Imagine a secret company tapping every word you say and email you read, all because someone decided you are a threat. It may seem draconian and futuristic, but this is the reality of human rights activists around the world under a mysterious spyware called Pegasus. Reminiscent of George Orwell’s novel 1984, Pegasus is an international symbol of decreasing privacy, invasion of privacy restrictions, and increasing digital surveillance of citizens by their governments.
Pegasus, named after the Trojan horse, is a malware created by an Israeli cybersecurity company known as the NSO group. The spyware was initially intended as a global weapon against terrorism and crime. Normally, most malware infects a device through an email or link containing the software, but Pegasus requires no action on the receiver’s device to become embedded in the device’s systems. Through the “iMessage zero click” exploit, Pegasus is automatically downloaded onto the target’s iPhone. Only a digital security lab has the resources to detect Pegasus on a device, because the program itself does not cause any disruptions to a device’s function.
Pegasus spyware can access GPS location, calls, texts, contacts, emails, and more dangerously, encrypted and private data such as passwords. Attackers can gain access to a device’s microphone and camera, as well, which opens the door to unauthorized agencies recording audio or video without the owner’s knowledge. The first use of Pegasus was traced to 2013 and has since impacted over 45 countries, but international investigations only began a few years ago. Earlier in 2021, an international collaboration of news media including Forbidden Stories and Amnesty International launched The Pegasus Project to investigate, country by country, the impact of Pegasus use. Evidence has shown that governments use Pegasus to target activists, journalists, and public officials although every country accused has denied the allegation or insisted that it was necessary.

India
In July 2021, the Pegasus Project found over 300 Indian phone numbers including those of activists, politicians, journalists, and lawyers being tracked by the surveillance software. Four years earlier, the Indian Supreme Court ruled that the right to privacy is protected under the Constitution. Despite the legal provision, the Indian government has used excuses of national security and protection when confronted with allegation of using the notorious spyware. This year, the Supreme Court appointed a committee to investigate the data produced by the Pegasus Project and determine whether the government did use Pegasus to spy on citizens and thus, violated the law.
The Indian government has expanded the umbrella of legal surveillance since the passing of the 1885 Telegraph Act and 2000 Information Technology Act, rendering any word of restricting unauthorized surveillance from them laughable. The country’s ruling party, the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), is responsible for enforcing the 2021 Information Technology Rules, but the legislation has increased the hunt for human rights activists and news outlets that criticize the government’s actions. Initially passed to prevent social media misuse, the rules act as an access card to control streaming sites, social media services, and online news sources that are crucial for citizens to become aware of accurate, although incriminating, investigative reports.

Middle East
Middle Eastern countries such as Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates (UAE), Bahrain, Qatar, and Turkey show similar patterns of digital repression over the last couple of decades. The UAE is already known for having the most surveillance over its people in the world. By claiming the invasive surveillance efforts for national security, the Emirati government tracked conversations of its residents, Qatari officials, members of the Saudi Royal Family, and other opponents. In 2016, a human rights activist from the UAE, Ahmed Mansoor, was targeted with Pegasus in 2016 before his arrest in 2017 and subsequent 10-year jail sentence. Fellow activists and scholars have sufficient evidence to suggest that governmental surveillance caused his illegal arrest.
In 2018, Jamal Khashoggi, a progressive journalist from Saudi Arabia, was murdered at the Saudi Consulate in Istanbul, Turkey by a team affiliated with the Saudi Arabian government. He was the editor-in-chief of the Al-Arab News Channel and went into hiding in 2017 after the government threatened him. From Turkey, he wrote articles chastising his home government. After his death, Pegasus was allegedly used to keep tabs on his son, fiancé, and other affiliations without their consent.
Palestine
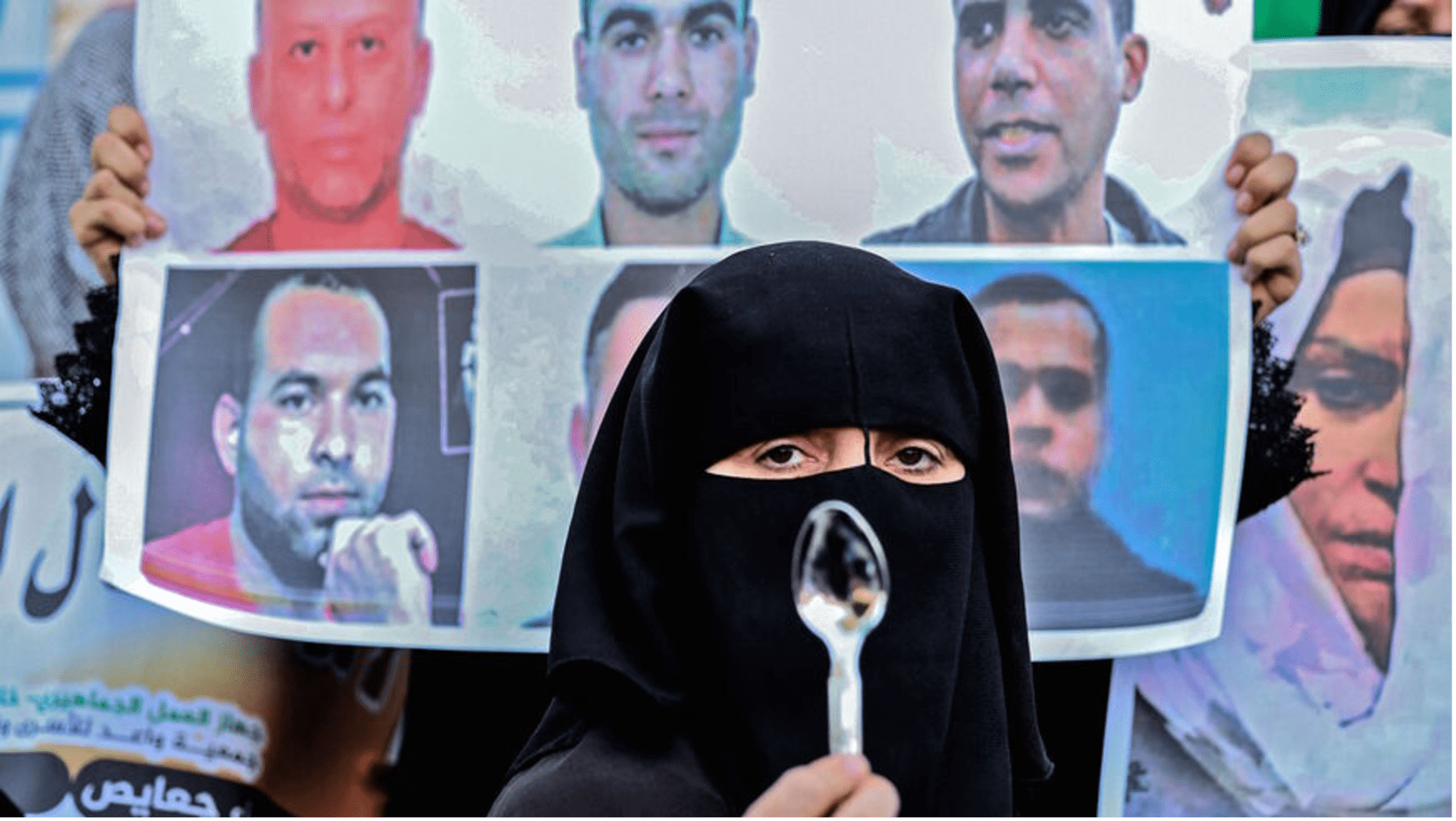
Frontline Defenders, an Ireland-based human rights organization, found Pegasus on the phones of 6 Palestinian activists that began in July 2020. The activists belonged to human rights and civil society organizations such as Defense for Children’s International – Palestine and the Union of Palestinian Work Committees in Israel of which 6 have been declared terrorist organizations despite lacking credible evidence supporting the designation.
Most Israeli surveillance laws do not apply to security companies and give them free reign to use the NSO’s spyware. In 2019, Facebook filed a lawsuit against the NSO Group for invading the popular international messaging platform WhatsApp on 1400 devices. And on November 23rd, Apple sued the NSO Group in California Court for violating a federal anti-hacking law by providing dangerous software to spy on their Apple customers. Despite the obvious unethical nature of spyware, the Israeli government fully licenses Pegasus and is a client of NSO Group. Experts speculate whether the Israel had a role in the hackings around the world, which may be considered an international crime if proven.
El Salvador
The Pegasus Project also uncovered illegal surveillance of investigative journalists in El Salvador, a region in Central America torn apart by frequent gang wars and corruption. Citizen Lab and Access Now forensically analyzed phones from reporters at El Faro and GatoEncerrado, media outlets that have been facing the brunt of President Nayib Bukele’s wrath in the race to retain his position. Evidence gathered by journalists and human rights organizations suggest that Bukele negotiated deals with El Salvador’s deadliest gangs in return for political advantage. Some individual’s phones were hacked over an extended period while others were infected intermittently when the media houses were investigating corruption in Bukele’s administration.
In 2021, the Biden Administration officially blacklisted the NSO Group and a lesser known surveillance company, Candiru, as well. This severs each company’s access to hardware necessary for maintaining servers and outsourcing the software.
Access to accurate information, freedom of press, freedom of speech, and privacy is crucial to maintaining autonomy and a fundamental human right. Backsliding democracies and military states are re-instituting citizen surveillance digitally – endangering the lives of millions that are fighting for the future of their people. To contribute to cybersecurity labs and human rights organizations working to increase legislation against digital surveillance, please donate to the Citizen Lab (https://engage.utoronto.ca/site/SPageServer?pagename=donate#/department/91) and Frontline Defenders (https://www.frontlinedefenders.org/en/donors).
Additional Information related to recent digital surveillance and human rights violations:
If you would like to learn more about the people the Pegasus Project, follow the link below https://cdn.occrp.org/projects/project-p/#/