In the United States, the earliest experiments with solitary confinement began over two centuries ago, during the Enlightenment. Champions of the idea of natural rights, thinkers of the era found that public corporate punishment was incompatible with the development of a free citizen. Instead, silence and solitude would allow prisoners to reflect and that would induce repentance that would drive prisoners to live a more responsible life, making individuals the instrument of their own punishment. However, as the United States’ first silent prisons and penitentiaries were publicized, renowned nineteenth-century thinkers such as Alexis de Tocqueville and Charles Dickens visited these institutions to observe these revolutionary systems. Once intrigued, these icons now condemned these silent prisons as de Tocqueville remarked,
This absolute solitude, if nothing interrupts it, is beyond the strength of man; it destroys the criminal without intermission and without pity; it does not reform, itkills.
As other physicians and experts echoed their concerns, reporting the high risk and evidence of insanity and death of inmates existing in solitude, it gained the attention of the United States Supreme Court which influenced a new philosophy in correctional administration and gradually reduced the regularity of the practice.
This period of relief lasted until prisons began using solitary confinement to segregate more “threatening” and “dangerous” prisoners who were considered a risk to the safety of other prisoners and staff. Then, retribution and deterrence replaced rehabilitation as the professional purpose of corrections. As the U.S. responded by institutionalizing longer sentences, building more prisons, and abolishing parole, the use of solitary confinement rapidly increased with prison growth.
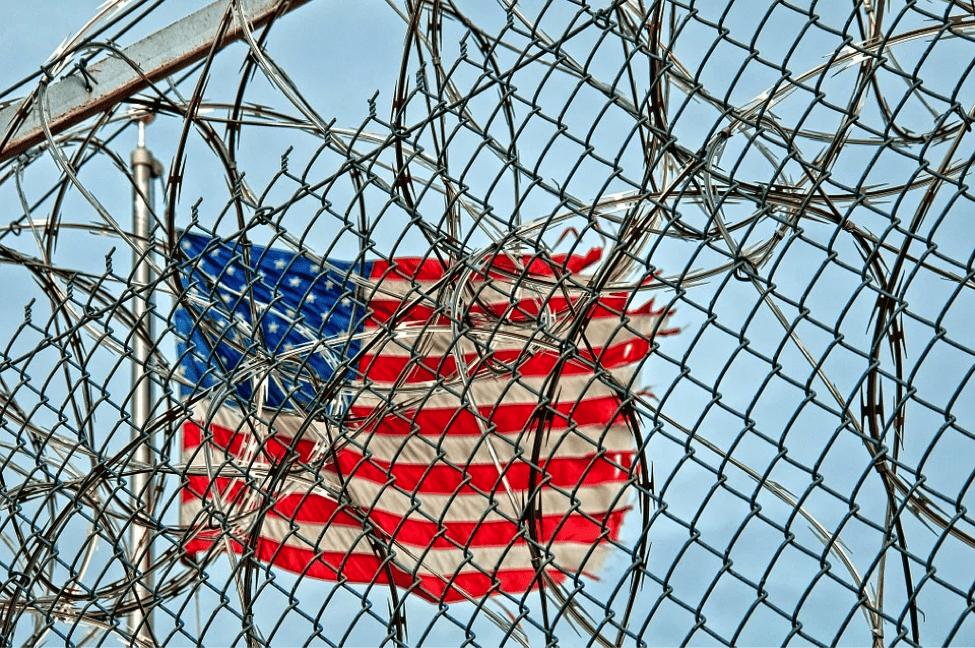
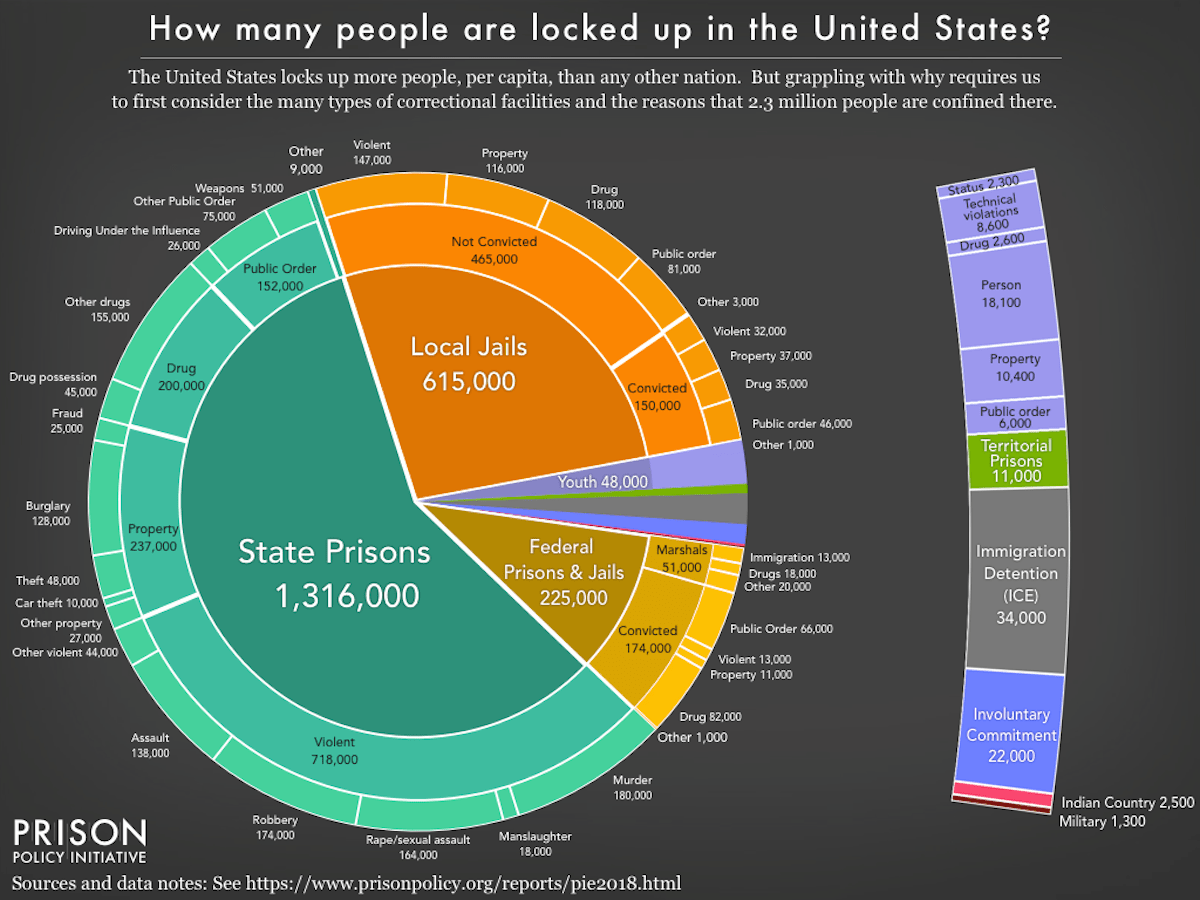
Today, the United States not only incarcerates more people than any other nation, but we also expose more of these people to solitary confinement than any other nation. The United States holds around 100,000 prisoners in solitary confinement typically as punishment, as a tactic to control overcrowded institutions, and as safety from or for the general population.
As individuals, inmates tell us what it is like in solitary confinement. In solitary confinement, your world is a gray concrete box. You may spend around 23 hours a day alone in your cell which are only furnished with a toilet, sink, and bed. When prisoners are escorted out of their cells, they are first placed in restraints through the cuff port and sometimes with additional leg or waist chains and tethered by the hooks on their cuffs to an officer. Prisoners are controlled by bodily restraints, with pervasive and unforgiving round the clock surveillance, and the restricting hallways and cells they exist in. They are lead to solitary exercise each day and a brief shower three times a week then back to their cells. Confined to their own concrete cells, prisoners are both physically and psychologically removed from anyone else. Prisoners depend on officers to bring them anything they may need and are allowed to have such as toilet paper, books, or letters they may receive. Many prisoners relate with dark thoughts that haunt them in isolation. Many become angry and hateful behind compliance.
Where many express anger, they all express a struggle to maintain dignity and a sense of self or humanity. Being alone, prisoners forget how to interact with others. Feeling as though they have nothing to live for in isolation, prisoners may give up on these things. Many interviews describe watching others who were locked in indefinite solitary choosing between giving up by either through suicide or turning into an unfeeling and uncaring creature. Correctional facilities’ workers express their concerns as to why and how they become desensitized through strict policy, regulation, and the specialized emotional stance necessary to interact with these prisoners. Acting as servants for the lives of some bad apples, observing civilized men be reduced to the natural man, and acting in adherence to authority with little voice heard by superiors, this work requires a specialized emotional stance.
Instead of regular and healthy social relationships important to human survival, these prisoners are embedded in a structure that extends itself into them. It enters their mind and sometimes switches off the human inside or sometimes forces it to become violent enough to compete. In this way, it also robs them of self-determination, liberty, and other forms of autonomy.

Because the practice of solitary confinement is a global one and brings claims of widespread abuse, the UN special rapporteur presented his report, or evaluation, of solitary confinement. This rapporteur defined prolonged solitary confinement as isolation for more than fifteen days because studies show that the effects of solitary confinement may become irreversible after this point as the rapporteur concluded that solitary confinement can amount to torture or cruel inhuman and degrading treatment.
International and domestic laws prohibit all forms of Racial Discrimination, which address variations in solitary confinement’s demographics, and rights of persons with disabilities which protect individuals with mental, or other, illnesses. They also guarantee the rights of women and children or juveniles, which are especially vulnerable under conditions of solitary confinement or isolation. Both sides address the minimum standards for the treatment of prisoners. More specifically, they address conditions of solitary confinement which always may apply to every individual.
Domestically, the Eighth Amendment reveals how the United States Constitution addresses Solitary Confinement. The Eighth Amendment prohibits the government from inflicting “cruel or unusual punishment” on someone convicted of a crime. This allows these prisoners to challenge their conditions while in custody and the actions of prison officials. To do this, prisoners must first show that the challenged condition is “sufficiently serious” and that prison officials acted with deliberate indifference to the condition. Close observation of court decisions reveals that there is no organized methodology to determine what makes a condition “sufficiently serious”. This decision is made in each case by the personal standards of judges. The judge may question why the prisoner was placed there; however, the Supreme Court has not made a ruling whether intent should play a part in this evaluation. Courts disagree whether it should matter why the individual was placed in solitary confinement. Also, the Amendment did not answer when a prison condition is punishment or not. The debate remains whether the effect of the conditions on the prisoner or the intent of officials makes them punishment. In court, Eighth Amendment analysis hinges on the motivations of state actors and prison officials it is supposed to act as a check against. The conditions of the Eighth Amendment fail to protect prisoners from inhumane treatment through the scope of prison officials’ intent and judges’ objective analysis.
The ICCPR is international law that prohibits torture or cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment. It later states that people deprived of their liberty shall be treated with humanity and with respect for the inherent dignity of a person and the treatment approach for prisoners should be aimed at efficiently improving their reformation and social rehabilitation.
In 2015, the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Mandela Rules that prohibited restrictions and disciplinary sanctions that could amount to torture or cruel and degrading treatment or punishment, such as Indefinite Solitary Confinement, Prolonged solitary confinement, or to place a prisoner in a dark or constantly lit cell. It defined solitary confinement of prisoners for 22 hours or more a day without meaningful human contact and prolonged solitary confinement for any time period over fifteen days. It states that solitary confinement should only be used as a last case resort for the shortest time possible and given due process to each case. Finally, it paid special attention to protect prisoners with disabilities which may be magnified, and especially vulnerable women and children from solitary confinement.
Through these treaties and agreements, States do not only assume obligations internationally but to their own people as well. Just like our own constitution, these international laws were agreed to and are legally binding to regulate the conduct of states with their citizens. However, without international forces to enforce and regulate these agreements, states may ignore or lose sight of their importance.
Despite these resolutions, Domestic laws are vague so that it is doubtful they meet minimum requirements regarding the ones set by human rights instruments. This creates debate and little guarantees in the legal system. They also undermine fundamental guarantees of due process, are applied randomly, and do not protect the prisoners’ rights.
Today tens of thousands of humans remain alone in concrete boxes in the United States. This report concludes that their conditions are emotionally, physically, and psychologically destructive. They are destructive because it robs us of many things that makes life human and bearable like stimulus through social interaction and interaction with the natural world. Under total control and out of the public eye, people may be subjected to incredible human rights violations. By allowing our government to ignore these people, we are accepting this indifference towards others under its care. By ignoring their human rights, in this way, we diminish our own.