by Andy Carr
In human rights, journalists usually are seen as chroniclers: reporters on the front lines of a conflict zone letting the world know of events as they unfold. As such, they also may serve as agents of human rights, since their reporting provides advocacy groups and committed global human rights leaders with vital information. Tragically, though, journalists often become the targets of human rights abuses unto themselves. Until recently, little attention had been paid systematically to this last point but shifting global events have underscored numerous threats to members of the media. In an era of politicians condemning the media writ large as “enemies of the people,” deteriorating discourse, extreme politicization of what constitutes “news,” and the polarization of both governing elites and societies at large have made the humanity and the human rights roles of journalists both more important and, troublingly, threatened.
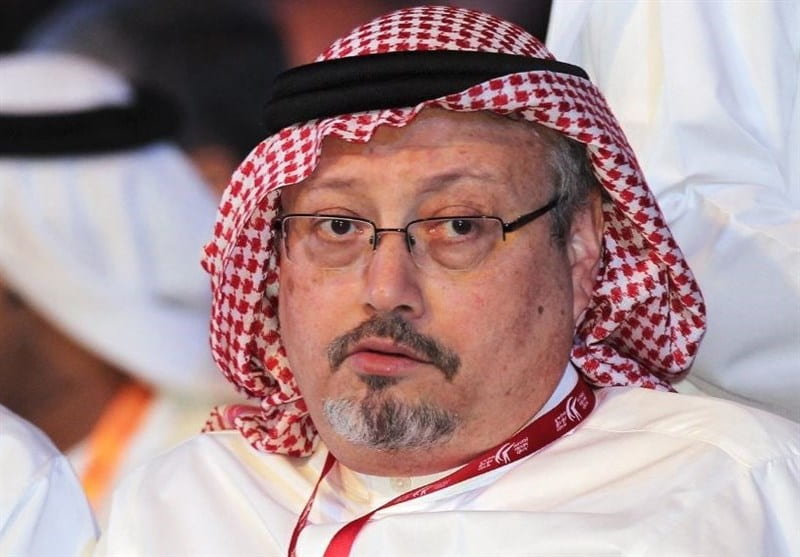

On October 2, 2018, Washington Post contributor and journalist Jamal Khashoggi disappeared after heading into the Saudi consulate in Istanbul. Shortly thereafter, Turkish officials leaked that Khashoggi had been murdered, with grisly details suggesting he had been cruelly tortured before his killing – a “brutal silencing of a prominent journalist,” and an event which “was met with outrage from journalists” and politicians around the world.
One notable exception to the global outcry, however, was President Donald Trump. While the President’s “business dealings with Saudi Arabia” leave him “personally conflicted,” regardless of his conflicts, Joel Simon flatly stated that the President has utterly “failed to articulate a coherent response” to Khashoggi’s murder whatsoever. The non-response is galling, in particular because of Khashoggi’s identity and profession. As Kyle Pope wrote for the Columbia Journalism Review:
The Khashoggi case has brought Trump unusual global blowback, though, for a distinction that the president plainly does not see. We care about the Khashoggi case, at least in part, because Khashoggi was a journalist.
Yes, his killing was horrific and barbaric and yes, it came at the hands of an American ally, which then lied about it. But the world has also been moved to respond because Khashoggi, as a journalist, represented something bigger than the man himself, something that leaders around the civilized world have come to value. He was a stand-in for a value we wanted to protect.
Pope continues, “We journalists, as individuals, are not special people. We have no unique right to support or sympathy. But the point is that we, collectively, represent something that our society has decided is worthy of protection.” Pope’s point goes directly to a growing subtext in present debates about “fake news” and risks to journalism as a profession, a recognition of its societal importance.
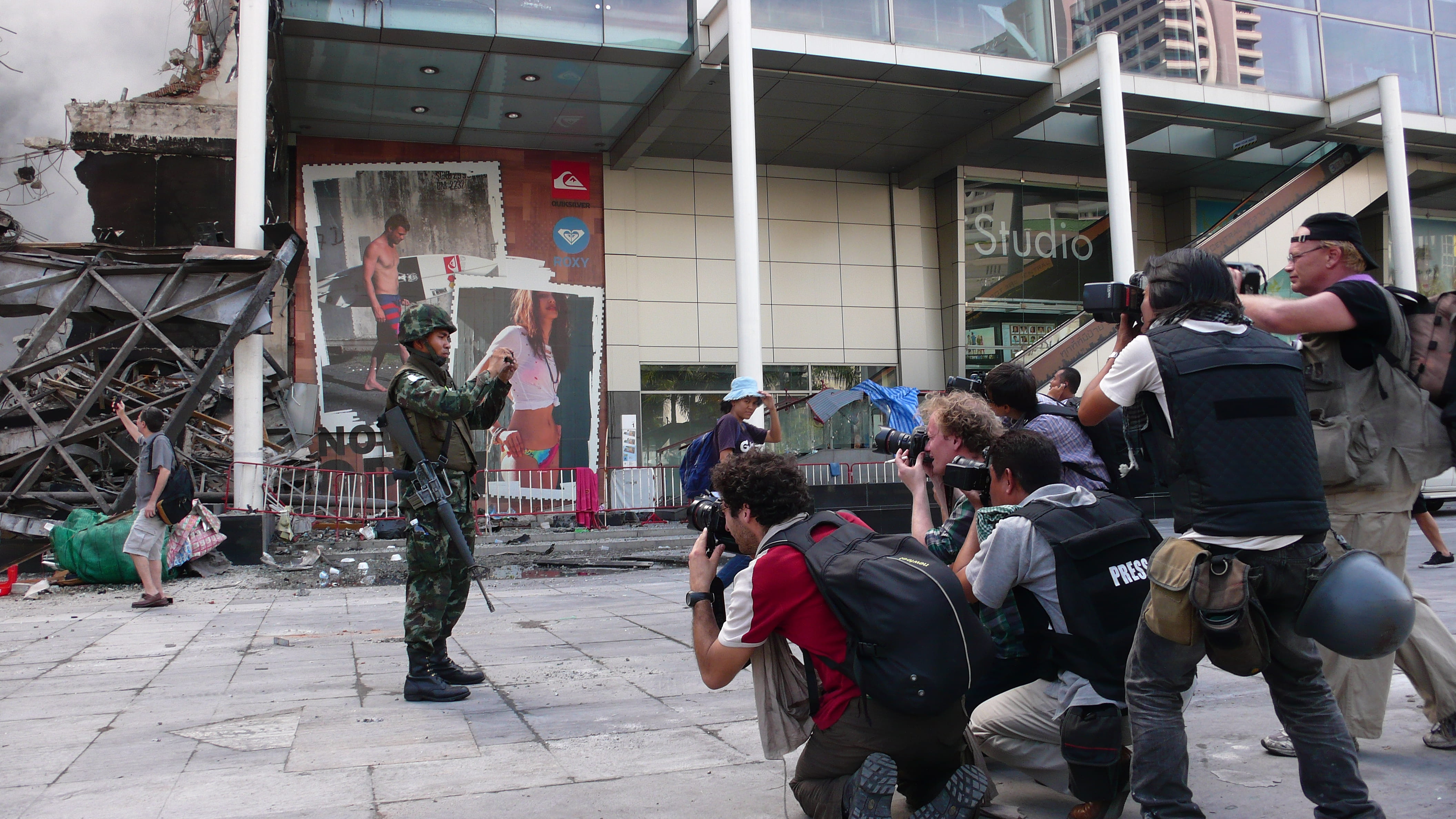
Our society, through the First Amendment to the Constitution (“Congress shall make no law … abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press”), surely had decided to protect the worthy contributions of journalists from governmental interference – and the individuals themselves. And journalists globally have begun pushing for international collaboration to expand guarantees more widely, such as a proposed UN-promulgated International Convention on the Safety and Independence of Journalists and Other Media Professionals, led by the International Federation of Journalists (IFJ). The IFJ’s proposal responds to the realities of a fraught few years for the profession. In Yemen, some 35 journalists have been killed since the country’s civil war began in 2011, and eight so far this year alone. At least 45 journalists, globally, have lost their lives in the first 10 months of 2018, among whom 27 were confirmed as murdered. To wit, the IFJ’s proposed Convention would include various protections aiming to deter violence, threats, and politically motivated intimidation of journalists, extension of humanitarian law concepts to ensure reporters’ safety in conflict zones, and similar measures.

The humanity of journalists—and their own individual rights—often remain overlooked. While the gruesome murder of the Post’s Khashoggi’s in Istanbul catalyzed global attention, the sentencing of two Reuters reporters to seven years’ hard labor on dubious grounds, following their later-verified reporting on a massacre of Rohingya civilians in Rakhine State, Myanmar, barely registered. Other recent politically motivated arrests of journalists include Austrian Max Zirgast, arrested by “anti-terror” authorities in Turkey, adding to the “dozens of journalists” earlier arrested following the “failed military coup attempt” against Turkish President Erdogan in 2016. At least eight journalists were arrested in late September in Uganda for covering the return of an opposition leader, MP Robert Kyagulanyi, “the latest incident of Ugandan security personnel assaulting, harassing, or arresting journalists covering political tension” in the country. Four journalists, including the deputy editor-in-chief of Xinjiang Daily, were arrested in China’s Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region the same month, accused of “publishing ‘two-faced’ articles,” a “vague term” indicating content “allegedly secretly [opposing Chinese] government practices.” As The Atlantic’s Krishnadev Calamur summarized, Khashoggi’s death was a signal of “a larger pattern of violence inflicted on journalists around the world … Year after year, reporters are detained, abducted, and, with some frequency, killed.” Calamur’s colleague, David Graham, decried the U.S. government’s at-best tepid response as “the end of American lip service to human rights.”
Unfortunately, all the foregoing trends appear present in the United States as well. In July 2018, Colorado Independent editor Susan Greene was “detained for ‘interfering’” with the police in Denver, Colorado, not far from the Colorado State Capitol. In May 2017, Montana Congressman Greg Gianforte attacked Guardian reporter Ben Jacobs after the reported “asked the then candidate a question about healthcare.” (Gianforte later pleaded guilty to assault, but nevertheless won his election.) And in late June 2018, the mass shooting at the Capital Gazette of Annapolis, Maryland—which left five Gazette reporters dead and two others injured—triggered mass responses from law enforcement agencies nationwide “to provide protection at the headquarters of media organizations.” From last week’s high-profile pipe bombs, sent to CNN headquarters along with noted Democratic politicians and backers, to the multimillion-dollar libel verdicts against The Raleigh News & Observer in October 2016, the world’s reporters face risks both legal and lethal.
Each of these cases—and especially the still-unfolding story of Jamal Khashoggi’s murder—highlights Kyle Pope’s earlier commentary on the importance of journalists to all societies. But each of these cases, of course, reflects an actual individual – a human being behind a byline or photo credit, with their own individual worth and singular humanity. These two understandings of journalists are not mutually exclusive, but instead are, or should be, mutually reinforcing. And policymakers and political leaders, perhaps following or building upon the IFJ’s proposed framework for a journalists’ human rights convention, must take seriously the risks facing the media at home and abroad.
Many reporters and photographers have lost their lives in crossfire, victims of the very conflicts they gave everything to shed light on. Many more have faced harassment, criminal charges, assault and, again, even death, far from the front lines. Our discourse—not to mention our laws, our policy priorities, and our foreign relations—must recognize and respond to these threats.
Authoritarian regimes have long threatened free media and free expression, as well as those who exercise those vital social functions. Today, however, we must be cognizant in all societies of these threats. Even if these values are enshrined in the First Amendment to the American Constitution, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, or the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union—all, in principle, inviolable—they must be vindicated and reaffirmed continuously. Revoking publication or television licenses remain obvious aberrations but preventing the dehumanization of journalists entails the same underlying concerns.
Again, as Kyle Pope eloquently noted, the murder of Khashoggi shocked global consciences because, “as a journalist, [he] represented something bigger than [himself], something that leaders around the civilized world have come to value.” That is, journalism and journalists reflect our commitment to information, to expression, to understanding governments and governance, as well as our commitment to seeing problems in the administration of our societies. The individual journalist, then, must be protected as an individual, endowed with human rights as much as any other. But as the guarantors of knowledge and understanding of human rights beyond themselves, journalists’ safety and capacity to work must be ensured – and we all must act vigorously whenever their safety and capacity are threatened, however overt or furtive the menace may be.
Andy Carr is a third-year law student at U.C. Hastings College of the Law in San Francisco, California. Previously, Andy extensively studied and researched in political science, receiving his BA and MA degrees at Christopher Newport University and Pennsylvania State University, respectively, and plans to return to complete his PhD beginning in fall 2019. In addition to human rights, media and journalism, and constitutional law, Andy is most interested in questions of democracy and democratic theory – what makes for a truly democratic society, what risks confront representative governments. In addition to his academic training, Andy has worked for a boutique campaign compliance law firm and two global human rights nonprofit organizations, in San Francisco and Washington, D.C.