by PAULETTE PATTERSON DILWORTH, Ph.D.

As I reflect on my experiences coming of age in the segregated south, I am reminded of my family and others in my community who dared to ‘live out loud’ during an era when Jim Crow was a defining feature that framed social and political interactions between Black and White people. For me, the time span is not a distant memory that happened long ago. It is a historical period that inspired the need for social change. A “watershed moment” is a point in time that provides significant space for clarity, and is often related to historical change. Since August 11th, I have engaged with colleagues and friends in thoughtful conversations about our own experiences after witnessing Charlottesville and placing the events in historical perspective. I was born in Selma, Alabama and raised in the very close knit “Summerfield” community. I came of age in Selma at the height of the 1960s Civil Rights Movement. I was most privileged to have a front row seat to many of the events, as they unfolded and eventually culminated in “Bloody Sunday” and the historic Selma to Montgomery March. Like many of the children, teenagers, and young adults who lived in my community at that time, I attended segregated public schools. As students, we were eager to get involved in the mass meetings and marches because we could sense the winds of change blowing in Selma. The opportunity to exercise the right to vote was a lifelong dream held by many adults in my family and the community. During the 1960s, the Civil Rights Movement was the most exciting expression of political activism in which my generation could engage. As historian Joyce Ladner said when she coined the term, the ‘Emmett Till generation,’ “there was no more exciting time to have been born than at the time, and the place, and to the parents that movement, a young movement of people were born to.” Today, the nonviolent activism and protest of the 1960s are a stark contrast to the protests that occurred in Charlottesville that is rooted in a movement predicated on hatred, racism, and white supremacy. Today, Charlottesville awakens a new clarion call that insists we revisit the propositions offered by Dr. King in 1964 when he responded to pressing social justice concerns in Why We Can’t Wait.
On August 11, 2017, white supremacists showed up in Charlottesville, Virginia for a “Unite the Right” call to action or a coming-out party for the white nationalist movement. The march was organized to protest the removal of a statue of Confederate general Robert E. Lee from a park in Charlottesville. At some point, the gathering of protestors and counter-protestors turned violent, and in the aftermath, three people died. Following one of the most contested elections in recent memory, it is safe to say that many of us are quite alarmed by the abundance of racial bias and hate on display in Charlottesville and elsewhere in the United States seen on our college campuses and in our communities across the country. Many of the hard-won gains for social justice, equity, and inclusion are under threat. Observers of the events that unfolded in Charlottesville continue to express shock and dismay to have witnessed such public display of hate and violence in a 21st century United States. The changing social climates and divided political landscapes reveal the character of a nation that continues to grapple with profound division and conflicts between groups that exist in our history and our present. Scholars who study social change and social movements agree that such events usually evolve from strained “relationships between those who have power and those who do not.” To some extent, these movements arise when groups in society feel discontented about some element or perceived injustice in their lives. What happened in Charlottesville is a 21st-century reminder that old wounds can reopen to allow the pervasive nature of racism and injustice to ooze to the surface.
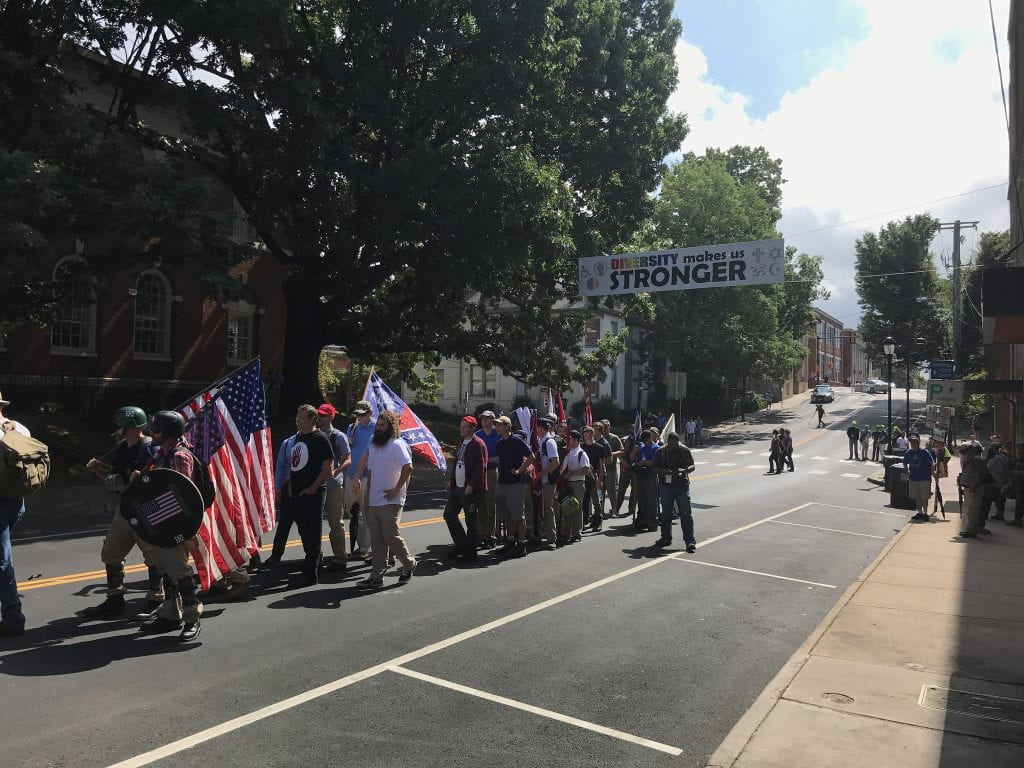

In the summer of 1963, after the conclusion of the Birmingham campaign for civil rights and the March on Washington for jobs and freedom, Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. further developed the ideas introduced in his iconic “Letter from a Birmingham Jail” in a book entitled Why We Can’t Wait. Dr. King tells the story of African American activism in the spring and summer of 1963. During this time, Birmingham, Alabama, was perhaps the most racially segregated city in the United States, but the campaign launched by Dr. King, Reverend Fred Shuttlesworth, and others demonstrated to the world the power of nonviolent direct action. The time span is not a distant memory that happened long ago. This year marks the 54th anniversary of the 1963 March on Washington.
It is a curious parallel that in 1964, Dr. King published Why We Can’t Wait as a call to action and an excellent political commentary on the fight for racial justice and equality in Birmingham and throughout the American South. Why We Can’t Wait begins with Dr. King’s “Letter from a Birmingham Jail” that he wrote while being held there. Dr. King wrote the letter in response to a public statement of caution offered by eight white religious leaders in the Birmingham community. Several quotes from Dr. King’s letter are now popular iconic sound bites that are used to frame social justice messages of hope and aspiration. For example, “Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere. We are caught in an inescapable network of mutuality, tied in a single garment of destiny” is a reminder of the relevance of Why We Can’t Wait. Although African Americans continue to bear the burdens of racism, King makes it clear that all Americans regardless of their race are affected and suffer when injustice is allowed to prevail.
The central proposition of the book is concerned with nonviolent resistance as a protest strategy that was used successfully to push the civil rights movement into the hearts and spirits of white allies. Dr. King was unapologetic in his demands for racial and economic justice, and he understood well the political implications of his role in the 1963 Birmingham Campaign. He explains what he calls the “Negro Revolution” and how it spawned quietly before bursting onto the national scene in 1963, and was “destined to grow in strength and numbers because three hundred years of mistreatment cannot be expected to find a voice in a whisper.” Why We Can’t Wait is useful for activists, educators, discussions, teachers, and researchers that grapple with the issues of social justice and injustice. It is also a useful text that encourages the reader to think intensely about what it means to pursue nonviolence in words and action. Although the book was published in 1964, it is quite easy to identify relevant narratives that align with today’s social justice movements. Further, Why We Can’t Wait introduces the reader to ideas that offer a compelling rationale for thinking through how to effect utilitarian social change. For example, in the section titled “Why 1963?” Dr. King invites the reader to explore the explanation he offered as to why 1963 was the year the southern freedom struggle gained momentum and eventually emerged on the national stage. In his analysis, Dr. King offered several plausible examples as to why 1963 was a “tipping point” that elevated the movement. Primarily, he outlined seven areas of influence:
- the southern resistance to school integration after Brown vs. Board of Education,
• a crisis of confidence in government after the failure of President Kennedy’s administration to deliver on the civil rights bill,
• the southern apathy and lack of support for African American voting rights,
• the growing anti-colonization movement in Africa and the psychological implications on racially oppressed African Americans,
• the 100th anniversary of the Emancipation Proclamation that clarified for African Americans just how far they still had to travel,
• the ongoing and persistent poverty in the African American community,
• and the rise of nonviolent direct action both in the United States and abroad as a viable means for social change.

In later sections of Why We Can’t Wait, Dr. King explains how direct action creates tension and exposes crisis in a community, thus, forcing the community to confront and negotiate the issue. As a political protest strategy, nonviolent direct action aims to create such a crisis and foster such a tension that community has to engage and respond. As noted in his “Letter from A Birmingham Jail,” Dr. King and his supporters had received much criticism for their efforts, with some critics claiming that the civil rights activists expected too much, too soon. In contrast, more militant activists argued that they asked for too little. At the same time, the civil rights legislation stalled in Congress. Although Why We Can’t Wait, should be viewed in historical context, Dr. King’s use of the past and ethical arguments to justify the Civil Rights Movement is timeless. Moreover, readers will gain richer insights into Dr. King’s development of the concept of nonviolent resistance and its necessity in combatting social injustice.
In the conclusion of Why We Can’t Wait, Dr. King ends the text by explaining that African Americans cannot afford to continue the slow movement toward freedom and justice. He states that they must demand and insist on it. Further, Dr. King advances the idea that poor whites and organized labor should consider joining the civil rights movement. He also calls for unity among all oppressed people in America, calling for a stronger relationship with Native Americans and clarifying that he believes the summer of 1963 made most white Americans receptive to his ideas. Dr. King expressed hope that if the civil rights movement was successful, it had the potential to expand non-violence worldwide and end the nuclear arms race. In the decades following Dr. King’s untimely death, his words have been used by future leaders across the globe, including President Barack Obama, to make the case that we can’t wait to take action. Before his assassination in 1968, Dr. King authored six books focusing on his nonviolent philosophy and call to political action for social justice. Why We Can’t Wait remains one of the most relevant political commentaries of the 21st century to elevate African-American voices in U.S. history.
As previously mentioned, this year, August 28th marks the 54th anniversary of the March on Washington. The March ended the Birmingham summer of 1963 that was filled with protests and organizations that lead to the Civil Rights Act of 1964. Now more than ever, we need to pause and gather as a community to connect, share histories and strategies, and prepare for the difficult social, political and economic challenges that lay ahead. The “fierce urgency of now” is upon us like a rising tide and Why We Can’t Wait is as relevant today as it was in 1964. After a careful reading of Dr. King’s work, a new and more thoughtful generation of human rights and social justice advocates will likely come away with a new and more critical perspective on a period in U.S. history that has often been reduced to iconic trivia. The summer of 1963 is not a sad portion of our history; it is very hopeful. However, the fact that Charlottesville happened in the summer of 2017 is a sad commentary on where we are at this particular time in U.S. history. Yes, it would be an extraordinary thing if all people of goodwill realized they do not have to wait to be invited to get involved and work for positive social change. The changing political climates and divided social landscapes insist that we work together to address the crisis of our democratic enterprise. That perspective has been helpful to me. I find a lot of comfort in that, as well as a lot of challenges and opportunities to make a difference.
Paulette Patterson Dilworth, Ph.D. is Vice President for Diversity, Equity and Inclusion and Chief Diversity Officer at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. Besides a strong affinity for art and music, Dr. Dilworth has accumulated more than 30 years of experience in higher education, diversity education consulting and training, recruitment, retention, research, teaching and outreach. Dr. Dilworth has devoted her professional career and much of her personal life to social justice and advocacy exploring issues of access, civic engagement, equity and community building.