by Marie Miguel
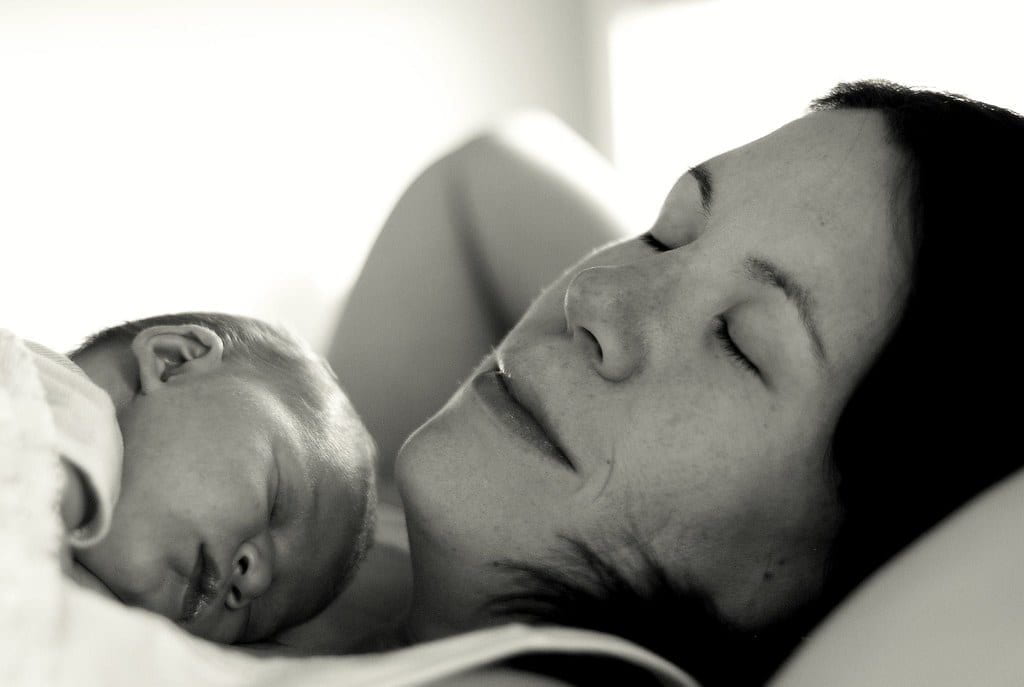

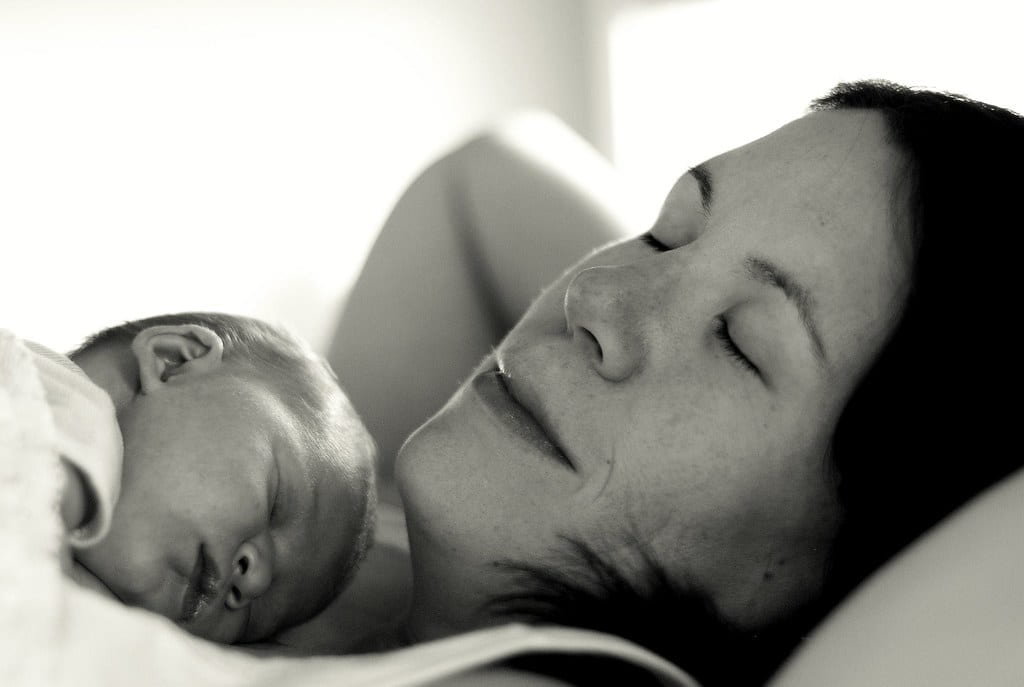
Maternity leave is necessary because it helps with postpartum depression
In the United States, maternity leave is almost non-existent. New parents in the U.S. get an average of three months of maternity leave, and some only get the twelve unpaid weeks of leave that employers are now required to offer under the Family Medical Leave Act. https://www.dol.gov/general/topic/benefits-leave/fmla Depending on where you work and how long you’ve worked for a company, you may not receive any paid maternity leave at all, which can cause a high level of stress for low-income parents and families. According to a study at the University of Maryland, longer maternity leave decreases the risk of postpartum depression. It’s suggested that this is because women can spend more time with their infants, and this is not surprising; if you don’t have the bonding time with your child that you need, it’s going to be depressing for you. You feel like you have to leave your child preemptively, and that’s not fair. Healthcare providers and policymakers need to think about how we can foster a more positive experience with maternity leave and help women get the care that they need. It’s essential that we think about maternity leave as being a preventative measure for postpartum depression.
Postpartum depression is serious
Postpartum depression is a severe mental health condition. Many women go undiagnosed with this mental illness because they unknowingly downplay their emotions to their mental health providers or general practitioners. Postpartum depression is a severe condition, and it needs immediate attention from a medical provider. It’s normal to be emotional after having a baby. But, there’s a difference between feeling down and having PPD. When you have a baby, it’s a huge life transition. You’re now responsible for taking care of a new life. Many moms have a difficult time with this change, and if you’re feeling overwhelmed, sad, or a variety of emotions after giving birth, that’s understandable. It’s when your feelings feel out of control that you need to worry whether or not you have Postpartum Depression. We’ll go over the symptoms of the condition, and you’ll see if you relate to them.
Postpartum Depression is not the baby blues
Postpartum depression is not just “the baby blues,” which affects up to 80% of new mothers. Postpartum depression affects childbearing individuals more severely. When you have PPD, it makes it nearly impossible to function. You feel severely depressed, hopeless, and scared. When a baby is born, you can have extremely intense emotions as a mother, which are frequently caused by changes in your hormone levels. Hormones make your experiences feel more powerful than they would ordinarily. You may be prone to crying or insomnia that occurs even after your baby is asleep, for example. Symptoms that can be considered part of the “baby blues” include mood swings, irritability, anxiety, and trouble sleeping. Postpartum depression, on the other hand, is a diagnosable disorder that exists as a potential side effect of giving birth. Unlike the baby blues, which is categorized by minor dips in mood, postpartum depression can be severely debilitating. Postpartum depression requires treatment, so if you have this condition or think that you might have it, don’t ignore it.
Symptoms of postpartum depression
The symptoms of Postpartum depression leave a mother feeling like she can’t cope with everyday life. You may be wondering what they are. The signs and symptoms of postpartum depression include severe mood swings, depression or depressed mood, feeling overwhelmed, not being able to sleep, feeling hopeless, fearing that you aren’t a good mother, restlessness, severe anxiety, inability to focus or think clearly, feeling worthless, thoughts of death or suicide, and intrusive, disturbing thoughts of harming yourself or your baby.
Postpartum psychosis is another condition to look out for and seek treatment if you think you have it. With postpartum psychosis, you may experience excessive thoughts about the baby, hallucinations or delusions, excessive energy or agitation, paranoia, and self-harm. If you believe that yourself or a loved one is experiencing postpartum psychosis, it’s vital that you seek treatment immediately.
What can we do as a society?
We need to take a stand as a society to help new mothers, and if we can prevent Postpartum depression, One of the things that we can do to help new mothers is to advocate for longer maternity leaves. Allowing new mothers to spend more time with their babies can prevent postpartum depression. In a society that’s so focused on productivity and getting back to work, one of the most important things that we can do to prevent postpartum depression is to push for employees to offer additional time for maternity leave. We want to spend time with our children; that’s only natural. If we’re not able to do that, of course, we’re more likely to experience postpartum depression, but it’s important to note that no new parent is immune to developing it. It’s nothing to be ashamed of, and it’s not your fault. Certain risk factors, such as family history or personal history of mood disorders, financial problems, unwanted pregnancy, and more, can increase a person’s likelihood of developing postpartum depression.
Getting help for postpartum depression
If you feel that you may have postpartum depression or if you’ve been experiencing symptoms of postpartum depression for over two weeks, it’s essential to schedule an appointment to talk to your doctor. Treatment for postpartum depression most often includes medication, if you need it, and most importantly, therapy. You can choose to see a traditional therapist or work with online therapy. New mothers can have the added challenge of trying to get out of the house, making it hard to get mental health treatment. Online therapy provides a forum to get therapy in the privacy of your home. A new mother may not have the energy to get out of the house to go to therapy. Online therapy can be an excellent resource for new mothers to get mental health treatment, prevent PPD or treat it. You can see a counselor with your partner or has individual therapy. Whatever your preference, it’s essential to seek treatment for PPD.
Marie Miguel has been a writing and research expert for nearly a decade, covering a variety of health-related topics. Currently, she is contributing to the expansion and growth of a free online mental health resource with BetterHelp.com. With an interest and dedication to addressing stigmas associated with mental health, she continues to specifically target subjects related to anxiety and depression.