**As the US government flip-flops on its “zero-tolerance” Biblical mandated immigration policy that isn’t a policy but enforcement of the law, this repost, from this February, describes some of state-sanctioned child abuse and human rights violations experienced those seeking safety in “the land of the free and home of the brave.” You can read more information and some of the latest reports: here, here, here, including former first lady Laura Bush, and this video of UN High Commissioner for Human Rights.
The United States has long been lauded as the land of the free. As Americans, we have a tendency to consider our country to be an almost utopian land, far removed from the bleak landscapes and brutal violence of foreign countries that appear on the news. However, this ethnocentric attitude blinds us to the human rights abuses that happen frequently within our borders. Family detention centers are one such environment where human rights are regularly violated. The United States has three remaining family detention centers, referred to as “baby jails” by dissidents. Family detention has dwindled over the years due to protest, but our government currently detains close to 3,000 non-criminal immigrant mothers and children in horrifying conditions.

“We are not delinquents who should be imprisoned.” – Eleven-year-old girl on her detention at Berks County Residential Center
Of the three family detention centers that remain open, the South Texas Family Residential Center (Dilley, Texas) is by far the largest. The other two centers, Karnes County Detention Center (Karnes City, Texas) and Berks County Detention Center (Leesport, Pennsylvania), hold less than 700 detainees combined. Dilley, as it is known, has a capacity for 2,400 inmates and, as of 2015, holds over 1,000 children and around 750 mothers. The fifty acres of land that comprise the Dilley center are dotted with small, two-bedroom, one-bathroom cottages with no kitchen, no telephones, and hold up to eight people per house. Nights in all centers are punctuated with officials checking in by shining flashlights on the sleeping families every fifteen minutes, reportedly causing insomnia and anxiety for the children. Medical care is essentially non-existent, as individuals report that the available doctors often only advise mothers to give their children water for any sickness they might have instead of prescribing medicine. On-site doctors have prescribed water instead of medical care for broken fingers, conjunctivitis, and even for a child who vomited blood, according to detainee’s reports.
“Simply, they don’t care. What is more important for them is control. These are delicate situations when someone is sick and vulnerable. They just care about control. I thought I came to this country to escape abuse, mistreatment and disrespect. But it’s the same here.” – a detainee at the South Texas Family Residential Center
The conditions at these centers are incredibly dangerous for children and mothers. Many mothers at the center have already faced sexual assault, brutal violence, or threats of murder against them and their family. This would normally grant these families asylum status, which is a status granted to people who are unable to return to their home country for fear of persecution. Asylum status is granted partially on the basis of past abuse or violence enacted on a person by a foreign government, but trauma survivors often struggle sharing details that would ensure asylum. Most asylum hearings do not have childcare available, so mothers must choose between either sharing explicit traumas in front of their children in order to be granted asylum or minimizing their struggle to protect their children but be denied asylum. The conditions of the centers themselves also are fraught with abuse. An increase in violence in Central America has led to an influx of migrants from unstable countries; most of the detainees at detention centers are of Central or South American origin and predominantly speak Spanish. However, few staff members are fluent in Spanish and the subsequent miscommunication lead to abuse. The women are rarely allowed to speak on the phone, and it is next to impossible to obtain legal advice privately within the centers. This denies women the ability to detail abuses of the center without fear of retribution by the staff. Detainees have been raped and assaulted by guards without adequate punishment; in 2016, a guard was sentenced to less than two years in prison after being found guilty of institutionally raping a nineteen-year-old Honduran woman.
Additionally, the children are deeply at risk for developmental regression and major psychological trauma. According to a report by the child advocacy group First Focus, over half of all children in family detention centers are under the age of six. Children under six are undergoing crucial stages in their development, and can easily be traumatized for the rest of their lives if exposed to the stress of detention centers. Children who have been detained are shown to have increased psychological issues such as anxiety, depression, PTSD, self-harming, and suicidal thoughts or actions. Even short durations of being detained can have the same impact of week-long detention on children. Mothers have frequently reported their children losing unhealthy amounts of weight quickly, but doctors reportedly overlook the weight loss by claiming that the children are simply not used to the food or even claiming that they are bulimic. Children have been forced to sleep in rooms with non-related adults, creating a vulnerable situation that puts children at risk for sexual assault. At a now-closed center, kids as young as eighteen months were made to wear prison jumpsuits and expected to sleep in locked rooms with open-air toilets. Though the detention center where this occurred was shut down several years ago, similar abuses that display a blatant disregard for immigrant’s human rights have occurred in all family detention centers.
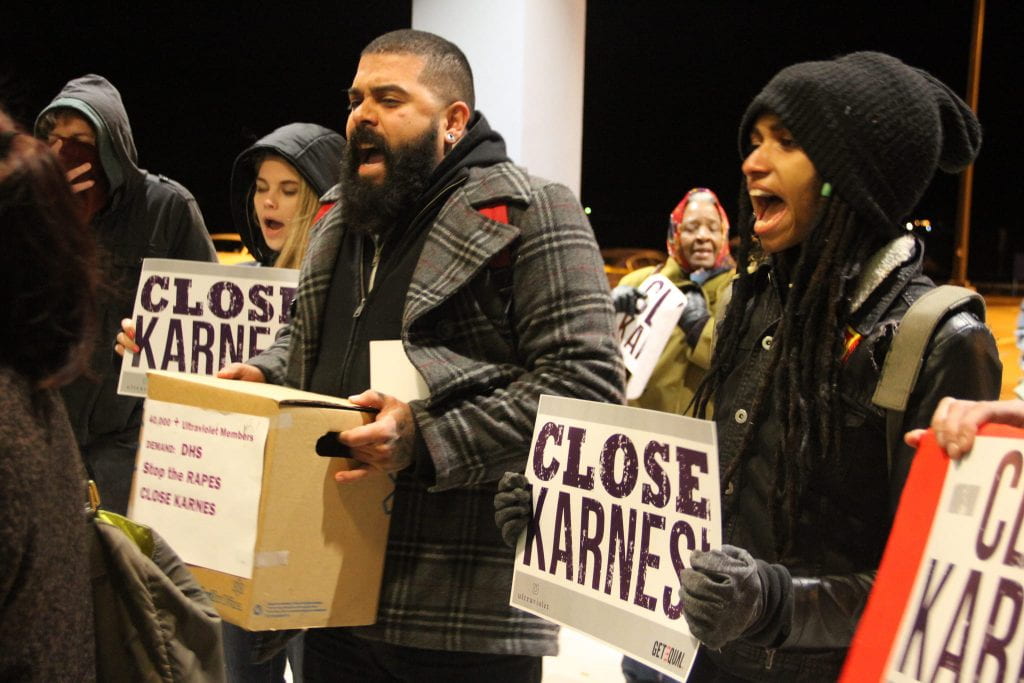

The overwhelming issue is that there is no legislation that ensures appropriate standards for immigrant detention. Management is left to the private companies who own the centers, and the desire for profit often overwhelms the adherence to ethical treatment. GEO Group, the company who runs Karnes, received $161 million in taxpayer dollars in 2015 from their contract with U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE). Dilley, run by CoreCivic, generates 14% of the company’s income each year, despite owning seventy-four other prison centers– CoreCivic took away $71.6 million dollars from Dilley alone. These detention centers generate huge profits, which encourages the prison owners to fill beds with more detained immigrants. Last year, legislation was introduced in Texas to allow family detention centers to obtain child care facility licensing without meeting the minimum standards that other child care facilities must meet. Eventually, the bill was not passed and licensing was revoked from the Karnes center. However, the center continues to detain children. This is in direct violation of the Flores Agreement, which states that detained children must be kept in the least restrictive environment possible, requires child care licensing, and states that detainment for over three weeks is unlawful. Inaction from the government enables these centers to continue substandard practices that have harmed and will continue to harm children.

The government justifies the practice of detainment through “aggressive deterrence strategy,” which is meant to dissuade more migrants from attempting to gain entry to the United States. This strategy is not effective; the mass violence that many immigrants flee from is far deadlier than the misery of detainment, though both are damaging to families. Women with children are the least mobile group among communities in conflict, and often only flee in the face of real danger. Essentially, families who have fled violence must go somewhere, and the United States is both geographically convenient and generally safe. To deny families refuge is cruel enough, but to create more misery, vulnerability and trauma through inhumane detainment should be an unacceptable practice. We cannot deny that the United States is violating the human rights of thousands of children and mothers. Children in detention centers have a right to education, a right to an adequate standard of health, and the right to freedom from torture, along with all other human rights as defined by the UDHR. Educational needs have not been met by any standard, available healthcare is abominable, and much of the circumstances for detained children could be defined as torture or degrading treatment. Beyond this, the practice of family detention alone is a violation of the human rights of many detained children, as the Convention on the Rights of the Child states:
“No child shall be deprived of his or her liberty unlawfully or arbitrarily. The arrest, detention or imprisonment of a child shall be in conformity with the law and shall be used only as a measure of last resort and for the shortest appropriate period of time.”
The conditions in which these vulnerable groups have been forced into are inhumane and dangerous. The detainment of children at U.S. centers rarely conform to the law adequately and detainment periods are often months long. Family detention is punitive by nature, yet none of the detained mothers or children in family detention centers are detained on the basis of crime. Data collected by the Detention Watch Network shows that the majority of families in the centers qualify for asylum status and therefore deserve to be freed, but institutional obstacles prevented the obtainment of that status. Families in detainment simply seek safety and protection from violent conflict in their home country. The mother who make the decision to uproot their homes in search of a better life have not committed a crime, and neither have the children who accompany them. The United States is actively harming a blameless population who has already been subject to trauma and abuse. This problem is not confined to the United States; family detainment occurs around the world in varying degrees of injustice from Australia to Israel. It is essential to call attention to this issue in order to preserve the human rights of children internationally. The global community must condemn the actions of any government that engages in the inhumane practice family detention.