In the last blog, we covered the contextual history of the American Education System, primarily, who was allowed education, who was not, and even the differences in the quality of education that children in America received. We also explored the historical treatment of people with disabilities, both in the larger society, as well as in children with disabilities within the school system. Understanding the past is crucial to analyzing why certain events occur as they do in the future. That is what we set out to do in this continuation of the conversation about disabilities and the American education system. In this second part, we will focus on the realities children with disabilities witness within the education system, including the challenges they face, the school-to-prison pipeline that exists, and how this impacts their development (both mentally and physically). We will then explore how the recent pandemic exacerbated these conditions, and what sort of rights the children possess in this post-pandemic world.
Children with Disabilities in the Education System Today

The many challenges faced by students with disabilities in the classroom
Children with disabilities today face many challenges within the classroom even without taking the pandemic into account. These challenges vary from physical barriers to socio-emotional ones. One thing that needs to be recognized is that not all disabilities are alike, and with various disabilities come various challenges. I don’t want to appear to be generalizing the struggles that children with disabilities face in the school system, because each individual’s experiences vary, even between different places. Some states within the United States may be very inclusive, while others may place the responsibility of accessibility on the people with disabilities themselves. Regardless of which state you live in, my goal here is to spread awareness of the various challenges that children with one or multiple disabilities face as they maneuver through their primary academic journey.
With that being said, one of the most common barriers that children with disabilities face is on the social level. Throughout history, children with disabilities have been separated from the rest of the able-bodied society, and this is also true within the school system. Many schools, when they began to accept children with disabilities into the school system, would educate them separately (in the basement or another room) from the other children. Even today, many children with learning and speech disabilities require additional help from trained professionals, which requires these children to spend extra time on their academics, and less time socializing with their peers. This naturally distances them from able-bodied children their age and can lead children with disabilities to become victims of many instances of bullying and harassment. A crucial element to consider is that while many children their age are dealing with the various emotions that come from development, children with disabilities have to deal with additional fears and insecurities surrounding their disabilities, as they learn to accept and adapt to life with disabilities. This can be challenging in and of itself, without having to deal with the social pressures from peers.
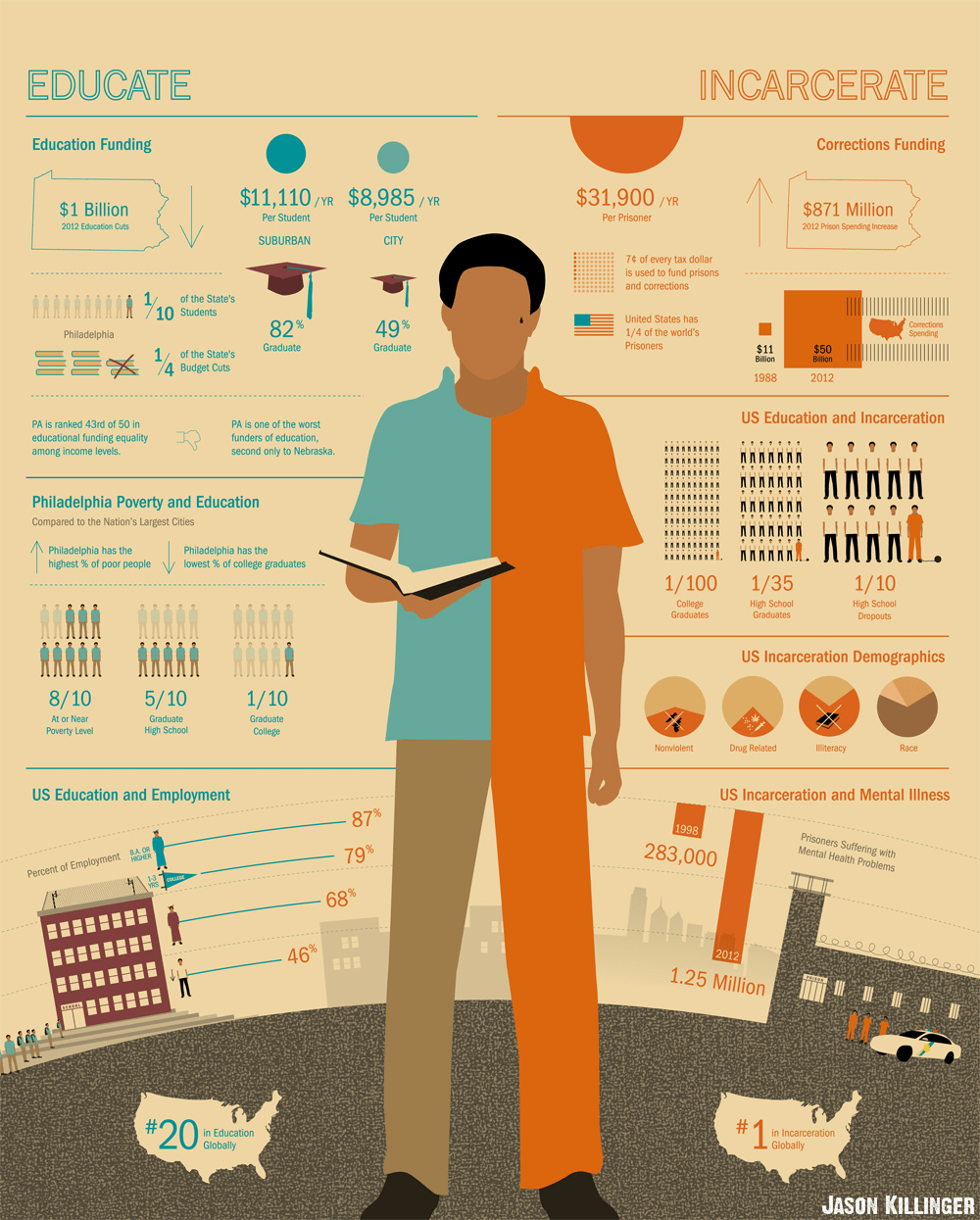
Additionally, while schools receive federal funding to meet the required measures for the children with disabilities within their institutions, this funding is limited, covering less than a quarter of the expenses needed to fulfill the required services for each student. The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) we covered in the previous blog allows Congress to allocate up to 40% of the average funding per student, but unfortunately, this has never been exercised by Congress, and funding for special education programs continues to be miserly. Schools receive 15% of the funding they are allocated, but they are still required to fulfill all the mandated regulations simply for receiving federal funding. This means that they have to come up with the remaining 85% of the expenditures on their own, in place of the 55% they would be responsible for covering if Congress secured the full 40%. This can place additional strains on these schools that are already struggling for funds.
Furthermore, children with learning disabilities require trained professionals to provide them with additional support throughout their academic journey. Someone who is hearing impaired may require additional resources to combat the auditory issues they face, or someone who is visually impaired may require additional lessons on how to read in Braille. Others with learning disabilities such as dyslexia (which is a disorder in which someone has difficulty reading and processing language), may need additional patience and support to process the information they are learning. Public schools, by law, are required to provide assistance to children with disabilities and those who have been through traumatic experiences. Licensed professionals that focus on educational needs for children with learning disabilities can be hard to find, and this has only worsened due to the pandemic. As many as 44 states experienced this shortage even before the pandemic, and this number continues to grow due to the issues of limited funding discussed earlier. Without the necessary help that students with learning disabilities require, they continue to fall behind their peers academically.
Many of these challenges can be addressed with more funding allotted to the education system as a whole, and professions within the field of special education can be incentivized by the government (by for example, making the training programs free and accessible to those who are interested) to address the shortage of licensed professionals. The education being taught in the schools can be more inclusive of children with disabilities, with opportunities for the children to share their experiences with their peers and help remove the stigma associated with disabilities by normalizing helpful conversations around disabilities. While these challenges can have a great impact on the learning abilities of children with disabilities, there are some challenges that can have drastic impacts on their futures as a whole.
The school-to-prison pipeline

Unfortunately, along with an increase in school shootings within the educational system, another phenomenon that has become all too common is the use of law enforcement to discipline children. More and more stories have been reported regarding children with disabilities and children of color being subjected to drastic disciplinary measures by school systems. When a child “acts out” or showcases any behavior not supported by the schools, the educators have resorted to involving the law instead of following disciplinary protocols within the schools (such as contacting parents, placing students in detention, or for more serious issues, using suspensions). Police are called on these students, and educators watch as young children are punished for their misdeeds by being harassed by the police. In many instances, these incidents have turned deadly, as police officers have used full force on young children, to force them into complying, at times jeopardizing the children’s well-being. Children as young as 7 years of age have been placed in handcuffs and threatened jail time, for childish behavior such as spitting or throwing tantrums. This can be especially dangerous when children with disabilities are involved because they are accused of “misbehaving” when they are simply reacting differently to situations than their able-bodied peers. The police, with little to no training on the different ways to approach people with disabilities, only escalate the already tense situations.
According to a CBS News analysis of data from the Education Department in 2017-2018, children with disabilities are four times more likely to be arrested than their able-bodied counterparts. Another research conducted by Cornell University reports that 55% of Black men with disabilities have been detained before they reach the age of 28. Young African American children with disabilities, therefore, are the most at-risk demographic to face legal repercussions for “behavioral” issues common among most children their age. This phenomenon, known as the school-to-prison pipeline, which disproportionately targets students of color, (and children with disabilities), involves the use of the criminal and justice systems as a tool to discipline children. Unfortunately, these disciplinary attempts remain on the permanent records of the targeted children and can have lifelong implications that determine their future.
An example of this school-to-prison pipeline is clear when looking into some of the instances where law enforcement is used to discipline children. Jacksonville, Illinois is home to a particular school that makes use of its law enforcement officers for behavioral issues. Garrison School, a public school where children with disabilities in that region attend, has been in the news recently for the staggering number of arrests made within a single school year. Although the population of this school is an average of 60-70 children, the police, who are located less than 5 miles from the school, have been called over 100 times for “behavioral” issues, such as throwing tantrums and spraying water. An investigation into this school found that in the school year 2017-2018 alone, more than half of the entire student body was arrested. As the only public school for children with disabilities in that region of Illinois, caregivers are limited in choices of schools for their children. In addition to having disabilities, the children at this particular school have also experienced immense trauma and violence in their past. Arresting these children for their “behaviors” continues to place these children in traumatic situations, further impacting their development.
Impacts on children with disabilities’ development
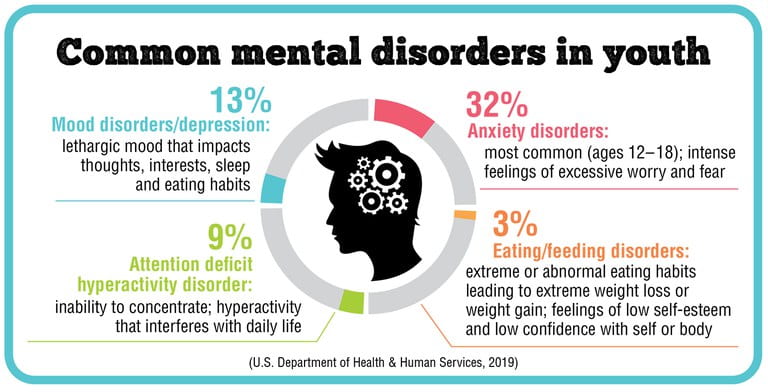
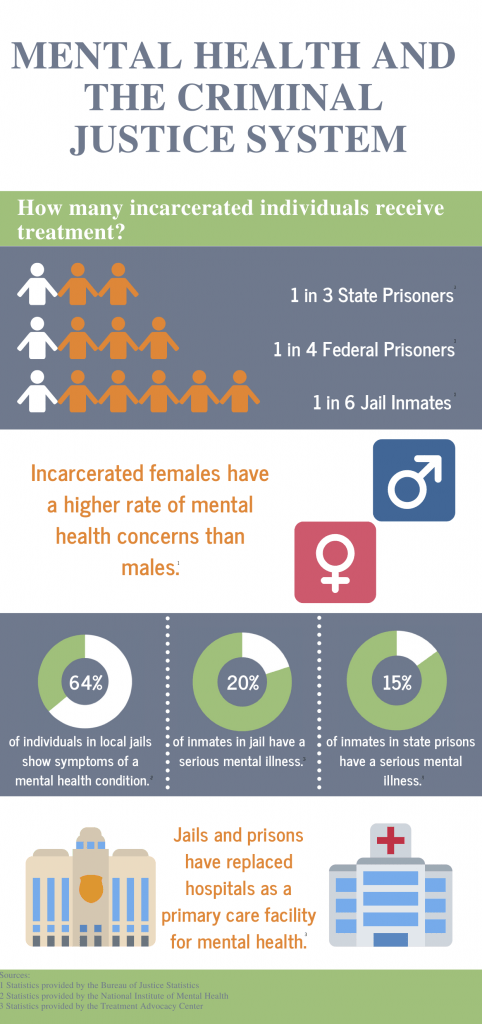
Using the criminal and justice systems to punish or “discipline” children with disabilities can have lasting impressions on the children’s futures. For one, especially children such as those from Garrison School, who deal with personal trauma and violence from their past, experiences with law enforcement can deteriorate their mental health even further. Even those without previous trauma can have lasting impressions on their academic success, meaning that children who have been disciplined with the use of law enforcement are even more isolated from their peers and can experience breaks in their educational journeys. Studies have shown that children who have their needs met are more likely to outperform those students who do not have their needs met. Linking back to the school-to-prison pipeline, those students who have been arrested and imprisoned as young adults are more likely to continue down this path of criminality. Additionally, students with disabilities that have been imprisoned have to face the added struggles of maneuvering the prison system with disabilities, and these struggles are increased with multiple disabilities, especially with invisible disabilities, in which case, many people may not even believe the existence of these disabilities. Studies have shown how incarceration can worsen issues of mental illness within the prison population, and when translated to the impact imprisonment has on people with disabilities, these conditions are exponentially worse.
How it impacts children with disabilities’ professional futures
In addition to the harm this causes to the development of children with disabilities, the practice of using law enforcement to discipline school children has far-reaching consequences. For one, the children who are constantly “othered,” bullied, or harassed by both students and teachers can internalize their experiences and react to them, increasing their chances of being disciplined again for behavioral issues. In addition to that, being imprisoned, even for a few days, can be a traumatic experience that can shape your worldview, and as a result, your future. For young, developing children, these experiences can be impressionable, and coupled with the isolation that many children with disabilities experience, this can be a devastating combination, resulting in the deterioration of the children’s physical and mental well-being. Furthermore, many of these zero-tolerance policies that end in the arrests of children happen due to the faculty members pressing charges against the children. These charges, though they can be sealed for juvenile offenses, can lead to more charges in these children’s future into their adulthood. A criminal history into your adulthood can result in slim educational and employment options. Research conducted more broadly on this subject has been reported by the Prison Policy, and it showcases how increasingly difficult it is to find decent employment upon exiting the prison system. The report adds that even when formerly incarcerated people do find employment, they are often paid fewer wages than their co-workers.
Applying this research to children with disabilities who are disciplined through the legal system, can be an even bigger challenge for their futures. People with disabilities experience many barriers to obtaining employment even without imprisonment on their records. Studies have shown how incarcerating children does not deter them from engaging in criminal behavior in the future; it might actually have the opposite impact. Finally, children who are incarcerated experience large gaps in their education, and this can impact their ability to successfully enter the job market. This issue is exponentially worse among children with disabilities because they are more likely to be imprisoned for “behavioral issues”, and expands the academic gap felt by so many children with learning disabilities who are already facing many social and learning barriers.
How did COVID make things worse for children with disabilities?

The pandemic was a time of uncertainty, and many of us were scrambling around not knowing what to do. Even as more and more information came out about the virus itself and how to safeguard it, there was a lot of anxiety and misinformation being spread around. Children with disabilities had to navigate not only their personal lives with their unique experiences but also the larger society that was falling apart around them in the face of a virus. Many businesses and schools shut down in the beginning, which meant that children had to adjust to different learning styles, something that may have been easier for some, but widened the academic gap for others. Children with disabilities as a whole had to be mindful of the threat that the virus posed on their lives. This virus was especially deadly to those with pre-existing conditions and for those who were immunocompromised, both of which apply to many children and adults with disabilities. So, constantly having to live with the anxiety of whether or not they might contract the virus would have been stressful enough without the masking and vaccine debates that have politicized this medical crisis. What is worse, COVID-19 vaccines for children were not available for over a year after the pandemic first began, leaving this population vulnerable to infections with no way to protect themselves against them.
Additionally, along with their children, parents, and caregivers of children with disabilities faced new challenges as everyone attempted to adapt to the “new normal”. While the mandated quarantine helped with transportation issues for some, it opened up a whole new set of issues for many. Children with learning disabilities who received additional help from professionals either had to go without it or transition to seeking their help through zoom. For some, accessing help through Zoom and Telehealth was extremely helpful in addressing the medical needs of people, and this had a positive impact on people with disabilities as a whole. However, accessing Zoom and Telehealth was a challenge on its own for many who lived in rural areas or marginalized areas where internet services were very minimal or nonexistent, or simply unaffordable. The pandemic was a time when many people also lost jobs, so children faced additional financial repercussions from the pandemic. These instances further widened the academic gap among children with disabilities.
This blog mainly focused on the struggles that children face within the American school system. Part three of this series will focus on some of the approaches that have been taken historically when addressing disabilities, and some ways in which we can take action, on a personal level, on a local or national level, and even on an international level.