On September 24, 2024, the state of Missouri executed an innocent Black man. Why did they kill him?
Marcellus Williams was convicted and sentenced to death for murdering Felicia Gayle. There was no physical evidence linking Williams to her murder: fingerprints, footprints, hair, and DNA found at the crime scene did not match Williams. The only evidence against Williams was testimony from two witnesses whose accounts were inconsistent and unverifiable. Gayle’s family favored life imprisonment. The county prosecutor favored life imprisonment. Only Missouri’s Attorney General wanted Williams executed – and he got his wish.
Williams was innocent of the crime for which he was executed. He never had a fair trial. The prosecution struck 6 of 7 Black jurors, one of whom was rejected “because he looked too much like Williams.” Missouri knew they were executing an innocent man – and they did it anyway.
History of the Death Penalty in America
Capital punishment has been a part of the American legal system since before the United States was a country. The first person executed in the British colonies was George Kendall, who was executed by firing squad for mutiny in 1608. By the early 1900s, public support for the death penalty was beginning to wane, and some states abolished the practice.
Utilizing capital punishment was briefly illegal nationwide. The 1972 Supreme Court Decision Furman v. Georgia ruled that existing death penalty statutes were discriminatory and therefore unconstitutional. That lasted until 1976, when the Court ruled in Gregg v. Georgia that Georgia’s updated death penalty statute was constitutional, and executions resumed. Since 1976, 1,601 people have been executed. Today, only 21 states still have the death penalty, and only ten have executed people in the last decade.
Methods for capital punishment have varied greatly over the last two centuries. Early in American history, the most common were firing squad and hanging. Over time, hangings have become associated with lynchings. Despite that history, in 2023, a Tennessee lawmaker proposed that “hanging by a tree” be used as an alternative method of execution in the state. In 1890, the first person was executed with the electric chair, which was the most common method for several decades until lethal injection became more popular after its first use in 1982.

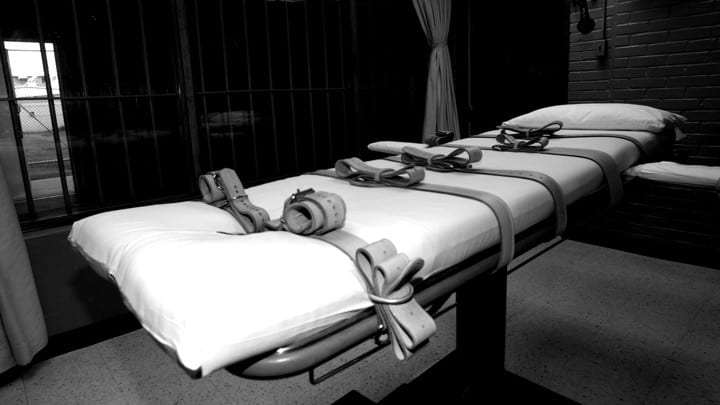
Lethal injection has faced challenges in recent years for a few reasons. Drug manufacturers do not want to be associated with homicide – and thus refuse to sell the required drugs to state governments – and medical professionals refuse to administer the medicines. Instead of medical professionals, correctional workers struggle to find veins and sometimes fail entirely, causing delayed executions. Roughly 3% of executions are botched, and people subjected to botched executions are disproportionately Black – 1/3 of executions nationwide are of Black prisoners, while 1/2 of botched executions are of Black prisoners. Even when not botched, lethal injections have been shown to be less humane than originally believed. The drugs used are painful and cause the lungs to fill with fluid – typically without proper anesthesia.
Black prisoners are also treated differently immediately before they are executed. Jeff Hood, who has witnessed six executions – three of Black prisoners, three of white – told NPR, “I can definitely tell you that the restraints that I have seen on Black folk have been unquestionably tighter than the restraints that I have seen on white folk.”
More recently, there has been controversy over a new execution method: nitrogen hypoxia. The state of Alabama has executed two people – Kenneth Smith and Alan Eugene Miller – by nitrogen hypoxia in the last year. The state had previously attempted to execute both Smith and Miller by lethal injection, but correctional workers were unable to place IV lines in either man over the course of several hours. There is another Institute of Human Rights blog post, published in the fall of 2023, that extensively details execution methods.
Problems of the Death Penalty
Two of the most common reasons given for keeping the death penalty are deterrence and justice. Justice argues an eye for an eye – that, for some crimes, the only possible form of justice is death. That is a philosophical debate, and one I will not discuss today. Instead, I will focus on the effect of the death penalty on homicide rates – deterrence. Deterrence is the idea that the existence of the death penalty deters crime – it reasons that prospective murderers are logical people who will be less likely to kill others if it will result in their death.
In 2012, the National Research Council conducted a literature review on studies examining any deterring effects executions – and the general presence of the death penalty – have on homicide rates. They concluded that studies had not yet demonstrated any effect capital punishment has on homicide rates and recommended that the “research… should not influence policy judgments about capital punishment.”
One of the most powerful arguments used by death penalty abolitionists is about wrongful convictions. Someone who is sentenced to life in prison can be released if they are found innocent; that is not so with someone who is dead, such as Marcellus Williams. Wrongful convictions are common; for every eight executions in the United States since 1977, one person sentenced to death was exonerated. 82% of death penalty exonerations are due to official misconduct and 36% of death penalty sentences are overturned.
Glynn Simmons was exonerated in December 2023 for a crime he did not commit. He spent 48 years in prison. The state knew when he was convicted in 1975 that Simmons was innocent; he was in Louisiana when the crime was committed in Oklahoma. Despite that, it took almost 50 years – 2/3 of Simmons’ life – for him to finally be exonerated. Imprisonment is reversible. Death is not.

What Can Be Changed?
Activists have worked for decades to reform or eliminate the death penalty. Two organizations that have been involved in numerous exonerations are the Innocence Project and the Equal Justice Initiative. Both organizations provide legal aid to innocent prisoners. Other ways to support change include petitioning state and federal legislators to end or reform the death penalty.