by Grace Ndanu

It takes a lot of love, effort and dedication to be a good mother. For that reason, I believe it is important that everyone has the choice whether or not to be a parent, and when to take on that responsibility. Unfortunately, many girls around the world do not get to choose. Globally, the COVID-19 pandemic remains a pain to society because it is definitely complicating the efforts of reducing teenage pregnancies. It has caused an immeasurable disruption to every aspect of our lives in the last few months. To contain the spread of the novel coronavirus, governments have taken drastic measures to minimise the spread. Learning has been suspended, with schools being closed indefinitely. Religious meetings and worship programs have been affected similarly meaning there will be no more youth programs in the religious institutions, including churches and mosques for the time being.
In Kenya, the Ministry of Education has put in place strategies to ensure continuity of education through distance online learning delivered through radio, television and the internet. However, these strategies have further widened the inequality gap, as learners from poor, vulnerable, and marginalized households are unable to benefit from continued learning through these platforms due to lack of access. Further, with the loss of livelihoods particularly in low income households, some children may be forced into income-generating activities to support their families’ survival. Also, school closure has stopped the provision of school meals and sanitary towels.
And it’s more complicated for girls living in refugee camps or girls that are internally displaced. For them, school closures are even more devastating as they are already a disadvantaged group. Girls at secondary level are only half as likely to enroll as their male peers. While the magnitude of the COVID-19 crisis is unprecedented, we can look to the lessons learned from the Ebola epidemic. At the height of the epidemic, five million girls were affected by school closure across Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone, the countries hardest hit by the outbreak. And poverty levels rose significantly as education was interrupted.
There is evidence that links poverty with teenage pregnancies during this pandemic. One reason is because many young girls are getting involved in economic activities to supplement what their parents are bringing home. On the other hand, as the cases rise day by day there is a strain on the healthcare system, leading to the disruption of healthcare services, re-prioritization of sexual and reproductive and health services and a. shortage of contraceptive commodities and essential drugs. As SRHR services are reducing, sexual behaviour is rising since the teenagers have nothing to do, and it seems to be more risky where parents don’t really care what their children are doing while at home. I feel that there will be more unintended pregnancies all over the world, many of which will occur among teenage girls.
As I have discussed, there is no culture or tradition, it just happens. There are girls, especially those who come from communities or families that are rooted in culture and traditions, these girls must undergo what their parents wants them to, and the girls have no choice in the matter because their hope was school where they would run for help.
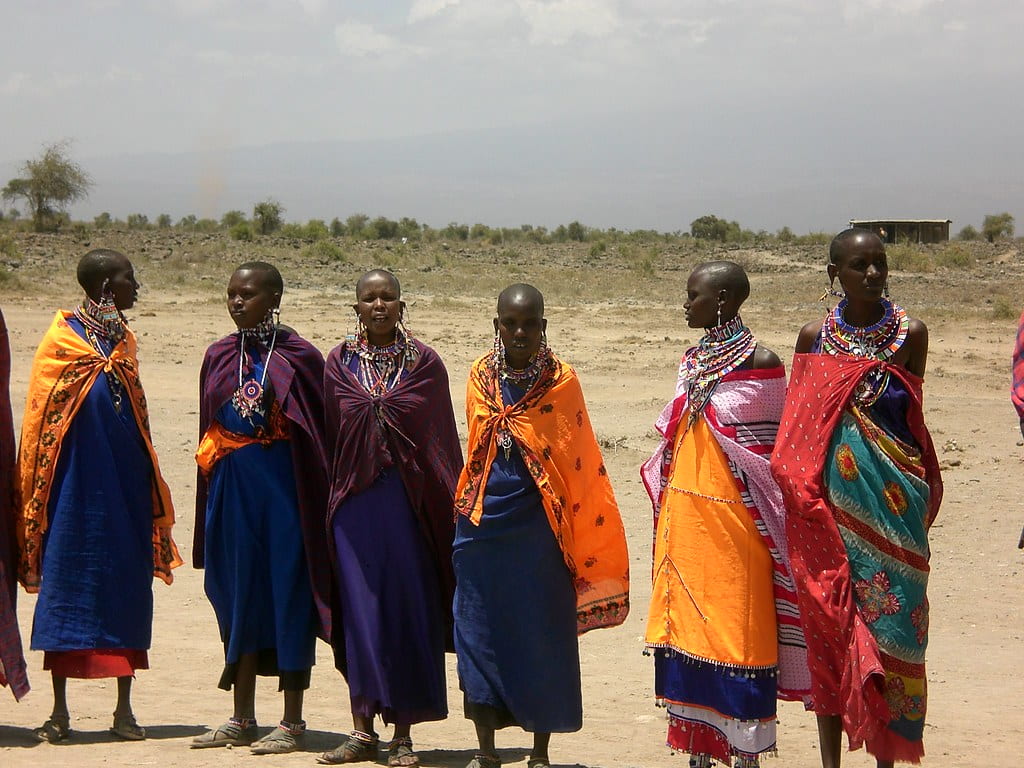
For example, in the Maasai community, when a girl is at least nine years old she is circumcised then married after two to four weeks. These girls are now expected to take care of their husband and to bear children at that early age.
Unintended pregnancies among teenagers may result in some difficulties in the lives of young girls. There are unsafe abortions, which may happen as a decision of the girl maybe to feel clean and also as a result of family decision in order to keep the family name clean. There is increased poverty where a girl who is being provided everything with the struggling parents bring another baby who needs to be taken care off and be provided everything as they are babies and as they grow all the way to adulthood. At some point there may be denial where by the parents kick out their daughters because of getting pregnant early because they have disgraced the family. This may cause psychological problems because she doesn’t have the supporting system which may force her to get married not only at an early age but also to an old man who may be violent on her. If not marriage she may have suicidal thoughts. Early pregnancies are the leading cause of deaths among the teenage girls because their bodies are not yet matured to give birth. The girls who are forced into marriage as teenagers, the responsibility that they are given drains them off because also their minds are not yet matured to do what is expected of them, which may lead them to be beaten and abused. Everyone deserves to enjoy their childhood.
Something has to be done before it’s too late. The governments should have committees that will develop and implement proven solutions. Different stakeholders should work to respond and to prevent by meeting the unique needs of adolescents by may be providing sanitary towels and also help them access SRHR services. The people responsible for taking care of pregnant teenage girls should teach them how to improve their sexual and reproductive health and well-being. Lastly I believe there are already existing activists in our towns and villages and they can potentially help to reduce negative coping mechanisms, such as child, early and forced marriage, especially during this time, where every energy is driven to the corona situation.



