Ubiquity of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) has drastically changed the way we behave in almost every corner of life. One silver lining drawn into these unprecedented times is that many people are more appreciative of their families, friends, and communities. However, the odds of being in a social network that knows someone who has been diagnosed or died from COVID-19 are greater if you are a racial/ethnic minority living in the U.S. As such, this blog focuses on COVID-19’s disproportionate effect on communities of color and how a human rights approach can help address racial/ethnic health disparities.
Racial/ethnic minorities are particularly vulnerable to reduced access of health services and the psychosocial stressors of discrimination which is why some argue that racism is a fundamental cause of health inequalities. These disparities are largely due to the disadvantaged economic and social conditions commonly experienced by many racial/ethnic minorities. Compared to Whites, racial/ethnic minorities are more likely reside in densely populated areas, live further from grocery stores and medical facilities, represent multi-generational homes, and be incarcerated. Additionally, racial/ethnic minorities disproportionately represent essential worker industries and have limited paid sick live. As a result, the living and working conditions for many racial/ethnic minorities put them at odds with threat of COVID-19.
Vestiges: Black American Health Disparities
Black Americans have disproportionate rates of COVID-19-related risk factors such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity. As such, they are disproportionately dying of COVID-19 in many counties across the U.S. These disparities are even more alarming at the state-level. For example, in Georgia, 83% of all COVID-19 cases linked to a hospitalization were Black patients despite the community only representing a third of the state’s population. Also, in Michigan, Blacks represent 14% of the state’s population but 41% of the COVID-19 deaths. On a national level, Blacks (13% of the total population) represent 33% of all COVID-19 hospitalizations, while Whites (60% of the total population) represent 45% of all COVID-19 hospitalizations.
Not only do Black Americans disproportionately live in many of the U.S.’s early COVID-19 hotspots (e.g., Detroit, New Orleans, and New York), they are also more likely than their White counterparts to experience poverty and have no health insurance. For centuries, the labor of Black Americans has been deemed “essential”, while the COVID-19 pandemic adds insult to injury. In the medical field, Blacks are less likely to be health professionals and more likely to represent personnel that cleans, provides food, or work in inventory. As such, Black essential workers who are not on the frontlines are more likely to acquire COVID-19 in the pernicious form of regularly contacting cardboard, clothing, or stainless steel. Thus, health disparities in the Black community demonstrate how the legacy of slavery and segregation thrive in the social and economic conditions of COVID-19.
Segmented: Latino American Health Disparities
Many Latinos in the U.S. have immigrant status and work in high-risk essential industries such as agriculture, food service, and health care. This largely explains why Latinos are up to three times more likely than Whites to be infected and hospitalized by COVID-19. These striking outcomes are compounded when considering that Latinos face other disproportionate hurdles such as inadequate communication resources and language barriers. Also, Latinos often socialize in “mixed status” immigrant networks which means those who are undocumented are not eligible for COVID-19 stimulus funding.
A recent Pew poll found that Latinos are almost 50% more likely than the average American to have been laid off or lost a job due to the pandemic. This is particularly salient to Latinos with a high school education or less and those ages 18-29. However, immigrant Latinos were less likely to lose their jobs but more likely to take a pay cut. As a result, the Latino experience during the COVID-19 pandemic is not only fraught with social and economic drawbacks, much like other communities of color, but complicated by the fact that their large immigrant population is ineligible for needed resources and often relied on in the essential workforce. These outcomes suggest the social and economic consequences of COVID-19 are uniquely challenging to Latinos, namely immigrants with limited access to resources that are often afforded to citizens.
Overlooked: Native American, Native Hawaiian, and Pacific Islander Health Disparities
Often overlooked in the racial health disparities conversation are outcomes for Native Americans. Some state health departments (e.g., Texas) classify Native American COVID-19 statistics as “other” which ultimately dismisses the unique health profile of this underserved population. However, early statistics from Arizona and New Mexico suggest Native Americans represent a disproportionate number of COVID-19-related deaths and cases, respectively. Reports from health authorities in Navajo Nation, which is comprised of areas in Arizona, Utah, and New Mexico, indicate this community’s confirmed COVID-19 prevalence rate is the highest in the country, although they have a test rate higher than most U.S. states.
In March, the Seattle Indian Health Board requested medical supplies from local health authorities but instead received body bags and toe tags. This callous response demonstrates that local authorities in Washington state have actively devalued the lives of Native Americans during these trying times. The Cheyenne River Sioux Tribe in South Dakota have responded to their state’s negligence by refusing to end COVID-19 highways checkpoints across tribal land. Cheyenne River Sioux Tribe Chairman Harold Frazier argues that the checkpoints are the best thing the tribe has to prevent the spread of COVID-19 because they are only equipped with an eight-bed facility for its 12,000 inhabitants. The nearest critical care facility is three hours away.
Also overlooked are COVID-19 outcomes among Native Hawaiians and Pacific Islanders (NHPI). Early reports from California, Hawaii, Oregon, Utah, and Washington indicate that NHPI have higher rates of COVID-19 when compared to other ethnic groups. A precursor to these outcomes is that NHPI have some of the highest rates of chronic disease which puts this demographic at higher risk of COVID-19. Much like other racial/ethnic minority groups, NHPI are more likely to work in the essential workforce and live in multi-generational households. Thus, these conditions allow COVID-19 to proliferate among NHPI enclaves.

Health and Human Rights
Health is argued to be a fundamental human right. Ways this can be achieved is through creating greater access to safe drinking water, functioning sanitation, nutritious foods, adequate housing, and safe conditions in the workplace and schools. As such, health exists well outside the confines of the typical health care setting. However, the U.S. has yet to officially ratify the Universal Declaration of Human Rights which ultimately prevents the government from being held accountable for the socioecological influences that generate health disparities across racial/ethnic minority groups.
These health disparities are not debatable and even acknowledged by the U.S. Commission on Civil Rights. In response, national efforts, state-level policies, and public health programs have successfully reduced these disparities but have only made modest progress. Thus, comprehensive, systemic, and coordinated strategies must be implemented to achieve health equity. Although solving this daunting task cannot achieved by the U.S. government alone. It must also incorporate non-profit and philanthropic on-the-ground efforts already seeking this goal as well as greater public awareness about the impact social and economic policies have on racial/ethnic health disparities.
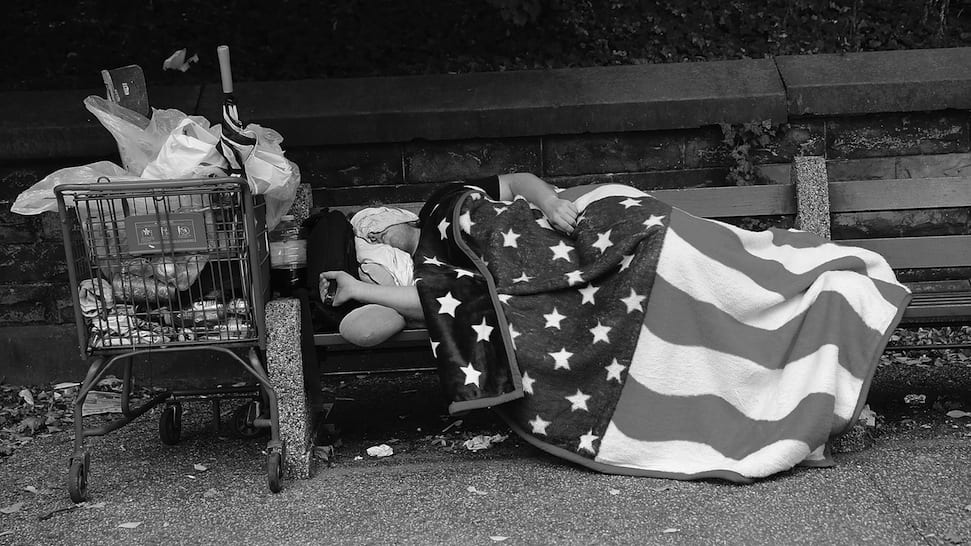
Despite these discrepancies, the COVID-19 pandemic serves as an opportunity for social change. More specifically, these unprecedented events bring greater light to issues such as poverty, homelessness, unemployment, and migration, all of which disproportionately affect communities of color. As a result, the ubiquity of COVID-19 has gathered people from every corner of the justice community to declare that health is a human right, thus bringing us one step closer to true equity and inclusion.