
COVID-19, otherwise known as the 2019 novel coronavirus, has spread to many countries around the world, affecting many immunocompromised populations and impacting millions of people worldwide. My colleagues have referenced hotspots where the response has impacted the most, from the Middle East to migrants right outside U.S. borders. They have illustrated how discrimination, isolationism, and plain ignorance have shattered families and populations, destroyed economies, and brought fear and terror into the hearts and minds of Earth’s people. It is in that essence that this article will continue to explain the impact of COVID-19 in another hotspot of the world, Asia.
The Asian continent, comprising 48 countries, according to the United Nations, encompasses immense diversity and roughly 60 percent of the global population within its boundaries. This diversity includes, but is not limited to, having the highest and lowest points on Earth, “the world’s wildest climatic extremes,” and “the birthplace of all the world’s major religions.” For the sake of this article, I will be focusing on three countries that are handling the virus very differently, India, China, and South Korea.
Food Insecurity
Having one of the highest populations in the world, India is often referenced as a case study when examining the impact of overpopulation, economics, and food security. In 2012, Uttar Pradesh, India’s most populous state, 60 million out of 200 million people were considered living below the poverty line. Economic inequality has further negatively impacted India’s poorest communities with “57 billionaires controlling 70 percent of India’s wealth” as of 2017. Such inequality has led to the increase in poverty, a lack of medical equipment and access, poor living conditions, and a lack of food.
However, this pandemic has exacerbated the lack of access to food by Indian residents that comes on the heels of Prime Minister Nahendra Modi’s announcement to begin a “21-day nationwide lockdown.” With such an announcement also came with rising panic from Indians, crowding grocery stores and shops with people panic buying everything in sight. Under Modi’s plan, the “Prime Minister’s Poor Welfare Scheme”, individuals will be able to receive five additional kilograms of rice or wheat for the next three months. Although proposed to benefit 800 million people, many are wary of its success due to the closure of interstate travel, trains, and flights. It is under this lockdown that residents could face two years in jail and a financial penalty if they leave their home for non-essential reasons. In an interview with Time, an autorickshaw driver expressed concern over Modi’s decree to lockdown the entire country. Before the decree, his main concern was to save enough money to help get his son through college. However, “as he stays home with no daily income, his main concern is putting food on the table. He’s not sure what he will do” once those savings run out. When examining a singular issue impacted by COVID-19, the situation in India highlights the issues that countries with an enormous informal sector may face due to economic hardship and lack of infrastructure. For example, India can grow enough food for its growing population, although millions are left underfed due to “bottlenecked supply chain[s], inadequate logistics, food wastage and sharp societal inequalities.” The virus has further called to attention the lack of food security that many around the world face on a daily basis which infringes upon their basic human rights and a Sustainable Development Goal that must be achieved by 2030, Zero Hunger.
Government Control
Being the most populated country in the world, China is often criticized for its drastic measures and horrifying treatment of Muslim minorities. When examining the pandemic, COVID-19 is known to have originated in the Wuhan province in China and was noticed by Chinese ophthalmologist Li Wenliang. Dr. Wenliang had used a private online chat to explain his worry for the novel virus, which quickly went viral, resulting in him being reprimanded by Chinese police. Following this observation, the province had shut down, cutting off transportation and sealing residents off from the outside world. In an interview with Dr. Bruce Aylward, “the leader of the World Health Organization team that visited China,” had praised the Chinese government’s decisive actions towards preventing the spread of the virus:
“I think the key learning from China is speed — it’s all about the speed.” — Dr. Bruce Aylward
Although the Chinese government has sought to demonstrate its prowess and handling of the virus, through building hospitals in 10-days and publishing photos of patients who have been cured of the disease, many human rights groups have expressed concern and worry over the treatment of those who have been critical of the government. For instance, Chen Qiushi, a Chinese human rights lawyer, was “put under quarantine”, Fang Bin, a citizen journalist, disappeared in February, and Li Zihua, another journalist, was taken away by a group of men. Dr. Wenliang had died due to the virus early February of 2020. With the news of his death, thousands of comments flooded Chinese social media site Weibo criticizing the Chinese government and censorship in the country with top hashtags such as “Wuhan government owes Dr Li Wenliang an apology” and “We want freedom of speech.” According to the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC), when they searched for the hashtags a day after Wenliang’s death, they disappeared having been censored alongside many comments aimed at the Chinese government.
From Wuhan province, we now turn to the Xinjiang province in Western China, where the imprisonment of millions of Uyghur Muslims could prove to be a breeding ground for the virus as it spreads throughout the world. You can read more IHR blogs about The Uyghur Muslims in the context of Crimes Against Humanity here and how this crisis is affecting refugees on the US-Mexico border here. In Xinjiang, there are an estimated three million people detained in re-education camps in Western China, mostly of Uyghur Muslims who have been suppressed by the Communist Party. As alleged by Jewher Ilham, the daughter of a jailed Uyghur academic, some of the “conditions at the detention centers offered the perfect chance for coronavirus to spread” citing “systematic abuse, serious overcrowding and poor sanitary conditions inside the camps.” Given allegations of China’s unwillingness to publish the truth about these conditions combined with the alleged suppression of critics and ethnic minorities, it is deeply concerning to gauge the risks of infection amongst those who have been cited as not having enough to eat or doctors on staff to treat those infected. This is also a signal to international groups and organizations to ensure that all people have the chance to be cured and not suffer as a result of the virus or violating the human rights to freedom of speech.
Some Potential Success?
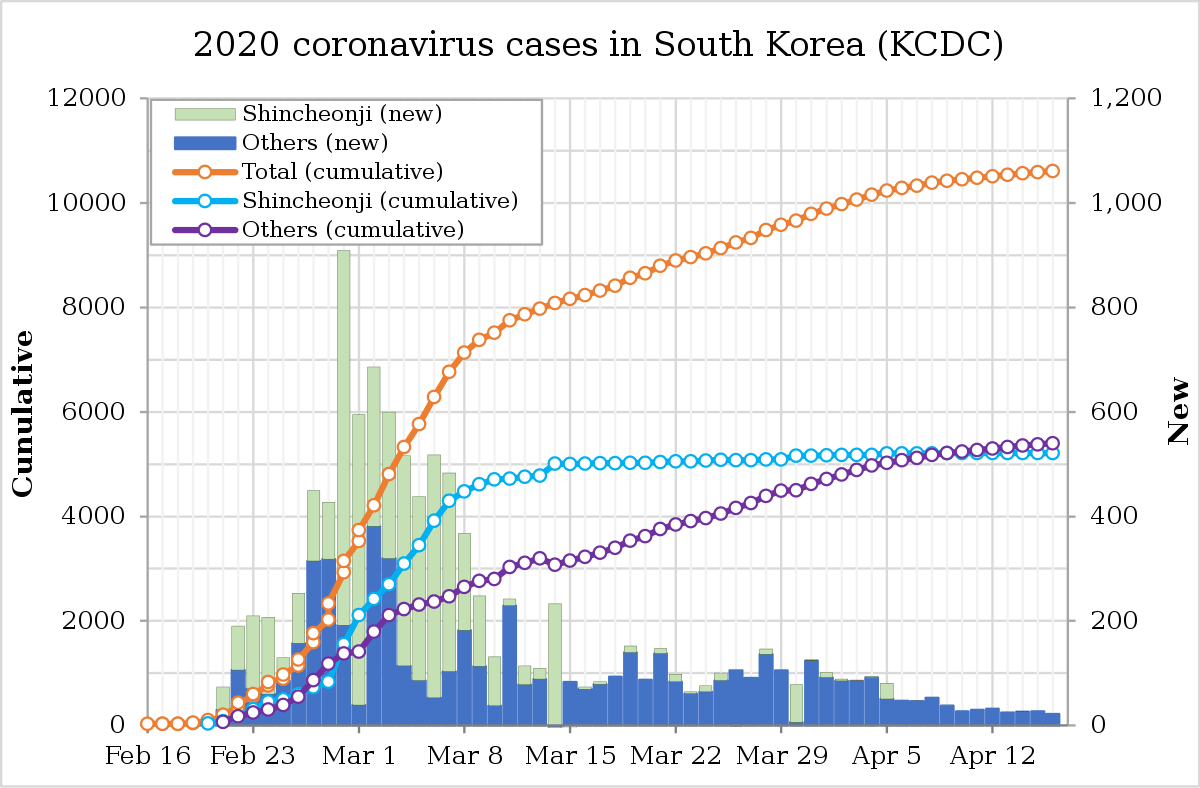
Amongst all the panic buying and the loss of toilet paper throughout the country, there seems to be some light at the end of the tunnel manifesting itself through ‘flattening the curve’. This method has seemed to be close to perfected by South Korea whose growth in COVID-19 cases has significantly slowed compared to the United States. When examining South Korea, many writers have explained the situation by comparing it to religion and culture, chalking it up to higher levels of social trust and the lingering aspect of Confucianism. However, that does not seem to be the case. By flattening the curve, South Korea has demonstrated that it is due to “competent leadership that inspired public trust.” Having tested more than 5000 people per million inhabitants than the United States, it is no wonder that taking early action and mobilizing health officials could lead to a successful response.
“No sacred Confucian text advised Korean health officials to summon medical companies and told them to ramp up testing capacity when Korea had only four known cases of COVID-19.” — S. Nathan Park
Compared to China, India, and even the United States, South Korea did not have to “lockdown entire cities or take some authoritarian measures,” rather, they learned from their past experience with MERS (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome). Such preparation allowed the South Korean government to be proactive and “improve hospital infection prevention and control.” Combined with South Korea’s industrial and developmental advantages over both China and India, the government was able to take a proactive approach and deter the worst effects of the virus. Once South Koreans started getting sick in early February, the government immediately began “testing aggressively to identify cases — not only testing people who are so sick that they’re hospitalized but also mild cases and even suspected cases.” This initiative has allowed South Korea to quarantine those at a high risk while also managing to keep their factories, schools, hospitals, and entire cities open while other countries around the world are having to shut down everything to contain the spread.
Conclusion
Looking back at India, China, and South Korea, it becomes apparent that a swift and proactive response is necessary in order to not allow for the lockdown of entire cities and countries. However, that proactivity must balance itself between being lax and aggressive. For example, China’s efforts to curb the spread of the news rather than the virus has made human rights concerns more apparent to the world, especially since the freedom of speech for civilians is being curbed to protect China’s global reputation. In India’s case, the pandemic has shown many human rights groups and countries the issues that a country with a massive impoverished population faces during difficult times. By being able to demonstrate good leadership and mobilizing experts, South Korea has ultimately done what many other countries would only hope to accomplish. Such success has already inspired other Asian countries to follow suit, especially Singapore, Japan, and others. And although South Korea’s population is significantly small compared to that of India and China, their success is one that can be successfully implemented worldwide. Instead of casting these successes aside as an element of Confucianism or culture, it is necessary for us to be able to model our response like South Korea’s so that were such an event to occur again, we will be able to swiftly contain the spread rather than suffer through weeks and months at home without physical human interaction.
