co-authored by Lindsey Reid, Ajanet Rountree, Nicholas Sherwood, and Nora Hood

Domestic violence, domestic abuse, domestic terrorism, intimate partner violence (IPV)—all refer to abusive patterns of behavior within the context of relationship. While a universal definition has not been agreed upon, this blog operationally defines IPV as “causing or attempting to cause physical or mental harm to a household member or engaging in activity toward a family or household member that would cause a reasonable person to feel terrorized, frightened, intimidated, threatened, harassed, or molested.” In other words, IPV transpires when an individual exerts abusive control over another, resulting in a pattern of physical and/or psychological pain. Due to the extensiveness of IPV, we concur with the CDC assessment that IPV is a public health and a human rights issue, as stated in Article 3 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, “Everyone has the right to life, liberty and security of person”. While we tend to think repressive governments or other sinister forces violate human rights, survivors of IPV experience and endure human rights violations within their home. With this blog, we aim to raise awareness of your rights in a relationship.
What is Intimate Partner Violence?
The vagueness of the term “IPV” makes recognizing and combatting this human rights violation difficult; as is the case with any vague definition in the human rights literature. One thorny issue in particular is the oftentimes (over)emphasis of the physical elements of IPV. To be completely clear: IPV, or any form of relational abuse or neglect, refers to physical and psychological maltreatment of an individual. Just because there are no physical scars does not mean it is not abuse. Psychological IPV includes behaviors such as: creating psychological isolation, sexual abuse (unwanted sexual contact, inhibiting access to birth control, unwanted sexual comments, and pressuring or threatening someone into sex), economic abuse (taking actions in order to maintain total control of the household’s finances), and digital abuse (using technology to control, stalk, or manipulate the survivor). This list is neither complete nor comprehensive; IPV as a human rights violation can take many, many forms.
Who are the victims and survivors of IPV? The classical answer is a wife or husband with a marriage; this is why the original term to describe IPV was ‘domestic abuse’ (implying this crime occurs within a domestic setting). The new term of IPV expands that outlook to include unmarried partners, as well as any form of relationship with emotional closeness and proximity. IPV can happen between married partners, and IPV can happen on a first date.
The Changing Demographics of IPV
As ‘battered wife syndrome’ has fallen out of favor, the IPV has been shaped and expanded to include male, female, and child survivors and perpetrators alike. While majority of IPV perpetrators are male, human rights advocates and laypersons alike must recognize perpetrators come in all genders and ages. In previous decades, cultural stigma against male victims may have pressured men from speaking out against their abusers; therefore, the actual gender breakdown of this crime remains unknown.
Male and female perpetrators themselves utilize markedly different forms of violence, which may compound efforts to qualify and deconstruct the gender breakdown of IPV. Machado et al. studied Portuguese men and discovered a pattern among their female perpetrators: “self-partner aggression”. They characterize self-partner aggression as the occurrence where the female injures herself in some way and then claims to be a victim of domestic violence to the police. She (the perp) takes advantage of confirmation bias, recognizing society generally believes that the male partner is abusing his female partner as it confirms gender stereotypes and social norms. Female abusers may also be more likely to use weapons or other objects to cause harm. One study involved a sample of 2,760 victims using the National Crime Victimization Survey from 1987 to 2003 found that 6% of the male victims had been stabbed with a knife, while 1% of the female victims had. Additionally, they found 10% of the male victims had been hit by an object that was thrown by their abuser, while 3% of the female victims had. However, male victims were less frequently found to have experienced violence through direct contact such as grabbing or pulling, with 20% of them having experienced it, while 53% of the females had.
Finally, IPV is not limited to adult perpetrators. Children can exhibit abusive behavior towards anyone in the household, whether another child or an adult. The normative assumption is parents possess the power in the home when compared to children, so it is difficult to imagine children as abusive. Control is the motivation for domestic violence and abuse; therefore, it is necessary that we pay attention when children perform violent actions, avoid brushing them off as merely “bad kids” because the behavior and consequences may have a serious impact on the present and future. Children exhibiting abusive behavior, if unchecked and untreated, may later show further signs of psychological deviance or disorder.

Controlling to Death
Social researchers have long sought to understand the motives of IPV perpetrators in order to predict violent behavior patterns. By predicting situations of relational violence, social researchers can empower advocates, policy-makers, and survivors themselves prevent occurrences of IPV. Several conceptual frameworks of IPV exist, including the stress-diathesis model, feminist / gender studies theories, and a pathological need for psychological control.
The stress-diathesis model suggests abusive behavior results from high psychosocial stress on the perpetrator. As the stress load increases, the perpetrator takes his or her frustration out on a less-threatening target (the victim). In this model, attempts to mitigate or prevent IPV focus on the perpetrator eliminating or healthily dealing with stressors. This theory has fallen out of favor, as its deterministic view of patterns of abuse at times ‘excuse’ perpetrators for their behavior. However, these theorists take a biopsychological approach to understanding behavior, which indeed aids in painting a holistic portrait of motivations and emotions in general.
By contrast, feminist and gender-studies theories focus on the broad sociocultural factors compelling IPV in perpetrators. Exploring the notion of male dominance in interpersonal relationships, Ornstein and Rickne sampled 714 post-separated and divorced couples in Sweden in 2001. They suggest separation between partners triggers a loss of control (especially for the male partner), weakening his domination of the situation, thus increasing the escalations of violence in the relationship. Violence reported by the respondents showed high variance, including verbal abuse (i.e. name-calling and cursing) psychological abuse resultant from emotional vulnerability of the perpetrator (i.e. feelings of inferiority), and finally physical abuse (including stalking and physical / sexual assault). Overall, feminist and gender-focused theories explore how fundamental issues of identity (such as gender) influences the occurrence of IPV.
Finally, the “control” theory of IPV posits an unhealthy need for psychological control, regardless of gender, is the most significant factor predicting IPV. This theory formulates relational abuse is symptom of a person’s subjective feeling of lack of control in a situation. Violence is therefore the means to an end, with the ‘end’ being feelings of control. Controlling behavior can take many forms, including stalking. The National Council commission in Sweden issued a 2006 report of 4000 surveys that found 362 (3/4 of whom are women) responded to questions of stalking in their lifetime, with 3% in the previous year. In 2011, the establishment of Swedish stalking law brought a four-year prison sentence for those found guilty. It is imperative to note justice systems, regardless of locale, treat the symptoms of violence but not the roots.
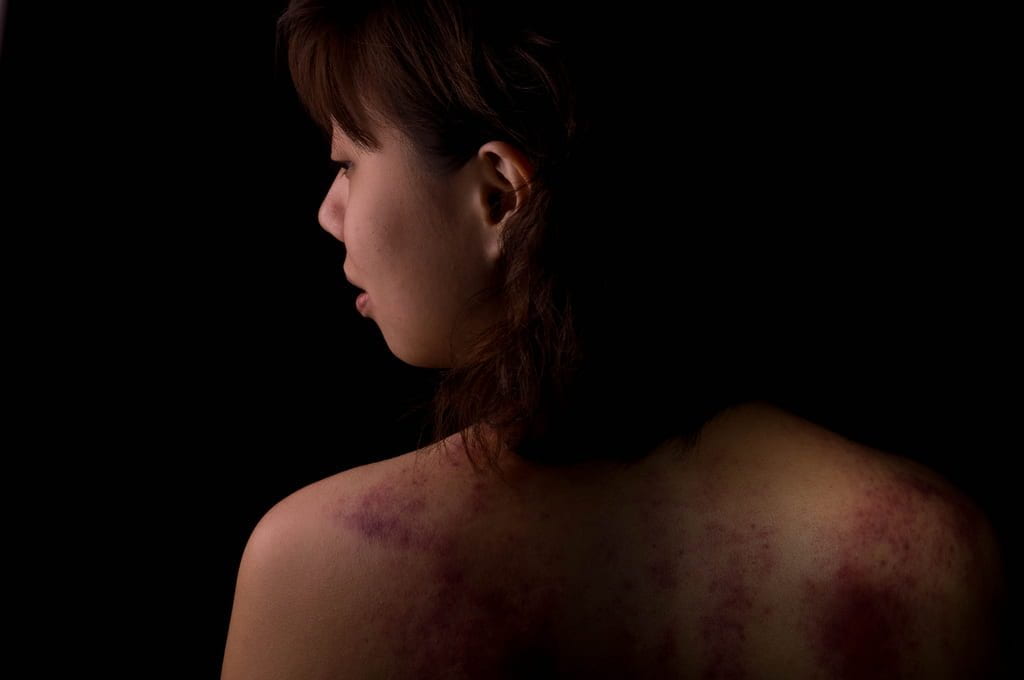
Regardless of the underlying causes (such as stress, gender roles, or a need for control), each case of IPV is unique and complicated. Recognizing signs of an abusive relationship is the first step and often difficult for the survivor to admit. Leaving the relationship itself is a whole other ordeal. Ornstein and Rickne affirm Kit Gruelle, a victim advocate in North Carolina (NC), who insists battered women are the experts on their relationships- no one knows more about IPV than someone who has gone through it. Gruelle suggests there is a noticeable pattern in abusive relationships—the couple has good days and bad days, just like every other couple. However, the ‘normalcy’ of the good days in no way makes up for the deviance of the bad days. Perpetrators often wear a façade of kindness and normalcy in mixed company, which makes spotting these perpetrators even more difficult.
Deanna remained married to her husband, Robbie, for nine years. She returned to him three times over the course of the years despite police knowledge of threats and violent tendencies. ‘The police knew he was violent but they believed he wasn’t violent enough to kill someone’.
When Robbie kidnapped and beat her across state lines, courts sentenced him to 21 years in prison—majority of the sentence for the kidnapping rather than the abuse. Assault on a female is an A1 misdemeanor in NC, resulting in 150 days in jail, whereas theft is a felony. IPV (or domestic violence) laws in Alabama have a stratified penalty process, ranging from Class A misdemeanor to Class A felony.
Controlling and abusive behavior may persist, even when the abusive relationship terminates. Prison, for many abuse survivors, is the only place they feel safe due to a system that does not protect them.
Latina returned to her abusive boyfriend numerous times because of love and at the time of his death, there was a warrant for his arrest. Courts charged her with first-degree murder when she killed him, after years of threats and abuse left her blind in her right eye.
Gruelle concludes, “our criminal justice system requires that she be beaten enough to satisfy the system, and by the time it get to that point, she’s already been so worn down psychologically and physically and emotionally. That’s when it’s really time for advocates to step up and begin to treat her like she has some value because she’s been told now systematically that she doesn’t. The courts have told her that she doesn’t have value; her partner has told her that she doesn’t have value… and all that strips away from her. Advocates, instead of stripping away, we have to build back up.”
If You See Something, Say Something
It is important to understand the difficulty of reporting cases of IPV. Who wants to get their partner in legal trouble? Who wants to report their wife, husband, girlfriend, boyfriend, and partner is abusive to them? Who is ready to accept they themselves are abused? IPV, like other forms of sex-based violence, often leaves the survivor in a traumatized state. This can manifest psychologically (irritable mood, overeating / undereating, splitting, dependency, fear of being along or fear of being with the abusive partner, and increasing isolation) or physically (exhaustion, severe weight gain or weight loss, and jumpiness). The symptoms of abusive relationships typically run deep, and the longer the relationship lasted, the more difficult these symptoms may be to spot. One critical symptom to look for is increasing isolation. The IPV situations typically result from an over-controlling or obsessive partner. These controllers may begin their abusive pattern of behavior by cutting off the victim from social contact with others outside of the relationship; the less face-time the victim has with others, the less likely to victim will be able to ask for help. In total isolation, the victim is hardpressed to find an ally, and he or she may fall prey to hopelessness and further traumatization. If you believe you know someone is in an abusive situation, reach out.
IPV is a complex human rights violation, and efforts to combat IPV must be flexible, durable, and persistent. Many social scientists work on deconstructing the psychopathology of perpetrators and patterns of survival in IPV victims. Advocates use their voice and social capital to broadcast the plight of IPV survivors and the identity of perpetrators. Ethical policy-makers codify punishments for IPV perpetrators, and enact funding for NGOs and government organizations that help IPV survivors. Finally, you can take action too. If you see something, say something. If you see a friend or loved one is in a relationship that does not seem right, initiate a conversation. Commit to naming and preventing intimate partner violence whenever you see it.
If you or someone you know is or may be in an abusive relationship, here are authorities to contact: in immediate danger, call 911 and The National Domestic Violence Hotline: 1-800-799-7233.
Ms. Hood considers domestic violence to be a form of domestic terrorism, and aims to raise awareness about the issue through her efforts including ThreeDaily.org.