Throughout the pandemic, I have found my social media use rise exponentially. I think it is a way to find human connection, when my primary form of social interaction is with my roommates. Apps like Instagram, Facebook, YouTube, and more recently, TikTok, allow me to check in on my friends and family across the world but they also allow for a version of political discourse to take place. From sharing news articles to posting pictures with informative captions, rallying cries have spread across the internet urging users to participate in social change as much as possible.
One of these rallying cries brought back a centuries old phrase. Jean-Jacques Rousseau said in the context of the French Revolution and its aftermath, “When the people shall have nothing more to eat, they will eat the rich.” This sentiment has returned in 2019 and 2020 in the United States, especially as class divides become even more apparent in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic. The phrase “Eat the Rich!” can be seen in captions, videos, and even as a spoken phrase. Rallies and protests have seen signs with the words “eat the rich” written upon them and cities have heard the ring of those words in the form of chants. It is important to understand that in the 21st century, “Eat the Rich!” is referring to the top 1 percent, the companies, corporations, and government officials who have profited off the suffering of others. This phrase is not geared towards upper middle class families, a common misconception that has created a backlash. Instead, it is geared toward the city of New York for installing new, high tech security measures to ensure payment for the subway and toward huge companies who directly contribute to climate change as we watch an entire state burn. These are just a few examples, but the class resentment is very apparent and perhaps rightly so.
In 2016 and 2019, American families were able to save substantially, according to the Federal Reserve data. Despite that, the wealth inequality did not shift much, and this was all before the onset of the coronavirus pandemic. The facts and figures of the Federal Reserve and the Survey of Consumer Finances of the past few years show a higher median income. Though these depict an improvement, the savings most Americans have do not even compare to the rates of savings before the 2008 recession and the amount of wealth the 1 percent has is nearing a three-decade high. To put this in perspective, in 1989 the top 1 percent held almost 30 percent of the United States wealth. In 2016, this number about 40 percent, and it has not shifted lower since. Stocks and other assets are starkly concentrated within the wealthiest 10 percent of Americans, with the median family within this 10 percent holding about $780,000 worth of stocks. For the bottom 25 percent of Americans, this number barely reaches over $2,000. This comparison disproves the performance of the stock market as a sign of success for Americans in general, a claim President Trump often makes.
This income gap is much starker when racial disparities are taken into account. The median wealth of a black family is less than 15 percent that of a white family’s net worth. For black families, this is $24,100 in comparison to white families’ $188,200 in 2019. The median wealth for Hispanic families reached $36,100. It is becoming increasingly clear that the gap is widening due to black and Hispanic families being disproportionately affected by the coronavirus outbreak. With the impact of coronavirus comes a sharp increase in unemployment for low skill worker and high interaction jobs, jobs primarily offered to Hispanic and black workers due to the rampant discrimination in the American job market.
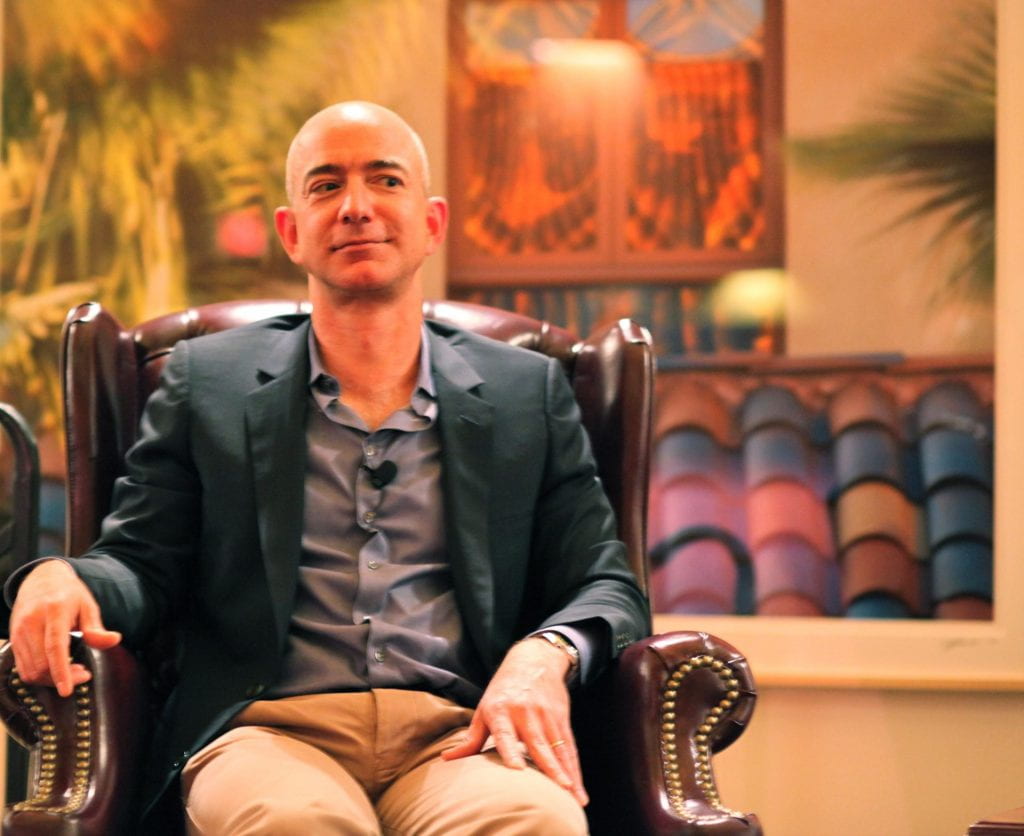

The top of the top 1 percent in the United States is Jeff Bezos, founder and CEO of Amazon. In August of 2020, Bezos became the first person to ever be worth over $200 billion dollars. Without a doubt, he is the world’s richest person at 56 years old. The third richest person in the world, LVMH chair Bernard Arnault, is $90 billion dollars poorer than Jeff Bezos. Amazon is one of world’s wealthiest companies and has profited greatly from the pandemic, much at the expense of its workers. The workers at Amazon have been providing essential supplies in a quick and secure fashion to quarantined individuals all across the world. While Bezos and the company of Amazon profit, these workers feel as if their own health and safety are being exchanged for Bezos’ next billion dollars. Amazon responded to the outbreak with the bear minimum: a temporary increase in wages by $2 an hour and implementing measures like temperature checks. In April, hundreds of Amazon workers protested the way Amazon had been handling the coronavirus outbreak by calling in sick to work. Groups like Amnesty International very quickly issued public responses in support of the workers and demanding Bezos respond to his workers requests. The manipulation and abuse of influence by Jeff Bezos has not been a new phenomenon.
In 2017, Bezos was awarded the National Equality Award by the Human Rights Campaign for his work in support of LGBTQ+ rights. He had pledged over $2 million in 2012 for the fight for same-sex marriage. A year after being honored by this award, Bezos and his wife each wrote checks for $5,400 to Colorado Senator Cory Gardner’s campaign, a Republican senator known for his anti-LGBTQ agenda. $5,400 is the maximum amount of money an individual can give to anyone seeking office, and eight other Amazon representatives followed Bezos example by donating the same amount of money to Gardner’s campaign. While Senator Gardner’s anti-LGBTQ+ sentiments may not be the sole reasoning behind the large Amazon support, it is incredibly hypocritical that in 2017 Bezos graciously accepted a human rights award for his work for the LGBTQ+ community.

In 2018, Amazon employees sent a letter to Bezos requesting that he stop selling the Amazon face surveillance product to law enforcement. They stated that it was a tool used to direct violate human rights. The letter came just a few days after the ACLU and other community partners delivered petition signatures, a coalition letter, and a shareholder letter to Amazon regarding the same subject of the dangers of the face surveillance product.
These are just a few examples of how a member of the top 1 percent is able to push their own agenda and further the widening income inequality gap to line their own pockets. Jeff Bezos is the richest person in the world and is a primary contributor of the income gap in the United States. The rallying cry “Eat the Rich!” is aimed in the direction of Bezos and those like him including Facebook’s Mark Zuckerberg and Walmart’s Walton family. This is not a call to cannibalism but is instead a call to action. The income inequality in America is devastating and tax holes and other mechanisms designed to keep the rich, rich and the poor, poor must be held accountable. The Covid-19 pandemic made the system inequity even more apparent and people are ready to fight to make the United States a more equitable place.