February is Black History Month. For the next few posts, I will review books by Black women who provide insight into the Black experience.

Zora Neale Hurston (ZNH) was a cultural anthropologist. With her very being, Hurston occupied a space of protest of the normative within the field of anthropology as she traversed through society and academia as a Black woman from the South. The intersectionality of her life may remain lost on some; however, it is essential to understanding her as an ethnographer, folklorist, and local colorist. She studied under Franz Boas alongside Ruth Benedict and Margaret Mead, but there is often an exclusion of her work. When listing the cohort of the generations of anthropologists or ethnographers, ZNH is often not among those listed, as the categories for her work are The Harlem Renaissance, folklore, or African American literature. To Boas, ZNH was an anthropologist who, through the application of anthropological methods and techniques, gave insight into Black life in a way no White person could do. In this way, she achieves “racial vindication” and qualitative results through the application of anthropological methods like observation and participation, unstructured interviews, and ethnographic data collection.
Barracoon is the oral history of Cudjo Lewis—or Oluale Kossola–the only living African “cargo” of the slave ship, Clotilda. Kossola was not born into enslavement. He was sold and captured from Dahomey (presently Benin) and brought to Mobile Bay in Alabama. His testimony offers a completely new perspective and firsthand account of colonization. Hurston first reveals insight into her reflexive research on Kossola’s life and story in her autobiography, Dust Tracks on a Road. “One thing impressed me strongly…The white people had held my people in slavery here in America. But the inescapable fact that stuck in my craw, was: my people had sold me and the white people bought me. That did away with the folklore I had been brought up on. It was a sobering thought” (164-8). Employing her trademark of writing phonetically, ZNH allows Kossola to tell his story in his language and style, rarely interrupting his stream of consciousness. This methodology would later become known as emic ethnography. Spending three months in one-on-one interviews solely with Kossola, a Yoruba by birth and a resident of Affriky town, she learns about his life in Africa, his survival of the Middle Passage and enslavement, and his life as a ‘free’ man.
Oluale Kossola was a man to many, but to others, he was an exploit of their contrabanded flesh: “’the black ivory,’ ‘the coin of Africa,’ had no market value.” He and the other enslaved were “Africa’s ambassadors to the New World,” sold as “brisk trade” by the King of Dahomey (5-9). Although she refers to him by his American name, Cudjo, throughout the book, ZNH makes a point to state that upon her initial reunification with him, “I hailed him by his African name as I walked up to the steps of his porch.” As his eyes filled with joyful tears, he exclaimed,
“Oh Lor’, I know it you call my name. Nobody don’t callee me my name from cross de water but you. You always callee me Kossula, jus’ lak I in de Affica soil” (17).
By the time ZNH sits down with Cudjo, he is the only one left and finds himself surprised and moved that someone would want to learn about his life. Hurston writes that she told him that she wanted to know all about him, to which he responded:
“Thankee Jesus! Somebody come ast about Cudjo! I want tellee somebody who I is, so maybe dey go in the Afficky soil some day and callee my name and somebody dere say, ‘Yeah, I know Kossula.’ I want you everywhere you go to tell everybody whut Cudjo say, and how come I in Americky soil since de 1859 and never see my people no mo’. I can’t talkee plain, you unnerstand me, but I calls it word by word for you so it won’t be too crooked for you. My name, is not Cudjo Lewis. It Kossula. When I gittee in Americky soil, Mr. Jim Meaher he try callee my name, but it too long, you unnerstand me, so I say, ‘Well, I yo’ property?’ He say, ‘Yeah.’ Den I say, ‘You callee me Cudjo. Dat do.’ But in Affricky soil my mama she name me Kossula” (19-20).
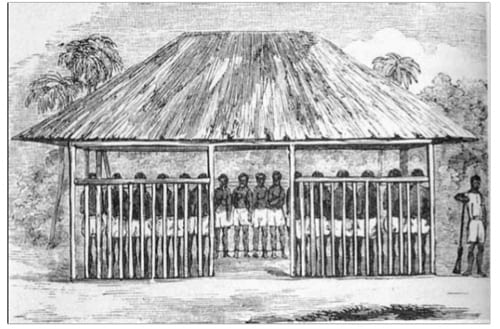
Kossola’s narrative differs from the account of Olaudah Equiano and the former slave narratives of Frederick Douglass, Harriet Jacobs, and Booker T. Washington. Additionally, it is unlike the ethnographic work of Eatonville, Florida as written about in Mules and Men and her most famous novel, Their Eyes Were Watching God. Scholars Natalie S. Robertson and Sylviane A. Diouf provide extensive supportive evidence about the 1927-28 anthropological research of ZNH, the Clotilda and the establishment of Africa town in Alabama in their respective books, The Slave Ship Clotilda and the Making of AfricaTown, USA and Dreams of Africa in Alabama. Although both books preceded Barracoon’s 2018 publication, they build upon the foundation laid and the way paved for by ZNH, even mentioning current residents of Africatown who met her during the visit. Robertson accurately identifies Kossula as a griot or native African storyteller, trusted to keep and share the stories of tribes over generations. There is “genius that is contained in oral tradition as chroniclers of phenomena and as vehicles for education in Africa…without dependency on written records. Because Cudjo hailed from West Africans who are masters of the spoken word, it was not difficult for him, even as a nonagenarian, to recall the circumstances that led to his capture and forced migration to Alabama” (9). As Diouf points out, slave and former slave narratives reveal what life was like during and after enslavement but the narrative of Clotilda survivors like Kossola “represents a unique group of people who grew up free, spent the majority of their years in bondage during the Civil War, and soon became free again.” Their perspectives also reveal the parts of African culture that adapted, sustained them and continued to unify them (4).
In her signature way, ZNH accomplishes several things with this book. First, she continually restores the humanity that enslavement and separation from Africa stripped away. With the one action of calling him by his African name, she imparted both his personal and cultural identity. By transcribing his narrative in his dialect, she maintains his character and dignity. Second, she allows Kossula to tell his story. Oral history and narrations are cultural and personal heritage. Kossula was the last survivor of the Clotilda; therefore, if ZNH had not traveled to Africatown when she did, this one-of-a-kind perspective might not have been told. Third, she does not gloss over or shy away from the brutality of colonization and the dehumanization that comes with the financial trading of human beings and comes to identify with him. As echoed in Dust Tracks, “Truth is a letter from courage” (31). Regardless of her role as an anthropologist and observer, she finds herself drawn in and experiencing his pain, tragedy, and joy. It is for these reasons that Boas concluded that the work of ZNH contributed to the “knowledge of the true inner life of the Negro” because she was not only a student of history but could “enter into the homely life of the southern Negro as one of them and was fully accepted” (xiii-xiv).
Hurston could have selected any group of people to study, anywhere in the U.S. or world, yet, she chose to return home and study the people she knew and the town she loved. In doing this, ZNH gave value and voice to the “inferior”—people who shared the same skin color and occupied the same category of within the social construction. She reflexively offers a distinct perspective on Blackness because she was Black and studied Black people to know herself more and to debunk the myths and stereotypes about who Black people were, how they arrived here, how they live and continue to live.
Additional resources include African American Pioneers in Anthropology and The History of White People