Growing up, I was resentful of the social freedoms my male friends naturally enjoyed. Unlike the parents of my male friends, my parents were very strict about things like curfews, not being outside at night alone, and avoiding certain neighborhoods. My dad would always say, “We trust you, but we don’t trust the people around you”. Although I was still resentful, I know my father enforced those stringent rules because he was trying his best to protect me from gender based violence (GBV). GBV is defined as violence towards an individual that is motivated based on his or her gender identity, biological gender, “or perceived adherence to socially defined norms of masculinity and femininity”. The term ‘violence’ encompasses physical, sexual, and psychological abuse along with coercion, threats and compromised liberty. Examples of GBV include sexual violence like rape, domestic violence, and human trafficking. Both men and women are affected by GBV; however it is recognized women and girls are at most risk for exposure due to the imbalanced power relations between men and women “which have led to domination over and discrimination against women by men … and that violence against women is one of the crucial social mechanisms by which women are forced into a subordinate position compared with men.”
Violence against women and girls is a prevalent human rights violation resulting in disproportionate negative consequences on females’ physical, mental and sexual and reproductive wellbeing including but limited to including, but not limited to: “i) fatal outcomes; ii) acute and chronic physical injuries and disabilities, iii) serious mental health problems and behavioral deviations increasing the risk of subsequent victimization and iv) gynecological disorders, unwanted pregnancies, obstetric complications and HIV/AIDS .”

Some troubling statistics on GBV:
- In 2014, a UNICEF study projected that ~120 million girls (almost 1 in 10) under the age of 20 have been forced to perform sexual intercourse or other sexual acts during some point of their lives.
- Almost half of the women killed in 2012 were murdered by a family member or intimate partner.
- Globally, the WHO estimates 35% of women worldwide have experienced either physical and/or sexual intimate partner or non-partner violence or sexual violence. Other national studies have estimated up to 70% of women experience GBV.
- “Women and girls together account for 71 per cent, with girls representing nearly three out of every four child trafficking victims. Nearly three out of every four trafficked women and girls are trafficked for the purpose of sexual exploitation.”
Although a pressing issue, it wasn’t until 1992 when the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW) formally adopted General Recommendation No. 19: Violence against Women (GR 19), which legally categorized violence against women a distinct form of discrimination. Likewise, it wasn’t until 1993 the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Declaration on the Elimination of Violence against Women (DEVAW), forming the first ever internationally-recognized definition of GBV. Both documents explicitly outline how GBV violates basic human rights mentioned throughout the UDHR such as the right to life, dignity, and health.
Health Effects of Exposure to GBV
Sexual and Reproductive Health
GBV is a major public health concern contributing to mass amounts of mortality and morbidity. Specifically, the relationship between GBV and HIV and other STIs has been recognized as an important pathway for the contraction and spread of such diseases. WHO states that, in some regions, women facing sexual partner violence are 1.5x more likely to contract HIV, and 1.6x more likely to contract syphilis. Here’s how:
First, increased vulnerability to HIV and STI’s stems from sexual violence such as rape. “Violence reduces victims’ abilities to influence the timing and circumstances of sex, resulting in more unwanted sex and less condom use, including situations where women are coerced or pressured not to use condoms.” For example, of the estimated minimum 250,000 women brutally raped during the Rwanda Genocide, 70% of those survivors tragically acquired HIV.
Second, another important pathway from GBV to HIV is men who are physically violent are also more likely to be HIV positive. Studies find violent men are more likely to engage in risky sexual behavior such as having multiple sex partners and utilizing transactional sex, increasing their chances of contracting and spreading HIV and other STIs.
Along with the spread of disease, women and girls experience unwanted pregnancies due to GBV. The WHO states that women with previous exposure to GBV are more likely to account having had a self-induced abortion. Globally, “80 million unintended pregnancies each year, at least half are terminated through induced abortion and nearly half of those take place in unsafe conditions.” A study analyzing the relationship between GBV and sexual and reproductive health among low-income youth in three Brazilian cities, supports WHO’s statement that women in abusive relationships are more likely to experience unwanted pregnancies. The study found adolescent females who became pregnant as teenagers were more likely to have been victims of controlling behavior or physical abuse compared to teenage girls whom have never gotten pregnant. Among the girls who got pregnant as a teenager during the study, “20% reported having suffered physical violence from a partner and 10% reported having been subjected to sexual violence from a partner, compared to 5% and 3% respectively of those who did not get pregnant as teenagers.”
Mental Health:
Along with physical harm, studies highlight women and children face serious mental health problems after enduring traumatic experiences with GBV. “Exposures to traumatic events can lead to stress, fear and isolation, which, in turn, may lead to depression and suicidal behavior.” According to the WHO, women abused by a non-partner are 2.3 times more likely to have alcohol use disorders and 2.6 times more likely to have depression or anxiety. A cross-sectional study based on the Australian National Mental Health and Well-being Survey in 2007 found that of the 4,451 female respondents, 1,218 (27.45%) of the women have experienced one of the four types of GBV analyzed in the study (IPV, stalking, sexual assault, and rape). Of the 139 women who experienced at least three types of GBV, the rates for mental disorders were 77.3% for anxiety disorders, 47.1% for substance abuse disorders, 34.7% for attempted suicide, and 56.2% for PTSD.

Potential Solutions to Address Gender-Based Violence
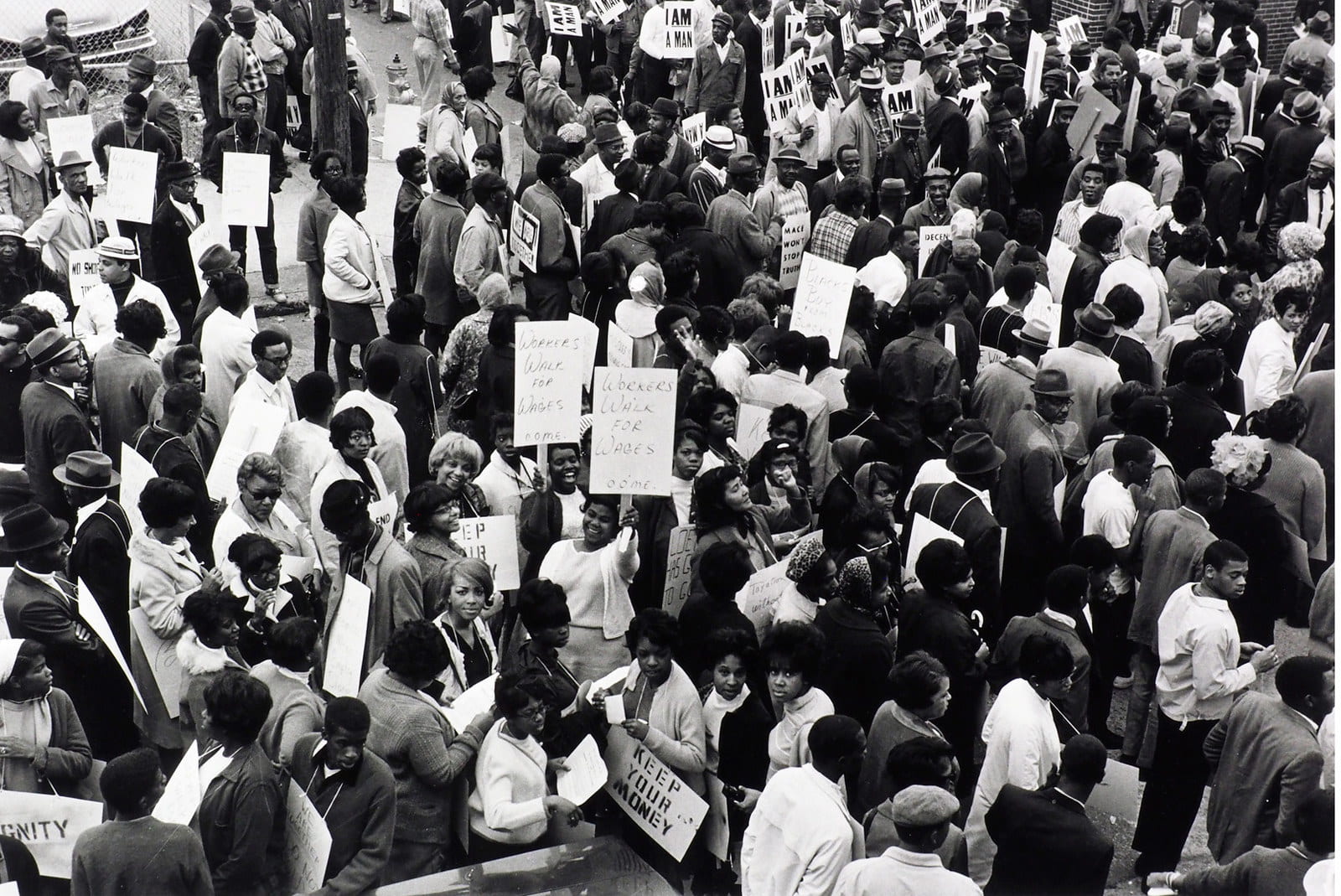
In light in of April being sexual assault awareness month, itself a form of GBV, it is essential to break through the culture of silence. Our health care system can be more active is addressing the prevention of GBV, and also the aftermath of GBV. First, providing survivors with mental health services such as counseling is critical for these women and girls to address their psychological trauma and progress with their lives. Mental health services are vital in providing survivors a voice to express themselves. Second, our health care system could potentially be a major stakeholder in identifying and stopping GBV.
“GBV is very common, but most health care providers fail to diagnose and register GBV, not only due to socio-cultural and traditional barriers, lack of time, resources and inadequate physical facilities; but even more so due to lack of awareness, knowledge and poor clinical practices with limited direct communication and failure to do a full physical examination, not to mention register and monitor the effectiveness and quality of care.”
Moving forward, there needs to be a systematic change within in the health sector. The World Bank, amongst other NGO’s, have provided approaches on how to address this issue. Some strategies to consider include, but of course not limited to:
1) Requiring GBV screenings during doctor visits to ensure early intervention
2) Train and educate health care personal about GBV to improve provider’s knowledge, medical services and attitudes towards GBV.
3) Providing survivors access to adequate infrastructure within hospitals which includes private counseling and examination rooms.
Women are approximately 50% of our global population, yet gender-based violence is one of the most prevalent and widespread human rights violations. Gender equity is an inalienable right protected in numerous human rights documents, however change will never be achievable until we break this vicious cycle of violence through education and strict policy changes. Ultimately, women have proven they are just as equally capable as men, and gender-based violence and discrimination over an uncontrollable biological factor is simply unjust.