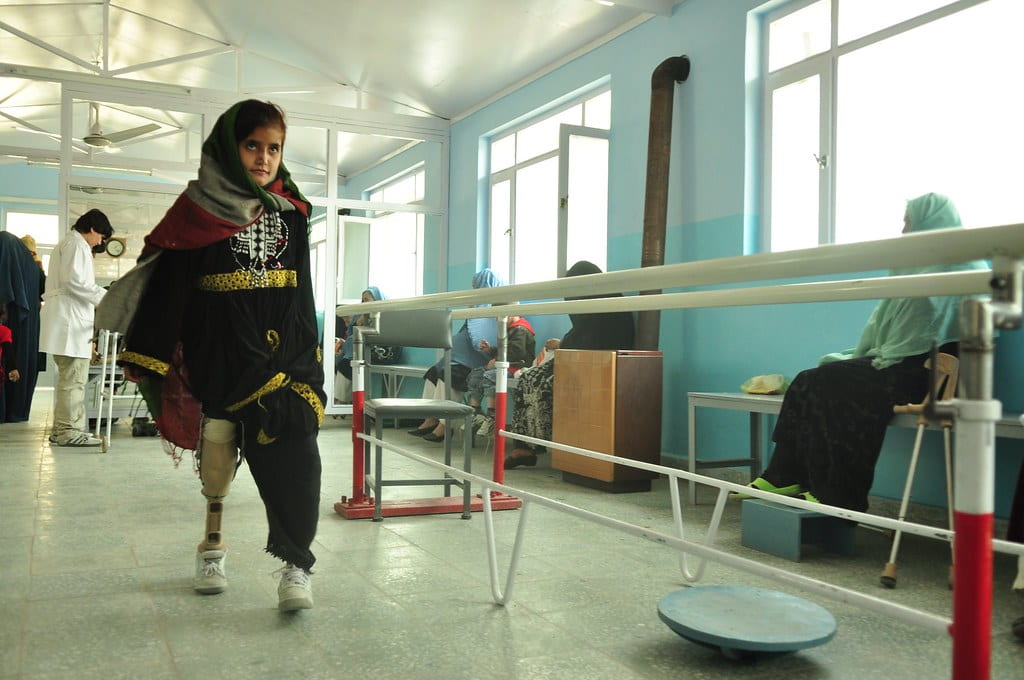
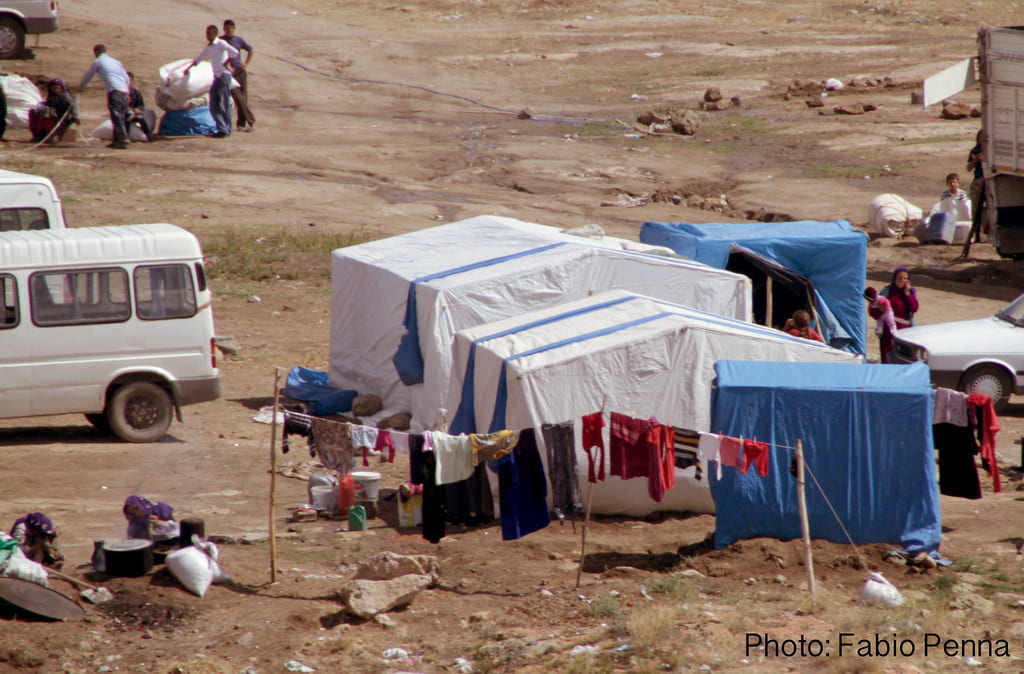
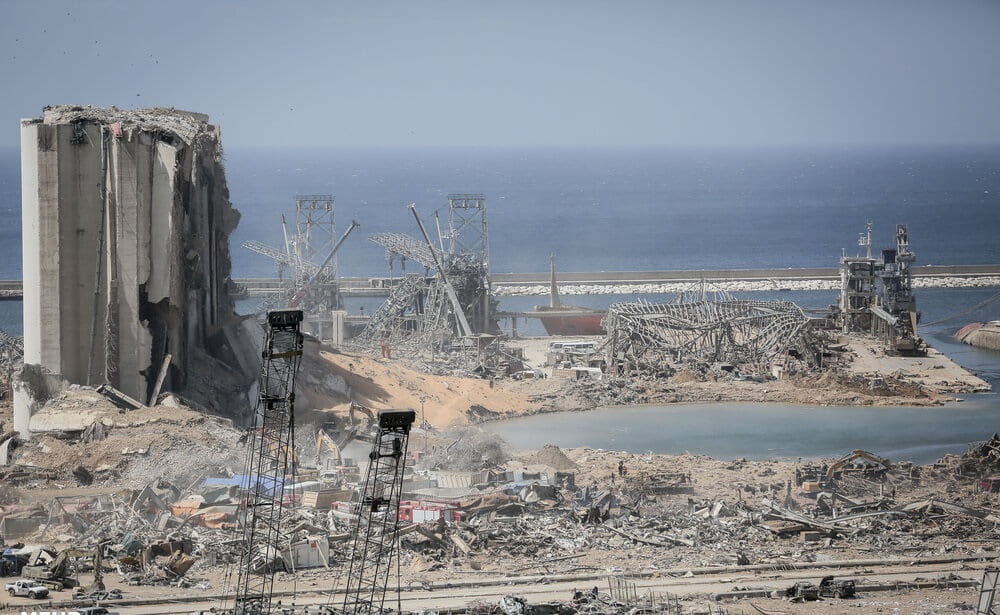
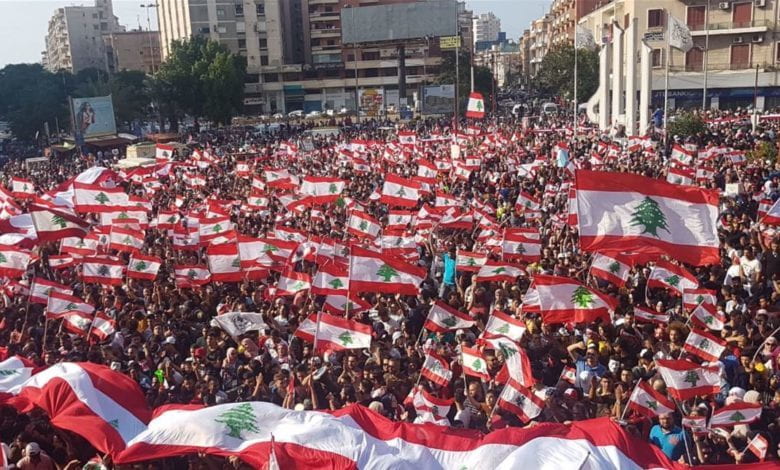
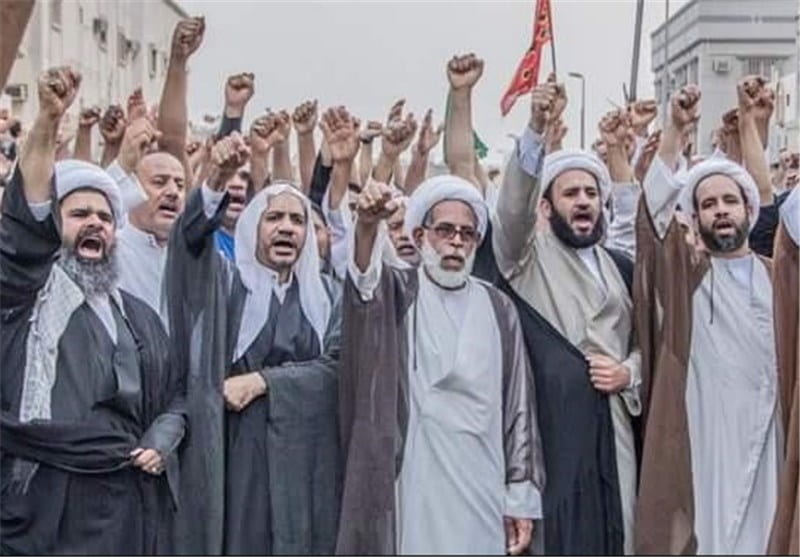
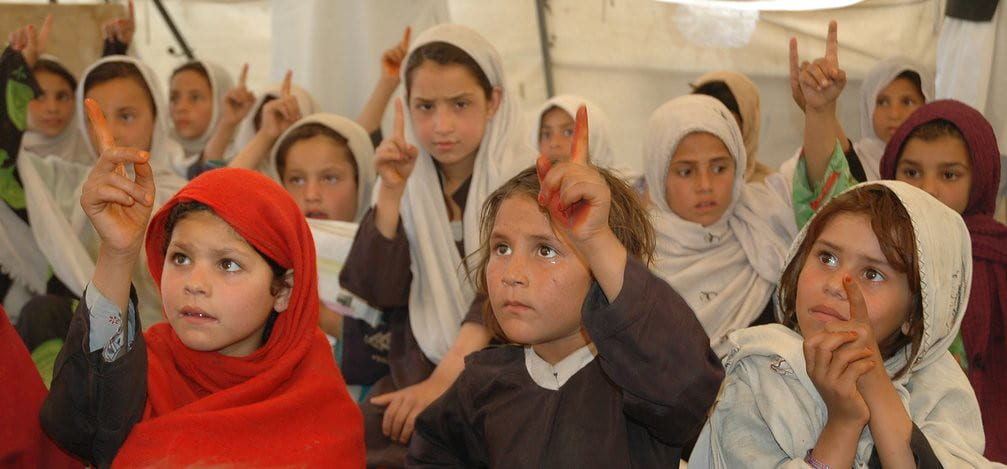
When the Taliban captured Kabul in August, a bleak future dawned on girls and women across the country. Despite the Taliban’s promise to be supportive of women’s goals under Islamic law, the deadly crackdown on the progress of women’s rights has already begun.
The Taliban regime, like the older one that ruled from 1990-2001, upon capturing the capital, shut down the Ministry for Women’s Affairs and replaced it with the Ministry for Protection of Virtue and Vice. Later, they announced that women cannot go out in public without a male relative or without being fully covered, and female workers have been instructed to stay home. Education, politics, sports, freedom of expression, and whatever else requires women venturing outside with a voice has been banned by the government, punished by beatings or floggings.

Education and Occupations
Girls’ education in Afghanistan took a lot of effort to achieve, but many obstacles, specifically financial security and accessibility, still stand in the way. Knowledge gives individuals mobility and power to decide their future for themselves — a source of pride that Afghan women have fought for. In Afghan villages and cities alike, many women and girls would work for low wages in poor conditions to finance their education, and now these efforts and opportunities have been ripped away.
Pride is now fear. After the fall of the Afghan cities Kabul and Herat, the Taliban prohibited girls over 6th grade from attending school and segregated universities between genders. Boys were allowed back weeks ago, but no indication was given to girls — a silence that told them to stay home. The regime previously stated that education will resume under the laws of Islam. Even if girls can go back to school, they may not learn certain subjects such as engineering, vocational education, cooking, and government studies.
Dreams of becoming pilots, surgeons, activists, and lawmakers have evaporated for Afghan girls, and women already educated under a democratically controlled Afghanistan are seeing their lives turn on their heads. A university student who was supposed to graduate with two degrees from the American University of Afghanistan and Kabul University frustratedly remarked that she must hide any IDs, diplomas, and all evidence that she received a higher education, throwing away decades of work for her career. If she does not do so, she risks the lives of herself and her entire family.

The Taliban is not their only issue, however. Many female political figures remaining in Afghanistan fear retaliation from men they jailed or sentenced. Despite the years of progress since the last Taliban occupation, women in powerful roles still made men in Afghanistan uncomfortable. The Taliban has not instituted strict restrictions on law and order — allowing incidents of physical and sexual violence against women to increase.
Female Workers
Women have taken to streets demanding their rights back as the Taliban prepares to deal with international questioning for their rise to power. Although once numerous after the fall of Kabul and Herat, protests are now few and far between. Organized protests were broken up by the Taliban’s gunshots, beatings, and killings in early September, effectively dampening the morale of activists. Now, the regime demands prior registration with a detailed account of the event and any slogans that are to be chanted, decreasing the right to assembly in the nation.
Female journalists, teachers, activists, and especially judges are also being targeted by the oppressive regime. It is common practice for the Taliban to break into homes of instrumental feminist voices and threaten their families, and the United States’ promise to protect Afghan women activists from the Taliban has fallen flat.
Former Afghan legislator Fawzia Koofi fled Afghanistan to Qatar after she was placed under house arrest and guarded day and night by the Taliban. Parliament members Shagufa Noorzai and Homa Ahmadi escaped to Athens, Greece, along with 177 other high profile female lawyers and judges with help from the Melissa Network and Human Rights 360. Even though activists like Koofiand Noorzai are far from their home country, they have already started networking to protect the rights of women and girls from where they are.
In late August, 15 members of the inspiring 20-member Afghan Dreamers fled Afghanistan, with 10 arriving safely in Mexico City, Mexico, and 5 in Doha, Qatar. This all-girls robotics team made waves after winning multiple international robotics competitions in the United States and becoming a luminescent symbol of the potential of girls in science, mathematics, and engineering. These girls left with the hope of continuing their education and competing in robotics tournaments. Some girls voluntarily stayed behind to help education efforts in Afghanistan. They all hope that their achievements and stories will empower girls in their home country to fight for their education and convince the regime to adapt to a new generation of women.

Education as a Human Right
The Taliban violated many articles of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR). Article 26 proclaims that basic and fundamental education should be free, compulsory, and equally accessible. Education is stated as the driving force to foster respect for human rights and personal freedoms all over the world which is crucial for women to rise from societal restrictions.
The head of the Afghan Women’s Network, Mahbouba Seraj, emphasizes that Afghanistan is not the same country that the Taliban left. Women will not sit and stand by while they try to take away their rights. Over 6 million women have established their presence in traditionally male-dominated fields such as media, medicine, law, and government. She believes that the gender equality movement in Afghanistan will prevail over the Taliban’s resistance.
Earlier in October, the United Nations Human Rights Council voted to approve a rapporteur on the grounds of Afghanistan to investigate and report civil and human rights violations. The European Union’s ambassador to the UN cited particular concern for the restrictive actions of the Taliban against women and girls. In addition to the UN, the public can offer donations to other international human rights organizations that are also working on the safety of female Afghanistan officials and girls seeking to continue their education such as Amnesty International, CARE, and Women for Afghan Women.