcerated people vaccinations. While some prison staff received vaccines, they were not required by the state to be vaccinated to work in the prisons, continuing to place the lives of incarcerated individuals in peril. As a result of inadequate protective gear (such as masks), and negligent behavior on part of the state and the prison staff, the prisons in Alabama encountered a large number of Covid-19 deaths.
Alabama Prison Strikes

After living through the grave conditions of the pandemic, and witnessing the unchanging environment within the prisons, the incarcerated individuals decided it was time to take matters into their own hands. In September of 2022, incarcerated people from all of the 13 prisons in Alabama began striking against the prison conditions they endured. They argued that the prison system was violating their basic human rights, provided inadequate healthcare, and did not in any way prove to be a place of rehabilitation for the imprisoned population. Instead, they initiated a strike, refusing to work their prison jobs (such as in the laundry department and the maintenance department) that they did not receive compensation for, called for improvements in prison conditions, and demanded reforms to the harsh sentencing laws currently in effect in the state of Alabama.
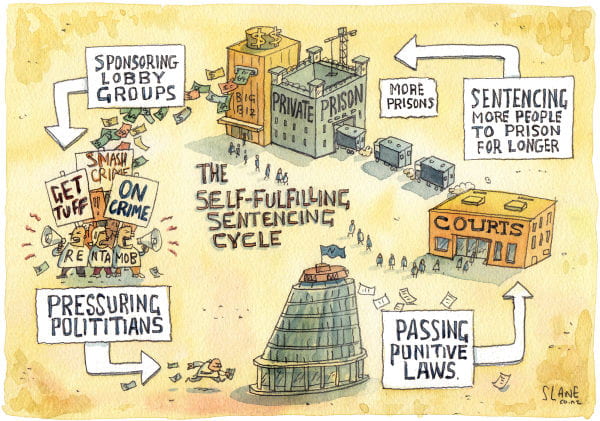
While imprisoned persons are demanding to be treated fairly in prison, the governor of Alabama, Kay Ivey, insisted that the demands of the prison population were “just unreasonable,” maintaining that the new construction of the two mega prisons in Alabama would solve all these issues of understaffing and overcrowding. These mega prisons, built with the use of funds designated to the state for pandemic relief, (causing public debate on this controversial subject), are supposed to provide more space for the overcrowded prisons in Alabama, and reports have surfaced about the possibility of hiring more officers for the newer mega prisons. This project will receive a total of over $1.2 billion in funding, of which $400 million comes from the pandemic relief funds.
What is vital to include here is that while these two new prisons will provide more space to house incarcerated individuals, (up to 4,000 in each), these prisons are replacing existing prisons with newer technologies and facilities. While this may seem like an improvement in some prison conditions, (such as more security and cleaner, sanitary units), it does not solve issues of overcrowding or staffing issues. The massive budget awarded to this project, instead of going toward building two mega prisons, could have been used more wisely to address the core issues of society that increase crime and criminality within its community. In addition, certain legislation and reforms could have been passed to overturn the harsh sentencing laws that exist in Alabama today. This would have solved both the issues of overcrowding and understaffing, as with fewer people being incarcerated and more people qualifying for parole, the total amount of people within the system would decrease, which would also lead to a decrease in the number of incarcerated people the prison staff is responsible for. A decrease in the prison population would also lead to a decrease in violence and more space for each individual within the prison walls.
Existing Resources
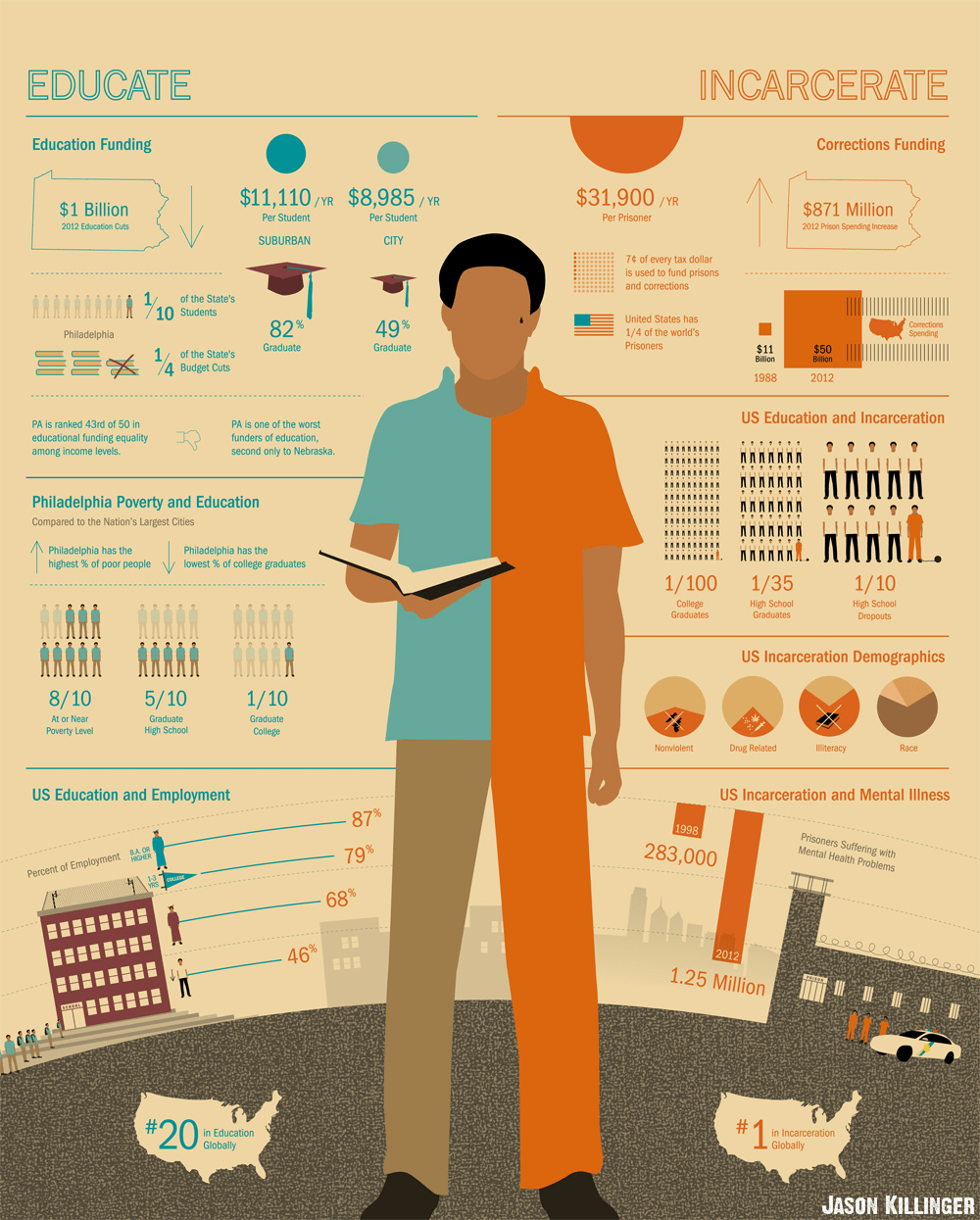
There are many organizations that have attempted to address both the various issues that incarcerated people face within the prison system and those face as they re-enter society after completing their sentences. These organizations include Alabama Appleseed, Offender Alumni Association, Shepherds Fold, One Roof, and Aid to Inmate Mothers. Alabama Appleseed, which belongs to the national Appleseed Network, is a Center for Law and Justice that focuses on equity and justice, and research around prison reforms in Alabama’s penal system. The Offender Alumni Association, recognizing the importance of human connection, focuses on providing support and engagement within the prison walls, and community and stronger familial relationships outside, all while aiming to end the stigma around imprisonment. This organization is a support system for incarcerated people run by people who have been formerly incarcerated and engage in community efforts such as their Heroes in the Hood program to help inspire meaningful goals within the younger generations of high-risk communities to channel their energy toward community restoration. Shepherds Fold, as a transition home, provides similar services from a faith-based approach, instilling Christian values within their participating members. One Roof, an organization whose mission is to end homelessness in Alabama, is yet another resource for people re-entering society after being incarcerated. Through their practice of Coordinated Entry, or an in-depth needs assessment, One Roof is able to secure housing for those in need and point them to additional resources they may require based on their assessment. This can be very helpful for many, especially those who have been incarcerated for decades long, and who may not be aware of what resources exist in the community, or how to go about securing them. Finally, Aid to Inmate Mothers (AIM) is an organization that provides assistance to mothers who are incarcerated, both during their incarceration, as well as their transition period into society after their sentences have been served. AIM provides transportation to children for visitations with their mothers in prison and provides incarcerated mothers opportunities to record bedtime stories for their children. Their reentry programs aim to reconnect mothers with their children, provide a few essentials for those leaving prison, provide classes on life skills, job preparedness, parenting, and other topics for those who are interested, and even provide transition housing for a year, though it comes with a few eligibility requirements, including rental fees charged weekly.
There are also educational opportunities that are provided for incarcerated people in Alabama’s prisons. The Alabama Prison Arts and Education Project led by Auburn University, and the Donaldson Lecture Series led by the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) are only two such programs. The Alabama Prison Arts and Education Project provides incarcerated individuals a chance to earn college credits while serving time. These courses are offered in the field of arts and sciences, and for those who can keep up with the standards of Auburn’s academic programs, this is a great opportunity for incarcerated individuals to pursue higher education, and as a result, be better equipped to handle the professional world upon their release. Similarly, UAB also offers lecture series at Donaldson Prison. While not as extensive or academically progressive as Auburn’s program, the Donaldson Lecture Series focuses on educational talks given to incarcerated individuals within the prison every other Tuesday for academic enrichment purposes.
Shifting the Mindset Around Crime and Punishment

These resources are well-intentioned and have helped save so many lives to date. Yet, this is not enough; there is a much-needed shift in the societal mindset around crime and punishment. The issue of the prison system is rooted in the racist founding of this nation, and as such, has systemic implications on various areas of a person’s life. Reforms can only go so far, as they are still pieces of legislation that try to make changes to the existing laws, but they still operate under those same laws. There needs to be a shift in the way incarcerated people are viewed within the larger society, and there needs to be a reexamination of the laws on the books since most of the institutions in America are rooted in beliefs of supremacy. Some things that can help us rethink the way we approach topics that involve imprisoned people are suggested below.
As explained earlier, changing the language around how people in prison are talked about can humanize the population and foster compassion towards the group. Refer to them as imprisoned persons or people in prison rather than branding them the title of “prisoner” or “inmate”. This helps shift the narrative. “Prisoner” or “Inmate” seems to imply that these individuals are criminals at the core, and brands them as “others” in the eyes of society. Instead, referring to them as “imprisoned people” implies they are human, with natural rights, and only living in a condition of imprisonment rather than being defined by their conditions.
Finally, I leave you with a challenge: rethink how crime and punishment are framed in our society. Who is held accountable? Who isn’t? What acts are considered criminal and what aren’t? Who decides which acts to define as criminal and which ones do not? Who benefits from the current criminal “justice” system? Does committing a crime make you a bad person, a “criminal” for the rest of your life, or should you be given another chance to reform? Should people be branded innately “criminal” or are their actions influenced by the conditions of the society they live in and dependent on the context and motivations behind the crime committed? Is it fair to punish someone based on actions (mistakes yes, but still actions) committed as young people for the rest of their lives? Why is it that our society places the label “criminals” on people who commit crimes, but refuses to see them as anything else? People can be “criminals” and still be artists, musicians, poets, writers, activists, metal workers, etc. Why does our society insist on placing a singular label on this population? Could it be to easily forget their existence, to remove humanity from their essence? All these are necessary questions to ask ourselves to understand our own biases towards imprisoned people and began to rethink our own actions that can have long-lasting consequences on the lives of so many. After all, this prison crisis is happening in our own backyard, and if we do not speak out against these atrocities, we are just as guilty as those committing them.