The Middle East is a transcontinental region. When people think of the term “Middle East”, a host of thoughts come to mind such as deserts, burkas and Saudi Arabia. However, whether they are accurate is a completely different story. Most countries in the Middle East are often forgotten about, ignored, or misconstrued.
Location
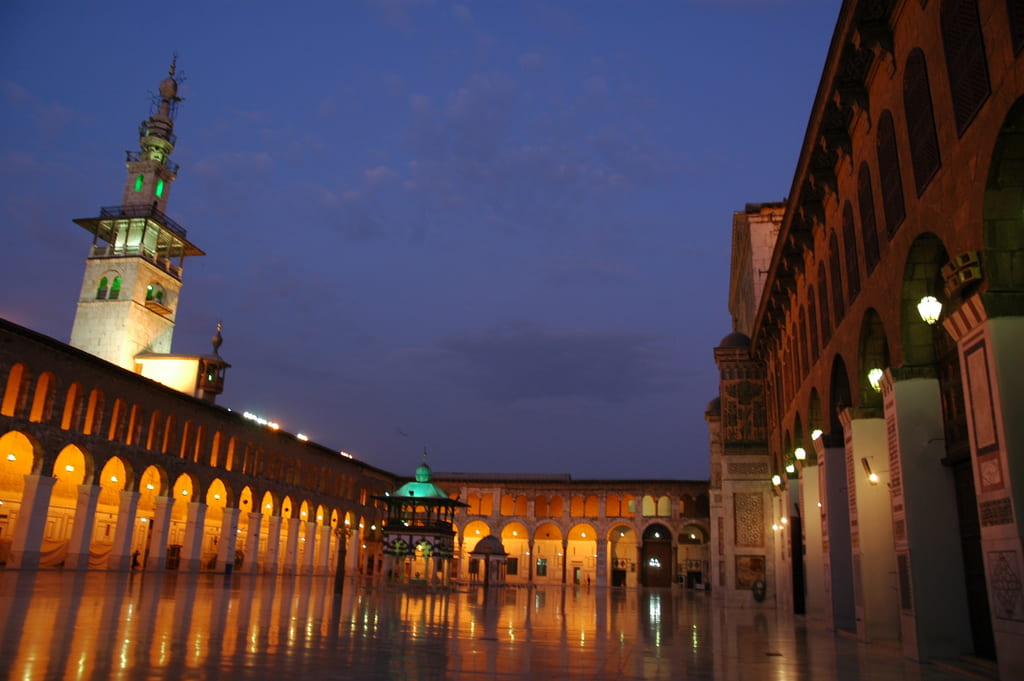
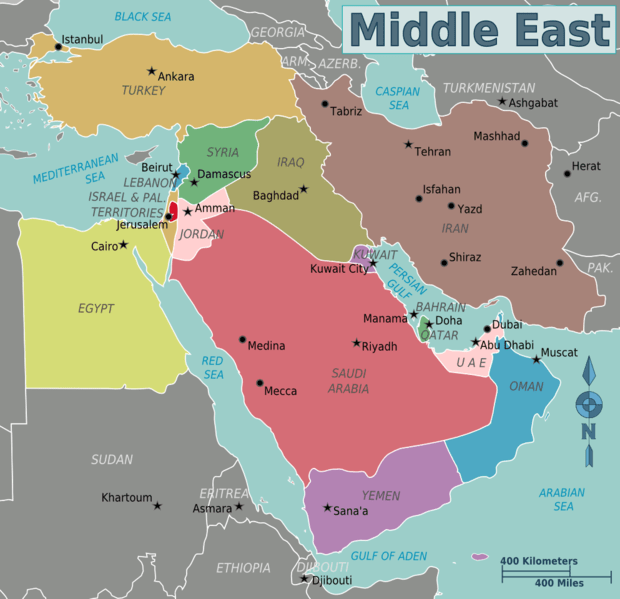
One of the most interesting questions to ask people is: Where is the Middle East located? Most people don’t even know what countries consist of the Middle East. One of the reasons why is, in the United States, geography is a dying subject. In fact, about three-fourths of the eighth graders in the United States test below average in geography. Furthermore, in most schools, geography is not required in middle school or high school. Out of the fifty states, only seventeen actually require geography in middle school and only ten in high school. The Middle East consists of fourteen countries shown in the picture below. What surprised me was how I found numerous websites that differed on what countries they thought were actually in the Middle East.
Arab vs Muslim
What does it mean to be an Arab? An Arab is defined as someone who identifies as being an Arab and whose native language is Arabic. On the other hand, someone who is Muslim practices the religion of Islam. Being an Arab and being a Muslim are not synonymous. For example, you could be an Arab who is not Muslim or you could be a Muslim but not an Arab. Furthermore, about 60% of people living in the Middle East are considered Arab. There are other ethnicities such as Persians, Turks, Kurds, and Jews.
What most people don’t realize is that there are over one billion Muslims in the world, the second largest religion in the world, and the majority are not in the Middle East. In fact, the country with the largest Muslim population is Indonesia. Also, the majority of Muslims live in Asia. While the majority of the Middle East does practice Islam, there are other religions practiced such as Judaism, Christianity, Baha’i, and Zoroastrians. Furthermore, there are different sects of Islam such as Sunni and Shiite.
Another misconception is that all the countries in the Middle East are considered Arab countries. However, that is not the case. For example, Saudi Arabia is predominantly Arab. This misconception may stem from the fact that much of the Islamic faith is written in Arabic. So regardless of which country you reside in, you would have some knowledge of Arabic.
Diverse Societies
There’s a certain stereotype in regards to the Middle East called orientalism that generalizes the region as deserts with roaming camels with olive-skinned people wearing robes, turbans, and garments that completely cover women from head to toe. The fact of the matter is that the style and environment depends on the area of the Middle East. We must also consider other factors such as education, socioeconomic status, and individual preference. The veil is looked at as a form of modesty. The concept of modesty is meant to be applied to both genders and not just on women, and how each person interprets its meaning is different. Some countries such as Iran and Yemen do require veiling to go out in public; however, most people who wear a veil add their own twist to it. When considering the environment, the Middle East is geographically diverse. The Middle East seems to be defined by its deserts but there are also mountains ranges and rivers. One section of the world should not be defined as one thing. Many people see the Middle East as a backward “country” when it is, indeed, the contrary. Some of their cities rival those in the United States such as Lebanon, Iran, and Turkey. Demographic trends show that the Middle East has the “youngest population and it has the second highest urbanization rate in the world”.

One dimensional portrayal of women
A common misconception is that Middle Eastern women are oppressed and denied their basic rights because of their religion. Also, it is assumed, they must cover themselves with a veil because they are weak and passive. However, the concept of the veil actually came from Christian Byzantium, not Islam. Surprisingly, Islam gave women more rights than Western women, until the 19th century. In England, women were considered the property of their husband until 1882. However, Muslim women have always been able to keep their own assets. A more current example is when Muslim women are married they tend to keep their last name, while most Western women do not. Notably, in the Quran, Islam’s sacred book, it “states that men and women are equal in the eyes of God.” As you can see, Islam is not the determining factor behind women being oppressed. While religion can affect women’s rights, culture is the main factor driving the question of gender roles. As a result, you cannot assume all of the Middle East is the same and deem it as such. Depending on the region, women have different statuses and rights. While it is true that in Saudi Arabia women cannot drive cars, that is not true in other Middle Eastern countries. Women do have political and social rights in the Middle East, they just vary depending on the country. In fact, women have served as ministers in Iraq, Syria, and Jordan and as Vice President in Iran. That is not to say that the Middle Eastern women do not have problems, just that it is not as extreme as Western countries seem to think.
The Middle East deserves to be seen as diverse. By discussing location, religion, society, and gender people can gain a more open outlook on the Middle East. It is easy to let fear, ignorance, or the media dictate one’s perception; however, to change the cycle conversations must be created.




