** As the IHR and other sponsors prepare for the “Symposium on Disability Rights,” the next few weeks will highlight some posts from the past as well as feature new posts written to provide some background into the various panel focuses.
* This is a repost from summer 2017.

The UAB IHR team had the opportunity to participate as rapporteurs in the Conference of State Parties (CoSP) annual meeting at the United Nations headquarters in New York City. In accordance with Article 40 of the Convention on the Rights of Person with Disabilities (CRPD), CoSP consists of convention signatories responsible for the implementation of the Convention. This annual meeting is the “most diverse international disability meeting in the world” because it brings together UN agencies, non-governmental organizations, human rights institutions, disabled persons organizations (DPOs), and civil society.
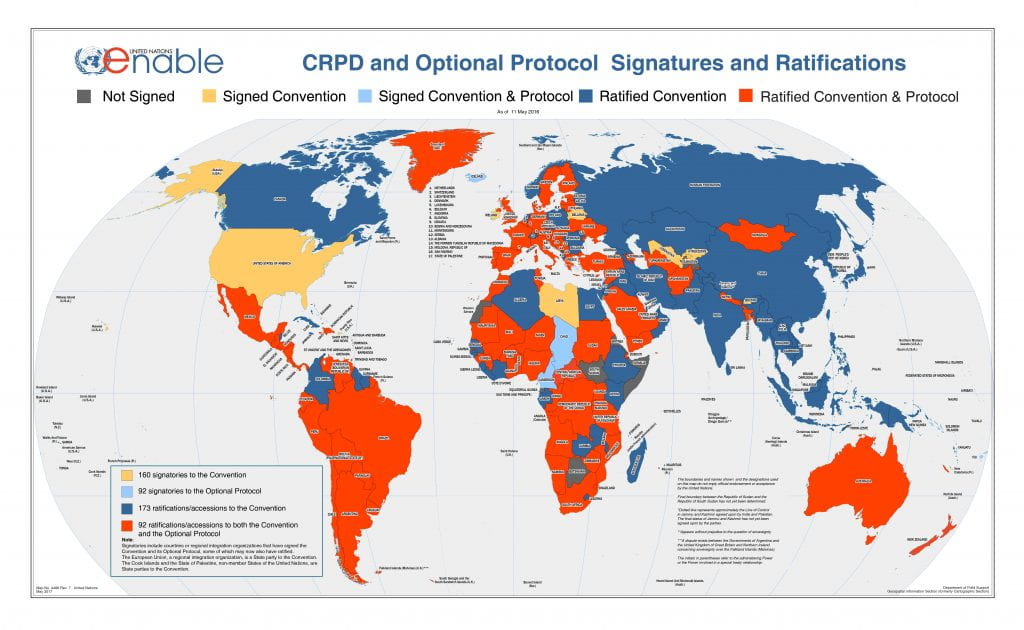
Estimated at 1 billion, persons with disabilities are the largest minority worldwide, facing considerable marginalization in every day life. The CRPD is the first human rights treaty of the 21st century, with the expressed purpose of ensuring that “all persons with all types of disabilities…enjoy all human rights and fundamental freedoms”. Adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in December 2006, the CRPD is the first treaty “open for signature by regional integration organizations” (app) who exercise the social development dimension by changing attitudes and approaches to persons with disabilities.
The UN Enable website designates the mandate of CRPD as “the movement from viewing persons with disabilities as “objects” of charity, medical treatment, and social protection towards viewing persons with disabilities as “subjects” with rights, who are capable of claiming those rights, and making decisions for their lives based on their free and informed consent as well as being active members of society.” In other words, CRPD focuses on the human being rather than the disability, and its implementation teaches the world to do the same. As of November 2016, 168 states and the European Union ratified the Convention; the United States has not.
The CRPD presents a disabled perspective to an able-bodied norm. Through the CRPD, persons with disabilities– disempowered through invisibility that is rooted in an able-bodied world, which often forgets their existence—benefit as their human rights infuse with other conventions, standards and norms of treatment.
Janet Lord argues that the language utilized in the CRPD reinforces the need to reframe disability as a contribution to society, rather than a hindrance. Pointing to the American Disability Act (ADA) as a stepping-stone to the CRPD creation, she makes a clear delineation that CRPD is not an international version of ADA. “[CRPD] provides a framework for the development of disability rights in countries that is, in large part, inspired by the principles and concepts found in the ADA—nondiscrimination, inclusion, autonomy, human dignity. Like any other human rights treaty, the CRPD seeks to ensure that the human rights to which all are entitle are actually implemented for persons with disabilities.” She hones in on two essential themes of the CRPD: non-discrimination and employment.
First, non-discrimination is all-inclusive as defined in Article 2 and outlined in Article 5. “Discrimination on the basis of disability means any distinction, exclusion or restriction on the basis of disability which has the purpose or effect of impairing or nullifying the recognition, enjoyment or exercise, on an equal basis with others, of all human rights and fundamental freedoms in the political, economic, social, cultural, civil or any other field. It includes all forms of discrimination, including the denial of reasonable accommodation.” Akiko Ito, Chief of the Secretariat for the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, insists the need for at least two perspectives, disabled and gendered, when mainstreaming disability as a measure to counter discrimination. Unfortunately, the layers of discrimination are not limited to two perspectives; therefore, it is necessary to include race and/or ethnicity, given the intersectionality of an individual life.
Second, barriers to employment reinforce exclusion and marginalization. While employment barriers differ depending on the disability, the overarching concept lies in accessibility. As an able-bodied person, I take accessibility for granted. Consider how a wheelchair user gets to work if there is not access to a bus, cab, or car that is accessible; or how a visually impaired person gets information from the internet, if there is no voice-over technology. Article 27 of the CRPD challenges and demands the labor market to be “open, inclusive and accessible…by taking appropriate steps” for persons with disabilities to participate and enjoy the right to work. UN Enable reports that there is difficulty in obtaining data on persons with disabilities, specific to employment; however, here some of what we know:
- In the US, a 2004 survey reported that 35% of persons with disabilities have employment when compared to 78% of the rest of the population.
- China has an estimated 83 million persons with disability – that is 6.3% of the country’s population
- In Ireland, 37% of persons 15-64 have a disability and are employed
- Thailand states that 1.3 million of the 4.8 million persons with disabilities are working age
- 70% of Russia’s disabled population is unemployed
The rights to employment and non-discrimination fall into the categories of economic and social affairs. While CoSP ensures the practical application of the CRPD on the local level, the Department of Economics and Social Affairs (DESA) advises, develops, and oversees policy creation and the implementation of CRPD on the national level. Ito explains, “DESA works to support the development pillars of the United Nations – peace and security, and human rights.” CRPD and its implementation align with the 1945 UN Charter that seeks to identify progress in economic and social development, and promote human rights through the creation and maintenance of a peaceful and prosperous world.
The role of civil society is imperative in the implementation of the CRPD. Article 33 makes allowance that persons with disabilities and their organizations are involved and participate in the monitoring process; this outlet is CoSP. Civil society participation is uncharted territory as no other human rights treaty acknowledges the advocacy, accountability, and the representation of NGOs. By recognizing the mandates and positions of NGOs within communities and around the globe, CoSP is striving to ensure the full inclusion of persons with disabilities into an accessible and accepting society. To be clear, the implementation process is complex, difficult, and far from over. Fortunately, having persons with disabilities led and dominate discussions, CoSP represents a microcosm of dedicated innovation and a relentless pursuit of excellence as they collaborate to create, maintain, and reframe equal representation of human rights through participation and partnership.
Over the course of this week, the team will share personal experiences and takeaways from this incredible week that included the official launch of the CRPD app and sharing of Making Disability Rights Real in Southeast Asia by Dr. Derrick Cogburn and Dr. Tina Kempin Reuter.






