Introduction
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Island peoples’ indigenous communities boast the oldest documented forms of culture in the world. For over 60,000 years (and some claim these communities have been in the Australian ‘neighborhood’ for 80,000 years), these societies were comprised of at least 500 distinct ethnic groups, sharing overarching worldviews and belief systems, but with widely diverse symbols and rituals, methods of exploring and explaining the world around them, and material expressions of their cultural heritage. Over the course of tens of thousands of years, Aboriginal peoples developed the oldest intellectual, religious, and artistic traditions in human history. As do all cultures, these traditions morphed and took shape over time, as the values of the Aboriginal peoples developed, as their surrounding ecological environment changed, and finally as colonizing forces destroyed much of the Aboriginal peoples and heritages. This post provides a brief overview of the colonization of Aboriginal communities and how, hundreds of years later, descendants of both Aboriginal communities and New Australians are working together to reconcile their shared traumatic history through the creation of shared cultural histories.
Colonial Past, Post-Colonial Future?
Broadly defined, colonization is the long-standing political practice of settling a population onto a new territory by subjugating and / or eradicating the current occupants. Colonization is rooted in domination – an assertion of power (e.g., political, economic, militaristic) for the benefit of the colonizing state. In essence, colonizers seek land or other natural resources, and they justify forcible expansion through various arguments from the religious (e.g., manifest destiny, divine rule) to the ethical (e.g., a ‘civilizing mission’) to the practical (e.g., terra nullius). Colonization is different from imperialism in the sense that imperialists seek absolute control over a territory, whereas colonizers seek to permanently settle a new population onto a territory. Colonization has ancient roots extending to the Romans, Moors, and Ottomans and likely beyond. Edward Said’s (1978) seminal text Orientalism helped usher in ‘postcolonial studies’, an intellectual framework intending to deconstruct the horrific consequences colonialism have had on global human development. At the most basic level, postcolonialism aims to explore and explain the world through the eyes of the ‘colonized people’, namely the indigenous groups that were and are repressed by colonizing forces and how this repression plays out in the modern day. In the case of Australia, this means Aboriginal communities.
For 200 years, contact between Aboriginal groups and outside world produced largely positive results, including trade relations and the sharing of technologies. Then in 1770, English Captain James Cook and his cadre begin settling in Australia, bringing with them disease, dispossession, and direct conflict. Within 10 years, the Aboriginal population was decimated; direct (e.g. violence) and indirect (e.g. alcoholism) effects of colonization murdered 90% of these communities. Even today, the violent legacy of colonization cascades into the lived experience of Aboriginal Australians. This collective trauma still impacts these individuals at the biological level (e.g., pathologically high rates of embodied stress), psychological level (e.g., higher rates of suicide), and the societal level (e.g., placing trauma as a central component of cultural production; Krieg, 2009). In the span of about 200 years, the historical and cultural legacies of the oldest societies on the planet were either intentionally destroyed or forcibly assimilated. In 1991, however, the Australian government moved to finally reconcile this violent past with surviving members of Aboriginal communities, drawing on the wisdom of these communities themselves.

Reconciliation: Measuring Success & The Canning Stock Route Project
In 1991, the Report of the Royal Commission into Aboriginal Deaths in Custody set the stage for reconciliation processes between Aboriginal and new Australians. The following decade saw the government-sponsored Council for Aboriginal Reconciliation and its successor, the NGO Reconciliation Australia, standardize and elevate reconciliation processes between Aboriginal and new Australians. Reconciliation Australia posits five dimensions must be addressed in successful reconciliation attempts: (1) race relations; (2) equality and equity; (3) institutional integrity; (4) historical acceptance; (5) unity. McIntosh (2014) further clarifies best practices of Australian reconciliation efforts by measuring these attempts through the Reconciliation Process Analysis (RPA). The RPA grounds its prescription in two critical factors: visioning (imagining the ‘end state’ of reconciliation, i.e. unity between Aboriginal and new Australians, as decreed by Reconciliation Australia) and backcasting (workings backwards from this vision and labelling tangible steps that have the potential to lead to this reconciliatory vision; McIntosh, 2014). He lists three stages in the RPA:
- Stage 1: “Search[ing] for all available information on the convergence of interests that created the agenda for reconciliation”; this emphasizes the “spaces of encounter or contact zone”.
- Stage 2: Understanding how these spaces of encounter can lead to ‘tipping points’, whereby reconciliation processes are unstoppable both in public and private discourse; in effect, how to move from theory to practice.
- Stage 3: Creating a reconciliation ‘report card’ by comparing the current state of affairs to visioning and backcasting efforts undertaken by reconciliation workers from both sides of the conflict.
Utilizing the RPA clarifies the success rate of reconciliation for the practitioner and, more importantly, offers concrete steps and directives for the actors involved in reconciliation processes. By utilizing this framework, Aboriginal and Western Australians now have a blueprint and a tool for functional analysis.
One documented reconciliatory success is the that of the Nguarra Kuju Walyja (translating to “One Country, One People” in a local Aboriginal dialect) Canning Stock Route Project (CSRP). The CSRP uses cartographic rendering from both Western and Aboriginal Australian sources to create a new transcultural map of portions of Western Australia that were colonized by the English (Milroy & Revell, 2013). This project involved combining colonial-era mapping (originally belonging to Surveyor Alfred Canning) with religious artistic techniques belonging to the indigenous communities forcibly displaced and murdered by Canning and his crew (Scott, 2011). The CSRP features a hybrid of Western and Indigenous art media (cartography, sand illustration, paint, etc.) for the purpose of intercultural apology, forgiveness, and reconciliation.
To learn more of the artists involved in the project, click here, and to see the artwork used in the CSRP, click here.
Processes such as these benefit not only the public who consumes the art, but also the researchers, artists, and practitioners who work together on the project (Milroy & Revell, 2013, Smithers Graeme & Mandawe, 2017). An autoethnographic and reflexive examination of the reconciliation processes enjoyed by the producers of the CSRP would likely reveal changes in outlook between these producers; the act of physically participating in the creation of a reconciliation project may have more tangible effects on the artists than the public. This and other initiatives similar to the Canning Stock Route Project should be analyzed using McIntosh’s RPA to assess tangible reconciliation outcomes and their impacts in the broader communities these projects serve. This form of reconciliation research would connect the general benefits of reconciliation, such as the integration of histories, with empirical support. Reconciliation is, after all, both an art and a science.
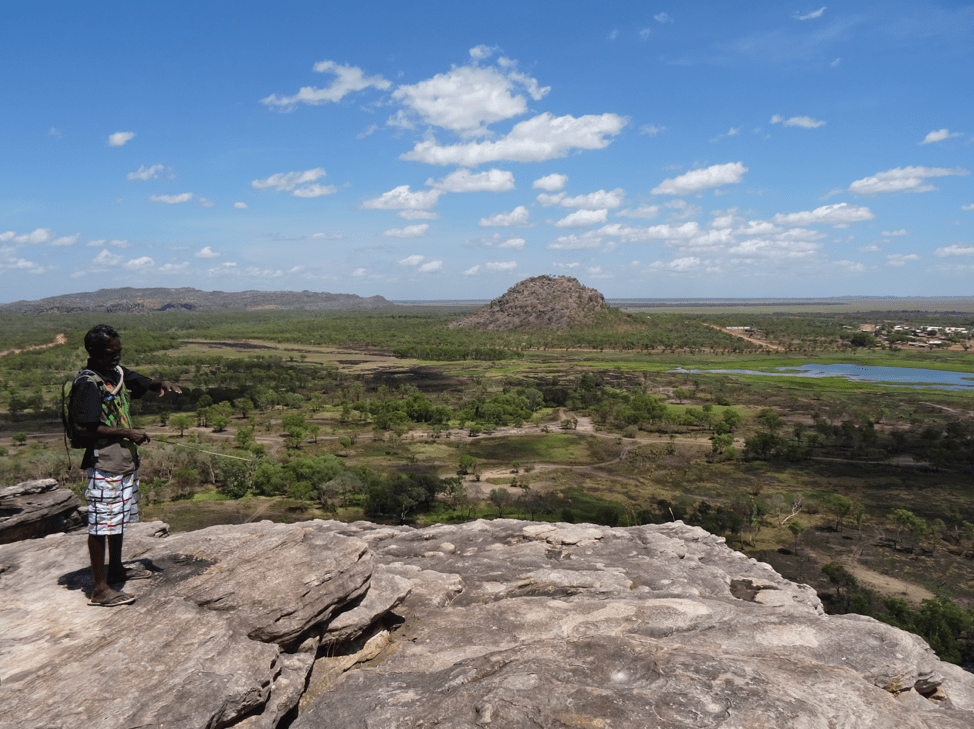

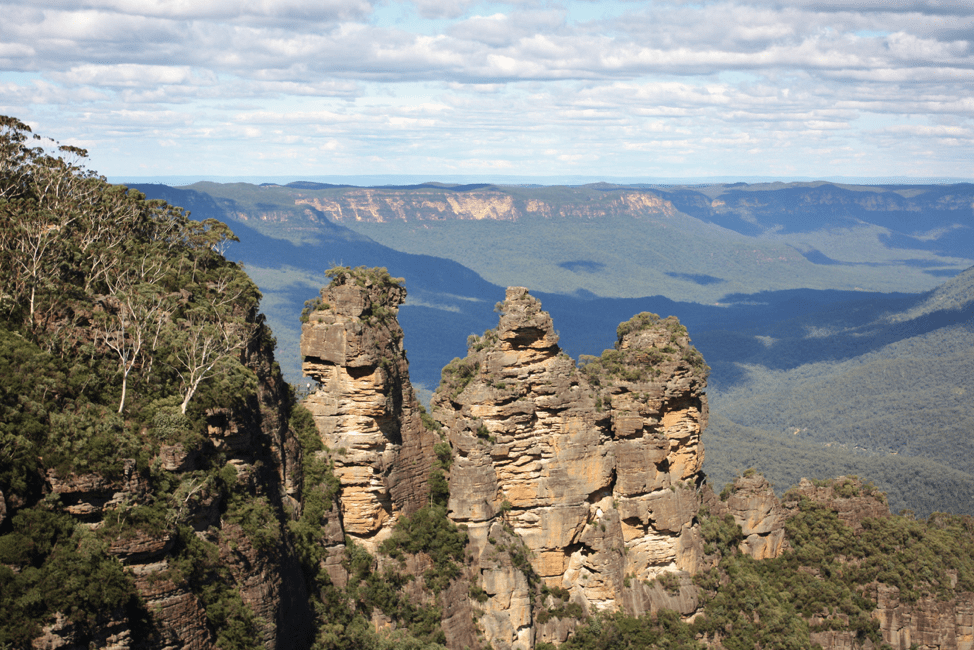
The Dreaming & The Land
A central aim of the CSRP was an intentional integration of European history (vis-à-vis ‘Western Geography’) and Aboriginal history (vis-à-vis the land-based worldview of The Dreaming). This history is co-written, it is co-owned, and it draws on cultural heritages and strengths of both parties. We are all familiar with the notion of Western Geography – but what is the Aboriginal Dreaming?
The Dreaming, loosely translated, means several things: the time of creation (when animistic spirits sang the world into existence), the spiritual / ethical code of an Aboriginal individual, and the cultural laws governing Aboriginal tribes (Milroy & Revell, 2013). The Dreaming is both a worldview and a system of behavior – there is no differentiation within many Aboriginal societies.
The Dreaming informs Aboriginal tribes of their cultural history and collective memory through story, art (with particular emphasis on performative aspects, such as dance), pilgrimage, and other rites / rituals (Petchovsky, San Roque & Beskow, 2003). The Dreaming is the spiritual and cultural tradition of Aboriginals, and the Dreaming is central to every facet of their lives. The Dreaming, Aboriginal Australia’s religious and cultural system, is literally rooted in the Australian landscape (Milroy & Revell, 2013). Landmarks are holy sites to the Aboriginals; some locations’ sacredness is shared by all tribes, some tribes, or one tribe. The unifying factor, amidst hundreds of Aboriginal traditions, is the relationship between person, spirit, and land in Australia. The spiritual lives of Aboriginal Australians are nourished by this relationship; by the same token, land theft and forced displacement robs the Aboriginal not only of his or her Country but also their spiritual home and fortitude. The CSRP, at its most fundamental, approached reconciliation through the land. Land theft cleaved the relationship between colonizers and Aboriginal communities, therefore land sharing may mend this relationship.
A Dream of Reconciliation
Initiatives such as the Canning Stock Route Project aim to engender sustainable peace and reconciliation between descendants of indigenous populations and their colonizers – this is at the heart of healing from cultural violence. Other similar reconciliation movements, such as those between European Americans and Native Americans, must take heed from the successes of the CSRP. Government policies, such as reparations, are not enough to successfully reconcile cultures dominated by violence and repression. Successful reconciliation also hinges on heritage – such as Aboriginal societies’ profound love of and respect for their land. nHeritage lives through art, through wisdom texts, and through stories passed down over the course of many millennia (in the case of Aboriginal communities, 60,000 years and more). nIf the modern world truly seeks to heal from its colonial past, the glorious histories, beliefs, and heritages of indigenous communities must drive future reconciliation.
Below are images of Aboriginal rock art and of the Australian landscape that may have once inspired the Aboriginal Dreaming.
For more information about rock art, visit here, here, and here.
For information on the powerful connection between Aboriginal communities and land, visit here.
For a greater in-depth explanation of the Aboriginal Dreaming, visit here.



References
Borer, T. A. (2006). Telling the Truths. Notre Dame, IN: University of Notre Dame Press.
Krieg, A. (2009). The experience of collective trauma in Australian Indigenous communities. Australian Psychiatry, 17(special supplement), 28-32.
McIntosh, I. S. (2014). Reconciliation, you’ve got to be Dreaming: Exploring methodologies for monitoring and achieving Aboriginal reconciliation in Australia by 2030. Conflict Resolution Quarterly, 32(1).
Milroy, J. & Revell, G. (2013). Aboriginal story systems: Re-mapping the West, knowing country, sharing space. Occasion: Interdisciplinary Studies in the Humanities, 3, 1-24.
Petchovsky, L., San Roque, C. & Beskow, M. (2003). Jung and the Dreaming Analytical psychology’s encounters with Aboriginal culture. Transcultural Psychology, 40(2), 208-238.
Said, E. W. (1978). Orientalism. New York, NY: Random House, Inc.
Scott, S. (2011). Yiwarra Kuju: The Canning Stock Route. Australia Historical Studies, 42, 289-294.
Smithers Graeme, C. & Mandawe, E. (2017). Indigenous geographies: Research as reconciliation. The Interdisciplinary Indigenous Policy Journal, 8(2), 1-19.
