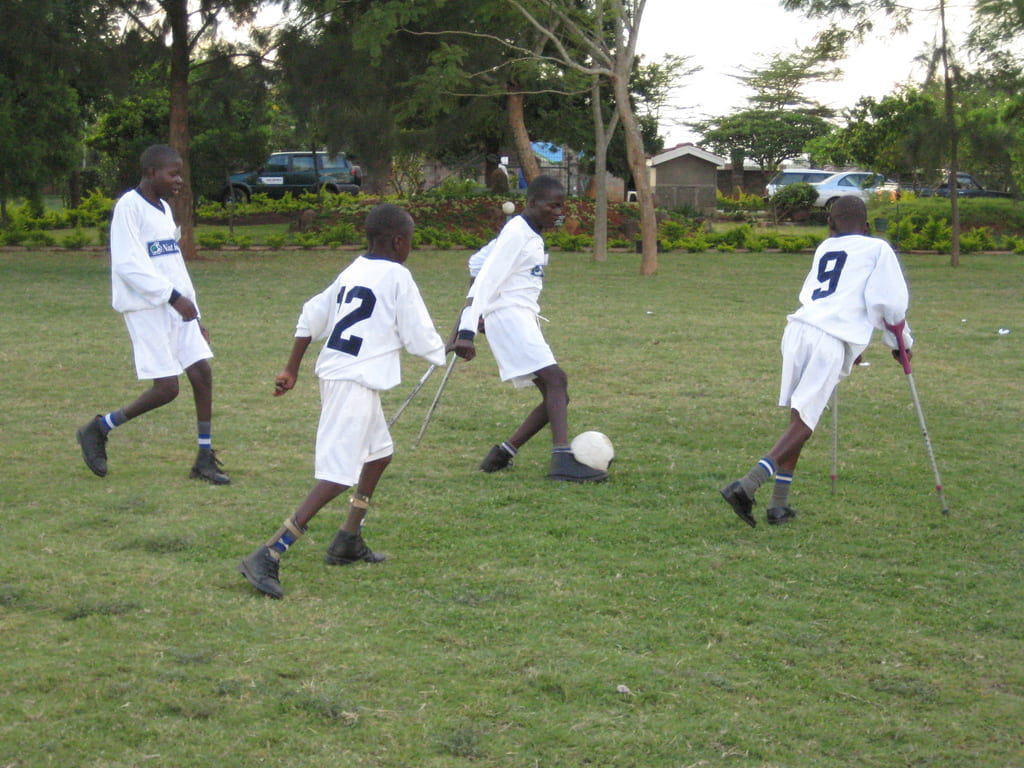
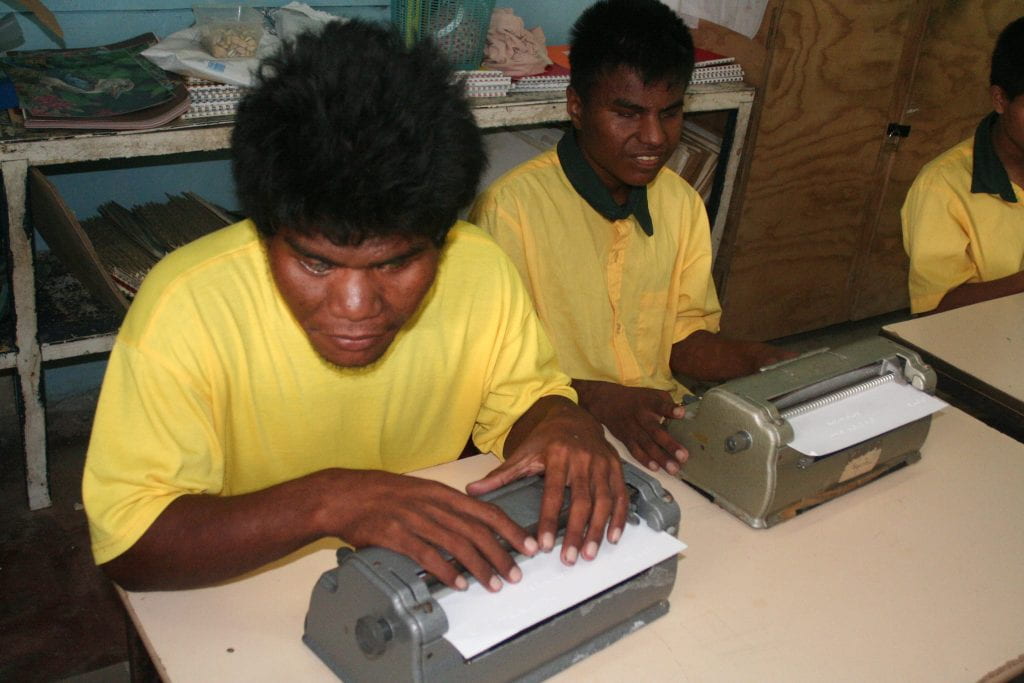
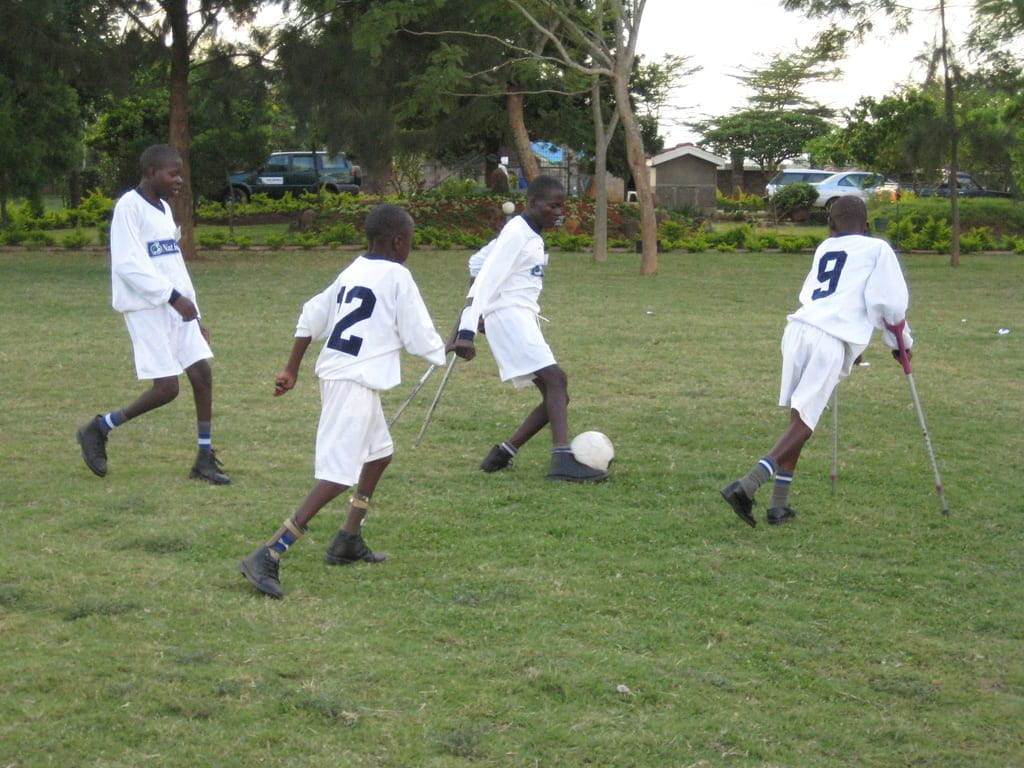
The ability to be rewarded for making meaningful contributions to society and to choose our own private residence are two facets of life many of us often take for granted. However, many individuals with a form of disability often encounter barriers during their journey locating work and housing. These barriers can arise from social isolation, discriminatory and / or inadequate governmental policies, economic hardship, or simply a lack of awareness of resources designed to aid persons with disabilities to find employment and housing. These material and immaterial barriers fall under the broad umbrella of ableism, defined here as “the intentional or unintentional discrimination or oppression of individuals with disabilities”. The following post explores four case studies surrounding the themes of housing and employment and how various cultures have either failed to address these needs or offered innovative solutions to persons with disabilities. Finally, for the purpose of this blog, disability is defined, in accordance with the Washington Group (2018), as “problems, such as impairment, activity limitation or participation restrictions that include the negative aspects of functioning” in the following six domains: (a) walking; (b) seeing; (c) hearing; (d) cognition; (e) self-care; and (f) communication. This blog post offers an anthropologically-informed context for to upcoming panel ‘Disability Rights, Employment, and Housing in a Cross-Cultural Perspective’ at the Institute for Human Right’s Symposium on Disability Rights.
Disability Rights & Employment: South Africa
South Africa’s government of apartheid came to power in 1948 and institutionalized a cultural and political zeitgeist of xenophobia, discrimination, and violence towards the Other. Throughout apartheid’s hold on South Africa, systems of cultural and structural violence were erected both within social life and in bureaucratic policy. Apartheid is most infamous for its impact on racially-motivated violence; however, other forms of discrimination were enabled by apartheid policy and philosophy as well. Engelbrecht (2006) notes that education systems institutionalized apartheid policies in curricula development and inclusivity within schools. This specifically barred children with disabilities from actively participating in the education system, from primary through tertiary levels. Englebrecht (2006) contends children with disabilities were actively excluded from South African governmentally-controlled education systems. This means children with disabilities during the apartheid regime did not receive adequate preparation for entering into the workforce, thus placing these individuals at a low ‘tract’ and preventing them from seeking or acquiring meaningful employment. Englebrecht (2006) emphasizes that discriminatory and / or prejudicial national policies focused on one marginalized population (e.g. apartheid) often seep into the experiences of other marginalized populations as well. In short, government-sanctioned racist policies immobilized the disability community. To repress one group is to repress all groups.
The South African Human Rights Commission (SAHRC) was inaugurated in October of 1995, as mandated by the South African Constitution’s Human Rights Commission of 1994. The SAHRC is charged with monitoring, preventing violations of, and educating the public about human rights within the South African context. A specific function of the SAHRC is to examine how apartheid-era policies impacted South African civil society and how to eliminate the vestiges of structural violence still propagated by the former apartheid regime. The SAHRC provides further evidence supporting Engelbrecht’s (2006) theory that the repression of children with disabilities would negatively impact South African workforce. The SAHRC (2017) summarizes trends of disability employment, demonstrating that workforce equity (equally considering and making efforts to hire marginalized populations, such as the disability community) is nowhere near the South African Department of Labor’s goal of 7% by the year 2030. In 2017, workplace equity was still under 2%, with 8 in 10 persons with disabilities unable to find employment (SAHRC, 2017). A variety of reasons are given for this abysmally low number, including: lack of reasonable accommodation, inequality and discrimination, and a persistent inability to obtain a quality education. The ghost of apartheid, it seems, haunts the disability community within South Africa, preventing a vast majority of persons with disabilities from obtaining education, training, and gainful employment.

Disability Rights & Employment: Ireland
In 2017, the British Conservative government announced plans to cut the Employment and Support Allowance for persons with disabilities who were deemed ‘capable of preparing to return to work’ by 30£ / week (~$40 / week). The British government implemented this policy as a ‘motivational tool’ for persons with disabilities and as an austerity measure, despite the fact that previous disability allowances (akin to welfare or social security measures in the United States) left 1/3 of allowance recipients struggling to afford food. However, the ministers of Ireland, taking cue from their outraged constituents, have chosen a different path to empower persons with disabilities to find employment. Instead of the ‘pull yourself up by the bootstraps’ strategy of British Conservative MPs, Irish Minister for Social Protection Regina Doherty and Minister of State for People with Disabilities Finian McGrath have chosen to listen to persons with disabilities themselves to assess the best way to promote gainful employment within the disability community. In response to a 2017 policy brief Make Work Pay, Doherty, McGrath, and other policy-makers are distributing questionnaires to adults with disabilities and parents of young children with disabilities to assess the employment needs of the disability community (Clougherty, 2017). This approach to governance, one defined by inclusivity and direct participation of the disability community, shows promise in exploring the complicated relationship between disability and employment.
Of particular importance in the employment-disability nexus is accounting for an individual’s preference for work and her or his form of disability. The Irish ministers understand that low-functioning persons with disabilities will, for the entirety of their life, be simply unable to work. These individuals require assistance from the government thereby ensuring these persons are included in society and are able to participate in decisions regarding their lives and livelihoods. On the other hand, some individuals are temporarily disabled and do not require the same social security from governments. By asking for input from persons with disabilities themselves, the Irish policy-makers are better equipped to make educated, inclusive, and effective policies and programs aimed at insuring equitable and equal employment within the disability community.

Disability Rights & Housing: Libya
The State of Libya, located at the Northern-most tip of Africa and bordered by the Mediterranean Sea, is in the midst of rebuilding civil society following the catastrophic Libyan Civil War of 2011. For over forty years, Muammar Gaddafi ruled over Libya, attempting to introduce a socialist regime and command economy to the Libyan State. During his reign, Gaddafi allegedly sought to implement a political philosophy of jamahiriya (جماهيرية), meaning “state of the masses” in Arabic – akin to ‘direct democracy’. Through this system, Gaddafi created the national General People’s Congress, whose directives (including any form of a Libyan Constitution) could be superseded by the Basic People’s Congress, municipally-led executive and legislative bodies. Hypothetically, this system placed most political power at the local level; however, Gaddafi’s actual dictatorial rule inverted the political equation. In the past half century, this political system (again, on paper) aimed to enshrine the rights of persons with disabilities through the passage of the 1981 “Law on Disabled People”, arranging for “government provision of housing, home care, education, prosthetic limbs and rehabilitation for people with disability in Libya” (Hamed el-Sahly & Cusick, 2016, p. 12). In political practice, Libyan persons with disabilities suffered major human rights violations, including lack of housing and home care, due to insufficient mechanisms of care and cultural taboos.
Although political and economic recovery may well be on the horizon for post-conflict Libya, cultural barriers prevent many Libyans with disabilities from securing independent and safe housing. In a comparative study, many Libyans express unfavorable attitudes towards persons with disabilities along three dimensions: (1) lower ratings of willingness to empower the disability community; (2) higher ratings of exclusion; and (3) lower ratings of similarity between disabled and non-disabled people (Benomir, Nicholson & Beail, 2016). Most pertinent to issues related to housing, Libyan participants scored high on the ‘need to shelter’ persons with disabilities – meaning intentionally secluding these individuals from broader society for fear of communal judgement and the social stigma attached to disability. Furthermore, efforts to facilitate the transition from being ‘sheltered’ (living with a family member) to an autonomous home life is seen as a problem ‘for and by’ the disability community – i.e., it is the responsibility of the disability community alone to solve social issues related to their situation in life (Cusick & Hamed el-Sahly, 2018). This demonstrates that governmental policies intending to enshrine disability rights are insufficient – societies themselves must be willing to tackle these issues head on.

Disability Rights & Housing: Native Americans
Persons with disabilities with another form of marginalized identity (e.g. members of an indigenous group) are placed at a heightened risk for social isolation / exclusion, for physical and mental health concerns, and having disability-related needs go unmet (US Department of Health & Human Services, 2017). Within American Indian / Alaska Native (AIAN) communities, this translates specifically into housing issues, as AIAN reservations already suffer from a lack of resources and infrastructural investment to provide for non-disabled AIAN individuals (US Department of Health & Human Services, 2017). An estimated 21 – 69% of homes on reservations are overcrowded and have serious physical deficiencies compared with 5.9% of non-reservation US homes nationally (US National Council on Disability, 2003). To address these intersecting concerns, the AIAN community, in tandem with the US government, have prepared and started implementing policy prescriptions to provide affordable, safe, and dignified housing to AIAN with disabilities.
Of primary concern in planning homes for persons with disabilities is utilizing principles of universal design – “guidelines for housing construction that would create a livable, marketable environment for everyone regardless of ability, age, or size” (US National Council on Disability, 2003, p. 94). Currently, the American Indian Disability Technical Assistance Center provides assessments of universal design within reservations and makes design prescriptions if the home in question is not fully accessible. Implementation of these prescriptions may fall to the American Indian Disability Legislation Project (AIDLP), a culturally-informed taskforce mandated to draft and pass legislation standardizing disability-related care (including autonomous and accessible housing) on Indian reservations (US Department of Health & Human Services, 2017). The AIDLP, in addition to ensuring reservations adhere to the Americans with Disabilities Act, acts as a cultural liaison between the disability community and AIAN community to ensure disability concerns are handled in a culturally-appropriate manner. Finally, the AIDLP and other AIAN-affiliated, disability-related advocacy groups ground their research and implementation efforts by tackling both material (e.g. physical accessibility) and immaterial (e.g. cultural stigma) barriers (US Department of Health & Human Services, 2017).
Towards a Global Culture of Disability Empowerment
The preceding case studies illustrate that disability rights, especially related to employment and housing, are high complicated issues. Historical events, such as apartheid and civil war, interact with governmental policies, such as austerity measures and indigenous sovereignty. Underlying each of these examples is the ‘culture’ surrounding disability – how peoples across the world value or stigmatize the experiences and perspectives of the disability community. In some cases, such as South Africa, systems of discrimination have erected structural barriers holding back people with disabilities, even though disability-related stigma may have lost its potency. In other cases, such as American Indian / Alaska Native communities, an additional marginalized identity may facilitate an even greater emphasis on seeking justice and equity for persons with disabilities. As local, national, and global disability movements aim to eliminate social exclusion and promote equality in life and livelihood, the myriad cultures of disability must be unpacked and explained. This post argues that moving towards a global cultural of disability empowerment is indeed possible. Once this culture of empowerment has been adopted, disability-related concerns, such as employment and housing, will be addressed and rectified across the globe.
Keep up with the latest announcements related to the upcoming Symposium on Disability Rights by following the IHR on Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. And don’t forget to tag your Symposium-related posts with our event hashtag: #DisabilityRightsBHM
References
Benomis, A. M., Nicolson, R. I. & Beail, N. (2016). Attitudes towards people with intellectual disability in the UK and Libya: A cross-cultural comparison. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 2016, 1-9.
Clougherty, T. (2017). Make Work Pay: A New Agenda for Fairer Taxes. Cork, Ireland: Center for Policy Studies.
Cusick, A. & Hamed el-Sahly, R. M. (2018). People with disability are a medicalized minority: Findings of a scoping review. Scandinavian Journal of Disability Research, 20(1), 182-196.
Engelbrecht, P. (2006). The implementation of inclusive education in South Africa after ten years of democracy. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 21(3), 253-264.
Hamed el-Sahly, R. M. & Cusick, A. (2016). Rehabilitation services in Benghazi, Libya: An organizational case study. Middle East Journal of Family Medicine, 14(9), 11-18.
South African Human Rights Commission (2017). Research Brief of Disability and Equality in South Africa. Braamfontein, South Africa: South African Human Rights Commission.
US Department of Health & Human Services (2017). Emerging LTSS Issues in Indian Country: Disability and Housing. Spokane, WA: Kauffman & Associates, Incorporated.
US National Council on Disability (2003). Understanding Disabilities in American Indian & Alaska Native Communities. Washington, DC: National Council on Disability.
Washington Group (2018, December 4). Statement of rationale for the Washington Group general measure on disability. Retrieved from http://www.washingtongroup-disability.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/Rationale_WG_Short-1.pdf