Recently, I had the pleasure of attending the Organized Radical Collegiate Activism (ORCA) Conference organized by the UAB Social Justice Advocacy Council on January 24, 2020. Various important and interesting social justice issues were discussed and presented by talented UAB students throughout the day. The presentation that stood out the most to me was “The State of Incarceration in Alabama” by Eli and Bella Tylicki. The brother-and-sister duo did a great job bringing attention to a very important human rights issue right here in Alabama.

The presentation started out with some questions for the attendees, such as what they thought were their odds of getting incarcerated at some point in their life? After some interesting responses from the audience, the presenters revealed that White men have a 7% chance of getting incarcerated at least once in their life, Hispanic men 17%, and African American men have the highest (32%) chance. However, women account for only 7% of the U.S. prison population. It was also revealed that the cost to imprison one person for a year in the U.S. is $36,299.25, or $99.45 per day.
As compared to other developed countries such as Canada, Germany, France, Italy, and the U.K, the United States has the highest number of incarcerated people per 100,000 population, almost three times more than these countries. The United States makes up roughly 5% of the world’s population but holds about 25% of the world’s prisoners. Shockingly, 31 U.S. states also have higher incarceration rates than any country in the world, and Alabama is among the worst in the country. Alabama exceeds national averages in virtually every category measured by states and the federal government, making the state’s prison system one of the most violent in the nation.
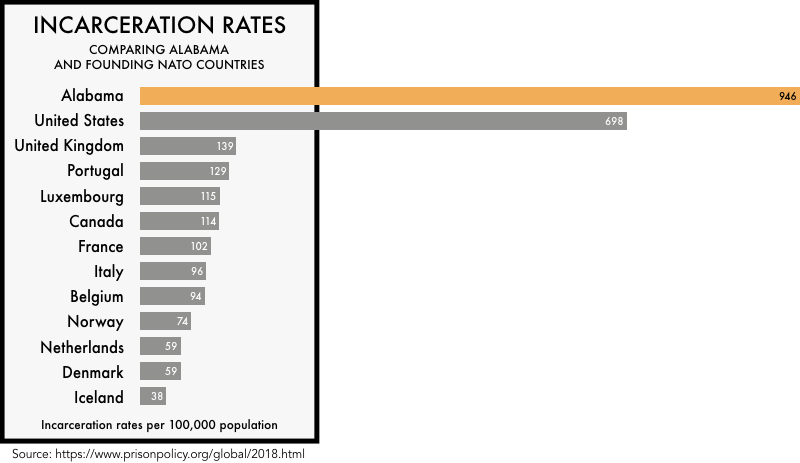
Now the question arises, why is the state of incarceration in the U.S. uniquely outrageous, and why is Alabama among the worst in this aspect? Many factors are responsible for such staggering statistics, including our economy built on slavery, poverty, tradition-based culture, fear and insecurity, systemic racism, educational inequity, and punitive cultural attitudes just to name a few. Focusing on Alabama, the presenters showed that Alabama’s prisons were revealed to be the most crowded in the country in 2017, with the prison suicide rate being three times more and the homicide rate ten times more than the national average. On April 2, 2019, the U.S Department of Justice Report concluded that “there is reasonable cause to believe that the conditions in Alabama’s prisons for men violate the Eighth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution. The Department concluded that there is reasonable cause to believe that the men’s prisons fail to protect prisoners from prisoner-on-prisoner violence and prisoner-on-prisoner sexual abuse and fail to provide prisoners with safe conditions.” Note that the Eighth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution prohibits the infliction of excessive, cruel, and unusual punishment.
The presenters then went on to show the various horrific accounts of prisoner violence, sexual abuse, homicide cases, and extreme physical injuries during a single week in 2017 as reported by the investigation. It was extremely shocking to learn about the various instances of such abuse and violence that took place in just a single week in our prisons. Those examples were used to illustrate the gravity of ongoing issues in state prisons and are not mentioned here due to their disturbing and triggering nature. Additionally, overcrowding and understaffing are some very important issues that contribute to the worsening situation of prisons in Alabama. According to the Alabama Department of Corrections (ADOC), the state houses approximately 16,327 prisoners in major correctional facilities which are designed to hold only 9,882. Moreover, prisons like Staton and Kilby hold almost three times the number of prisoners than their capacity. As for understaffing, Alabama’s prisons employ only 1,072 out of the 3,326 needed correctional officers according to ADOC’s staffing report from June 2018. It also reported that three prisons have fewer than 20% of the needed correctional officers. This illustrates the increased threat to the safety of both the staff and the prisoners in those facilities due to the lack of required personnel in case of an emergency.

The Department of Justice also reported the excessive number of deaths due to violent and deadly assault, high number of life-threatening injuries, unchecked extortions, illegal drugs, and the routinely inability to adequately protect prisoners even when officials have advance warning. The report also threatened a lawsuit within 49 days if the state does not show that it is correcting what is said to be a systemic failure to protect inmates from violence and sexual abuse.
In response, Alabama’s Governor Kay Ivey has proposed a public-private partnership to lease three “megaprisons” from a private firm as a solution to the understaffing and cost-ineffective conditions in state prisons. Department of Corrections Commissioner Jeff Dunn said that “we are convinced now more than ever before that consolidating our infrastructure down to three regional facilities and decommissioning the majority of our major facilities is the way to go.”
Bella and Eli Tylicki gave an overview of the potential pros and cons of the megaprison proposal. Some advantages may be that the upfront costs will be covered, and it may prove as a quick fix with less red tape (a reduction of bureaucratic obstacles to action). However, privatized prisons may lead to a decreased quality of life, is economically inefficient, and there is no change in cost for taxpayers. The Equal Justice Initiative explains how building new prisons will not solve the state’s prison crisis:
Alabama’s primary problems relate to management, staffing, poor classification, inadequate programming for incarcerated people, inadequate treatment programs, poor training, and officer retention. None of these problems will be solved by building new prisons, nor does a prison construction strategy respond to the imminent risk of harm to staff, incarcerated people, and the public.
Therefore, the presenters proposed an alternative to this solution in the form of decarceration and rehabilitation of prisoners. This aims at fixing overcrowding and understaffing, decreases the inside violence, and costs less for taxpayers. Additionally, there is no change in crime rate outside the prisons and rehabilitation leads toward GDP growth and a more productive society. Studies have shown that incarcerated people who participate in correctional education programs are less likely to recidivate and have a higher chance of finding employment when they are released. Plus, these valuable educational and rehabilitative programs cost the state nothing while having significant positive effects on successful re-entry of prisoners and protecting public safety. Of course, there will need to be more done other than just an emphasis on decarceration, such as fixing the infrastructure, improving healthcare, and incentivizing an increase in Correctional Officers. Low-cost reforms such as effective use of video surveillance cameras, implementation of an internal classification system, skilled management, and other basic management systems such as incident tracking systems, quality control, and corrective action review can result in significant improvements in conditions for both the staff and the prisoners. These low-cost reforms helped the nation’s worst women prison, the Tutwiler Prison for Women, become a model for reform.
The Tylickis ended their presentation with a call for action by urging the audience members to call their state representatives and senators to take responsible action, as they will be voting on this issue in the coming weeks. Additionally, they asked us to volunteer with reentry organizations and educate ourselves and others on the issue. Some initiatives that we can support include The Dannon Project, Alabama Appleseed, and the Equal Justice Initiative. We, as responsible and active citizens of this state, need to play our part in making our society safe, just, and productive for all.


Thank you for sharing the message of our presentation and bringing more attention to such a pressing and pervasive human rights issue!