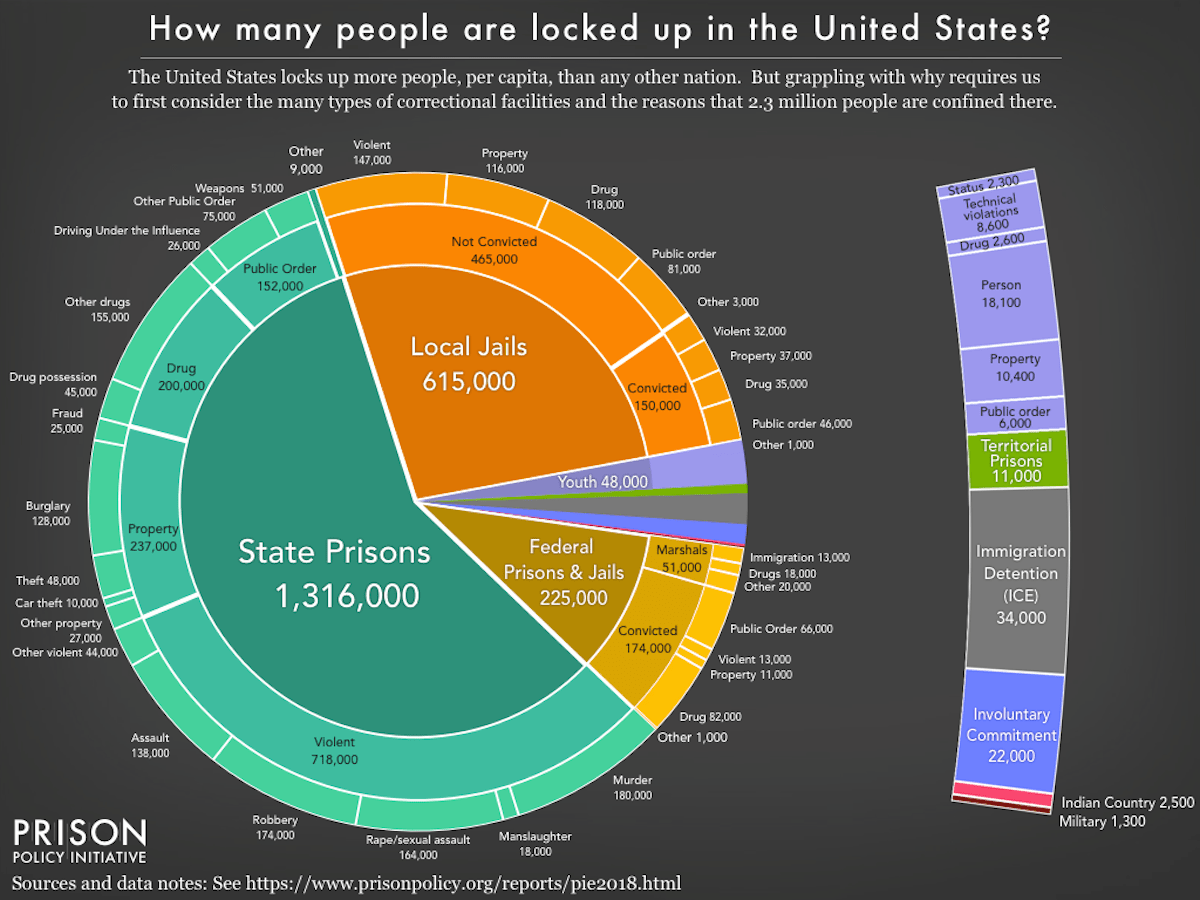
This past winter break, I visited Saudi Arabia with my family. While there, I noticed that many women were active in the work force, working as police officers, salespeople, and even airport security. Under the preconceived notion that women were not allowed to work in Saudi Arabia, I was surprised to see this. Slowly, I began to realize that the Western perspective about women’s rights in Saudi Arabia was not entirely correct. So, after I came back from my trip, I decided to look into different sources to try to get an accurate portrayal of women’s rights in Saudi Arabia.

Women’s Rights Narrative
After conducting extensive research, I realized that while there is no denying that Saudi Arabia still has many improvements to make in terms of gender equality, there are several women’s rights that have been historically implemented or are currently being established. Almost always, women in Saudi Arabia are portrayed as oppressed, and again, while there is an undeniable lack of many rights for women, it is not a fair assessment to only discuss what rights are not realized; it is important to recognize the rights that they have as well. While I cannot say for certain why this particular narrative is often propagated, it can be argued that the mainstream media is committed to portraying Islam in a negative light, and because Saudi Arabia is governed by Sharia Law, or Islamic Law, it follows that it will be portrayed negatively. As the media does this, people begin to argue that Islam is in and of itself misogynistic and is thus incompatible with progress and civilization. While I will not be going in too much depth about the rights Islam gives women, I will note that it is important to remember that culture and religion are not interchangeable terms and should not be treated as such; Saudi Arabia may govern using Sharia Law, but many of their restrictive practices are rooted in culture, not Islam. Thus, the purpose of this post is to provide a counter-narrative to show that what the media portrays pertaining to women’s rights in Saudi Arabia is not an entirely accurate depiction.
Employment Rights
While there is a dearth of women in the employment sector, seen through the fact that only 22 percent of Saudi womenparticipate in the workforce, there are no legal restrictions on which jobs women are allowed to work in, with garbage collecting and construction being the only exceptions to this. Sharia Law encourages women to work, so the lack of women in the work force is not due to restrictive religious practices, but rather to restrictive cultural practices. Further, Sharia Law allows women to earn and manage their own finances, making employment especially appealing to women who want to be financially independent. While the number of working women is low, Saudi Arabia is currently attempting to further integrate women into the workforce, with a goal of a 30 percent participation rate by 2030. While this is mostly due to the fact that Saudi Arabia wants to replace non-Saudi workers with Saudi Arabian citizens, it is still commendable that women are a part of this plan.
Education Rights
Perhaps most interesting is the emphasis Saudi Arabia has placed on women’s education. Saudi women have had access to education for several decades; women have been attending universities since the 1970s. Recent advances made highlight the country’s commitment to providing opportunities for women in education, namely the 2005 study abroad program, which sends thousands of Saudi women to the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom, among other countries, to obtain an education. Another very impressive advancement is Saudi Arabia’s first all-women’s college, Princess Noura bint Abdulrahman University, founded in 2010. The purpose of the school is to give women better access to fields that are traditionally male dominated, such as medicine and pharmacology. Due to these improvements and the general importance placed on women’s education, women currently represent 52 percent of university students in Saudi Arabia.
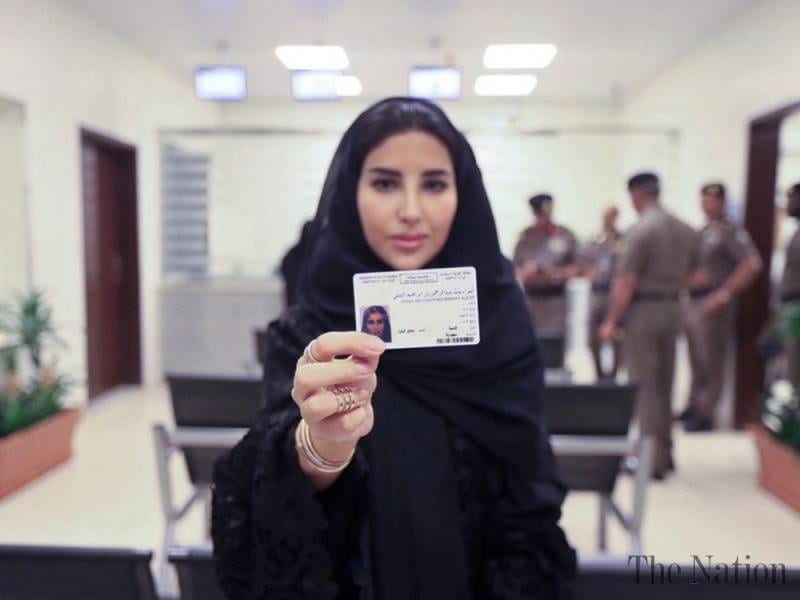

Recent Progress
Recently, steps have been taken to reverse restrictive practices, such as lifting the ban on women driving and reducing male guardianship. The former, implemented in 2018, saw the legalization of women driving. Thus far, tens of thousands of women have received their driver’s licenses, highlighting the success of this change. The latter, implemented a few months ago, saw changes made to restrictive guardianship laws. Historically, these laws heavily restricted women’s rights, specifically the right to freedom of movement; women were not allowed to obtain a passport or travel abroad without a male family member’s consent. While I could explain how changes to these guardianship laws will have a positive impact on women’s lives, I think it is best to share the perspectives of a Saudi Arabian woman on this issue. In an article for BBC News, Lulwa Shalhoob, a Saudi journalist, wrote that “the new rule means the relationship between a husband and his wife becomes a partnership between two responsible adults, rather than guardianship of a minor.” She also notes that an increasing number of Saudi women “no longer want to be framed as women of special circumstances who lack rights that women around the world take for granted.” For Saudi Arabian women, then, this move not only grants certain rights they were long deprived of, but it also fosters an unprecedented sense of agency and personhood.
Historically, Saudi Arabia has invested in specific spheres of women’s rights, such as employment and education, and in recent years, the Saudi Arabian government has made progress by rescinding many restrictive practices and laws. When Saudi Arabia is included in the discourse pertaining to the rights of women, none of this is mentioned; only the shortcomings are. While I am the first to admit that Saudi Arabia still has much work to do in terms of women’s rights and human rights in general, it is important to acknowledge what they have done right.