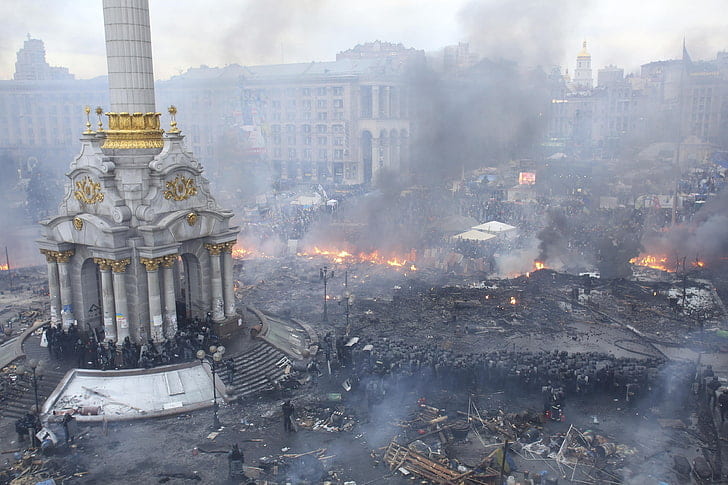
These past few decades have been filled with destruction and devastation, and the increasing severity of the climate crisis signals that what we are experiencing is just the beginning. The climate crisis will transform the way we live, whether we adopt to it or not, and it is crucial now more than ever to take all the necessary actions to slow down, and maybe even stop this growing existential threat to humanity. With that being said, there have been some attempts around the world at doing just this. In the midst of all this chaos, it is important to cherish and acknowledge some of the more innovative responses to alleviating the climate crisis. These are some of the sustainable ways other nations are attempting to address climate change, and the United States would do good to implement some of these ideas into its own society.
Planting Trees to Save the World
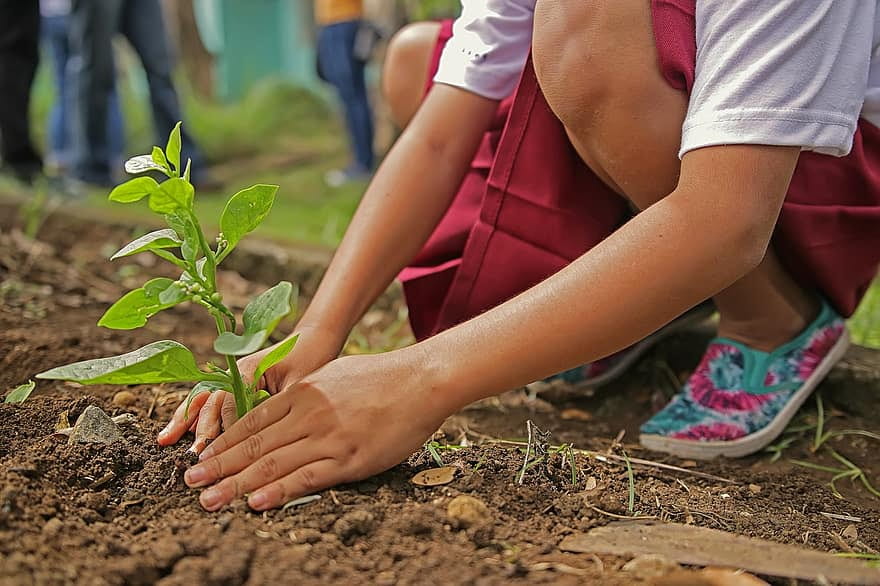

Countries all over the world are taking a simple approach to the climate crisis; they’re planting trees! Nations like India, China, Ethiopia, Pakistan, and the Philippines have planted hundreds of trees as part of their promise to the Paris Agreement. In July 2019, India planted over 220 million trees in a single day, while Ethiopia planted over 350,000 trees in one day! Students in the Philippines are expected to plant ten trees each before they are allowed to graduate, and in this way, a guaranteed number of trees are planted annually. All these nations are taking unique efforts to do their part in combating climate change. While planting trees alone won’t address some of the more serious environmental issues we face today, it does make a huge difference. For one, planting trees can help remove some of the carbon emissions and other greenhouse gasses from the atmosphere and release more oxygen into the air. This provides cleaner air for all living forms in the area. Planting trees can also encourage biodiversity, and depending on what type of trees are planted, can provide food sources that nourish the region’s species. In this way, biodiversity provides natural services, which are services built into nature that nourish and sustain the ecosystem for all life forms on Earth. These services include the food produced by the trees, the roots that guard the soil from erosion and flooding, and it even includes a natural filtration system that purifies water. In addition to this, biodiversity, (and the calculated, methodical planting of trees) can moderate temperatures, enrich the soil, and stabilize an ecosystem. As such, biodiversity is just as necessary for the continued existence of humans as it is for other forms of life. Of course, without stopping the use of nonrenewable resources and exploiting forest lands, any number of trees planted can only neutralize the carbon emissions. In order to fully benefit from the trees being planted, we have to shift to using renewable, sustainable forms of energy to rebuild our infrastructures and power our homes. The actions these countries have taken to combat climate change is one that ensures sustainability and inspires change, and it is with this mindset of sustainability that we, as a world, should proceed.
Europe’s Pollinator Highway
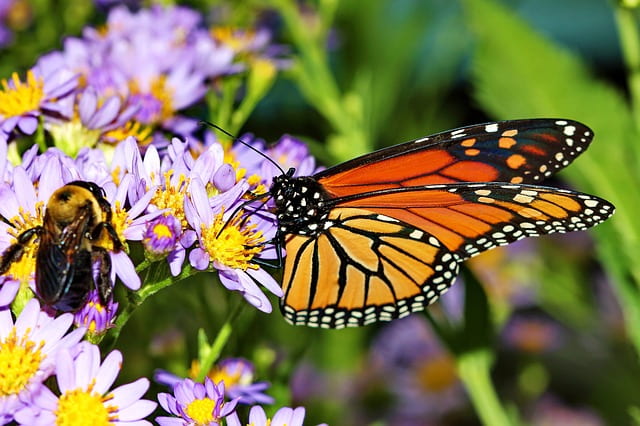

Along this framework of sustainability, Europe seems to have taken a different approach in addressing some of the environmental issues we are facing today. One such environmental issue they have attempted to address is the decreasing number of pollinators in the world. Pollinators are insects, like bees, wasps, and butterflies, who play a vital function in our existence, by transferring pollen from the female part of a plant to the male part of the plant to being its reproductive process that later blooms into fruits, seeds, and flowers. Without the crucial role that pollinators play, there would be no nourishment for millions of species worldwide, including humans. These pollinators play a key role in the survival of any ecosystem, and without their services, the world would be plunged into a food famine. To address this issue, the city of Tallinn, the capital of Estonia, has constructed an eight-mile walkway that connects six districts of the urban area. This was an attempt to encourage an increase in insect pollination, as well as provide city dwellers clean, green spaces to enjoy. Known as the Pollinator Highway, it is one example of how nature can co-exist in urban centers alongside humans. While the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has attempted to address the pollination issue, the use of pesticides and herbicides, which the United States continues to allow, leaves pollinators exposed to these harsh chemicals, resulting in their deaths. There has been more awareness about this issue, however, and many scientists have even suggested drones and robotics to mimic pollinator behaviors and artificially pollinate plants. These advanced technologies, however, can be very costly to produce and maintain, and their creation and upkeep only adds to the issues of depleting raw materials. As a result, it would be cheaper and more sustainable to protect our natural pollinators and appreciate their natural, free services, by promoting a safe environment for the pollinators to flourish.
Studies have also shown that greenery and time spent in nature can have positive impacts on an individual’s mental health, so Tallin’s Pollinator Highway would be mutually beneficial for both humans and pollinators alike. This walkway they created not only ensures the safety of bees, but also, through incentivizing citizens to walk and bike, has led to a decrease in emissions released by cars and other motor vehicles. This is also partly due to Tallin’s legislation which has made public transportation free since 2015, incentivizing citizens to switch from personal vehicles to public transport systems and making room in the urban center for cyclists and walkers to enjoy a breath of fresh air. The free public transportation system runs all day long, every day of the week, and Estonia was the first nation in the European Union to implement this system. Many European nations have included similar features since then, but the United States continues to fall behind its European counterparts. As one of the richest nations in the world, the United States has the ability to build more sustainable infrastructure and transform public transportation to better connect all parts of the nation. Then, American citizens too could incentivize the public to use free transportation provided by the state. Having a free public transportation system that runs 24/7 would also increase accessibility for many Americans living in rural areas and on the outskirts of urban centers. These are just some of the ways in which elements of climate change can be addressed.
Virtual/Hybrid Conferences and Climate Change

Along the same lines of promoting a safe and more sustainable environment, another interesting way to combat climate change is by simply continuing to use virtual spaces for conferences, meetings, and other such events. The pandemic has drastically forced people around the world to adapt to its contagious spread, and as a result, the entire world had to find new ways to keep functioning without meeting face to face. This is really when zoom became one of the most important tools for students, teachers, professionals, and artists alike. In the midst of all this trauma and loss, it is good to know that we accidentally discovered that hybrid and virtual conferences can actually help combat climate change in a significant way. The greenhouse emissions released so far from the conference industry worldwide are equivalent to the amounts released by the entire US; this is a significant amount of emissions, as the United States, in 2020 alone, released 13.5% of the global emissions. Virtual or hybrid conferences can help decrease those amounts significantly, and we can do this from the comforts of home. While people still use energy and electricity at home to attend these events virtually, it is nowhere near the amount used during in-person conferences. Additionally, this is a profitable development for businesses because it costs them less to host virtual conferences than in-person conferences where they have to pay for the attendees’ transportation, their housing, and for the actual conference hall where the event would be held. Also, virtual conferences increase the accessibility of the events to those who may not be able to travel the long distances due to other obligations in their lives. Virtual and hybrid conferences and meetings can also be timesaving for all those involved, from the attendees to the hosts themselves. Virtual and hybrid meetings should in no way replace face-to-face meetings because in-person meetings are more personable, and generally fosters more community among like-minded people. With that being said, this accidental victory we seem to have stumbled upon should not be dismissed or ignored. Rather, we should explore ways in which this newfound knowledge can benefit us as we begin to reshape our future.
Nature’s Right to Exist

Another innovative approach to reshaping our future might include the securing of rights to the environment itself. This is exactly what Panama, in league with other nations like Italy and Mexico, has decided to do. Panama has passed a new legislation that declares nature’s right to exist. This law forces Panama’s legislations to consider its impacts on the natural world, and whether the existing laws on the books violate nature’s right to exist. This applies to its national policies, but also extends to its foreign policies as well, meaning that Panama cannot take any foreign policy actions that might endanger the environment’s right to survive. Some of the other nations which have passed similar legislations aim to protect the entire environment, while others have given specific protections to rivers, enabling human representatives to sue on the behalf of rivers that have been harmed or polluted. This is an important piece of legislation for environmental justice, as grievances against the environment can be heard in a court of law, and violations against the environment can be addressed and held accountable. This would be especially significant in the US, because corporations already have a voice through the Citizens United ruling, which equated money with speech, allowing corporations to exercise their “freedom of speech” through campaign contributions to potential and elected officials. Passing such a law that protects the environment’s right to exist in the US would provide a voice for the environment, to fight against some of the harmful injustices caused by environmental racism and exploitative behavior from corporations, and would serve as a check on the power and influence of multinational corporations on US policy, both in domestic and international affairs. If the United States were to do what Panama did, issues such as the Flint water crisis, or the countless instances of exploitation of indigenous lands by big industries, could be stopped, and the perpetrators of such damages caused to the environment can be legally held accountable. Nature, with its many ecosystem services, and resources it provides to all life forms on Earth, deserves to be protected, and using such a rights-based language to call for environmental justice is another way to reduce our dependency on non-renewables. Ensuring the smooth functionality of these ecosystem services (which are free to everyone), is an essential aspect of fighting the climate crisis and without protection, these services would otherwise be jeopardized, costing us money, time, and lives as we try to mimic these services to simply survive.
The Fight for Humanity’s Future

So, what more can be done? For one, we should continue to support green initiatives and pressure our representatives to propose legislations such as the Green New Deal, or pass our own version of Panama’s “Nature’s Right to Exist” legislation. When proposing policies, we should consider the many ways in which climate change impacts different communities, and craft our policies through a rights-based approach. While ethical consumption under a capitalistic world can be challenging, we as consumers should be more aware of the brands we consume and the products we consume, to incentivize businesses to be more aware of their impact on climate change and actively try to address it through their operations. We also should start publicly questioning some of the corporations that exploit the nature and its resources, and hold them accountable for their actions. This tactic is known as “naming and shaming”, where we publicly challenge some of the exploitative practices these companies may use, and as a result, enforcing them to be more conscious of their operations. We also need to educate others about the reality in which we live in, and how each individual can make an impact on the climate crisis through changes in habits and lifestyles. We need to bring attention to the growing climate crisis through healthy civil agitation and educate others on their carbon footprint. Ask friends and family members to be mindful of their purchases, and boycott businesses that exploit the Earth and its vulnerable populations. This is exactly what the Fridays for Future movement is attempting to do. Created by a young generation of climate activists, this global phenomenon centers around awareness and action against the climate crisis. Students sacrifice their Fridays to fight for the protection of the Earth and their own future existence. We too, as students passionate about environmental justice, can support their initiative by hosting our own climate protests here on campus, or by simply boosting the movement in our own communities. Or, as India, Ethiopia, and many other nations around the world has proven, we can simply plant more trees. Whatever it is we do, the environment depends on the actions of everyone, and how we respond to this crisis will determine whether the human species, (and many other organisms with it), will be able to exist in the future.