Paducah, Kentucky.
This is the first school shooting I remember. All these years later, I still remember what I thought once I saw the photos: “How did this happen? Surely this is a random tragedy that will never happen again.” The writing of this blog comes just over five weeks on the memory side of the Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School shooting in Parkland, Florida and on the same day as the Great Mills High School shooting in southern Maryland. The shooting at Heath High School is a distance memory, eclipsed by Columbine High School in Littleton, Colorado, Sandy Hook Elementary in Newton, Connecticut, and Huffman High School in Birmingham, Alabama.
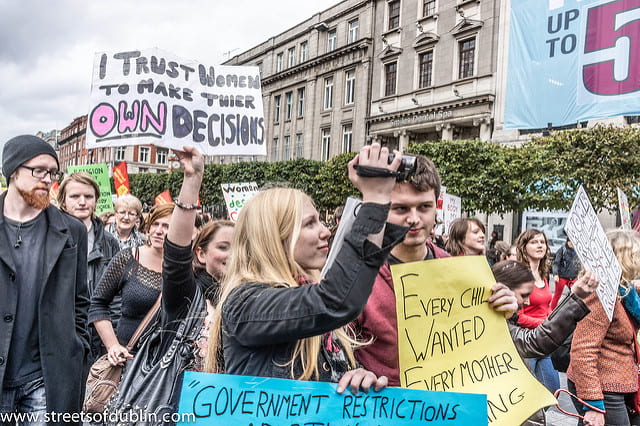
Many conversations and references, in recent weeks, center on the complicated nature of the gun control debate in the United States (US) due to the Parkland shooting and uncharacteristic demands of the teenage survivors. This blog does not directly address those conversations or references. There are many sides to the issue and other blog writers this week gave voice to some of those issues. Therefore, this blog explores the peculiar request of the teenage survivors, which is, seemingly lost among the defense of the Second Amendment.
The right to life.
It seems peculiar that children are demanding adults to protect their lives, to look out for their best interest, specifically when many in the US pride themselves on their pro-life stance. They champion every bill, legislative act, or protest which positions them as the protector of the “rights of the unborn”. As protectors of the unborn, they label women who choose to have abortions and the medical practitioners who perform the abortions as murderers. Some pro-life advocates stand outside Planned Parenthood centers, shouting vile, hurtful words and phrases at patrons and workers. They object to numerous women’s rights issues. All this occurs because of their belief in protecting the innocent, unborn baby who deserves the right to live.
Where are the pro-life advocates joining the protests initiated by the Parkland students who are demanding the protection of their right to life? These children lost their innocence when their classmate murdered their friends and teachers in hallways and classrooms on Valentine’s Day. Many pro-life advocates are standing on the sidelines, protecting their Second Amendment constitutional right to bear arms. Yet, at what point did adults abdicate their responsibility to protect the lives of children to protect their rights to own weapons? Does the “pro-life” label still apply when there is a willful and complicit allegiance to a hobby and lobbying group than to children?
Perhaps a reclassification needs to occur wherein we label pro-birth rather than pro-life.
The Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC), in accordance with the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) asserts, “A child means every human being below the age of eighteen years… [and] in all actions concerning children, whether undertaken by public or private social welfare institutions, courts of law, administrative authorities or legislative bodies, the best interests of the child shall be a primary consideration.” When the best interest of the child is the primary consideration, how has the brutal transformation of schools and universities continued? It seems implausible that for the last 20 years, parents across the US have sent their children to school with hopes and dreams for the future, only to have to bury their 5-18-year-old days later. The Children’s Defense Fund (CDF) reports “children are learning there is no safe place in America.”

When No Place is Safe and Those Who Can/Should Help, Don’t
The US is the ONLY member of the United Nations to not ratified the CRC.
The cliché ‘no parent should have to bury their child’ seems redundant considering needless tragedies of gun violence. Its redundancy comes from the very real reality that pictures and videos from schools, universities, and playgrounds, as well as the rhetorical thoughts and prayers of government officials has yielded minimal results. Unlike natural disasters like tornados and earthquakes, controlling the impacts of gun violence is possible as evidenced in Australia, Great Britain, and Switzerland. Therefore, it is the normalization of violence in the US which continually isolates us from the rest of the world. Data reveals the hypocrisy of the ill-spoken narrative that children are the future of this country. CDF reveals
- Children are forced to witness tragic mass shootings that occur with regularity in public spaces including schools, churches, concert venues, community centers, nightclubs and movie theaters.
- Since 1963, the number of children and teens killed with guns on American soil was more than three times higher than the number of U.S. soldiers killed by hostiles in wars abroad. Nearly 180,000 children and teens died from guns in the U.S. between 1963 and 2015.
With less than 5% of the global population, American civilians own 310 million guns (35-50%) of the global civilian gun-ownership, whereas the US military and law enforcement possess nearly 4 million. The US spends considerably more on defense than on early childhood and education, than every other country with smaller federal budgets.
Children are not a priority in the US.
Who’s doing the shooting?
Brown et al. analyzed two cases, identified four characteristics, and concluded “school violence is a somewhat distinct form of aggression that should not be viewed through standard lens.” The typical mass shooter is a white male who exacts revenge on those he deems dishonored him in some way. Research identifies this cultural phenomenon as “culture of honor”. In a culture of honor, people favor the death penalty, more tolerant of expressions of aggression as a response to threats/insults, and conflate a high degree of connection with status or reputation. This culture fuels the overall feeling of slight through a lack of interpersonal conflict resolution skills. The culture of honor creates a cultural standard wherein brutality becomes the recommended response to a perceived affront to one’s dignity or reputation; thus, a misguided sense of justice.
This misguided sense of justice positions whites as unapologetic for the behavior of shooters. Mingus and Zopf studied four mass shootings: two with white shooters (Columbine High School and Northern Illinois) and two with non-white shooters (VA Tech and Fort Hood). Using “Racial Formations” by Omi and Winant as a key text on racial projections, Mingus and Zopf assert, “The historical significance of race is important in understanding the way in which race affects any interpretation of shooting rampages.” They find that white privilege allows for the addition of race as a factor when identifying the “abhorrent behavior of non-whites” and the subtraction of race when redirecting “focus away from whites as a distinct population by pathologizing their aberrant behavior”. They conclude that non-whites groups often advocate for themselves as a means of not facing retaliation, even offering an apology in the VA Tech tragedy, whereas being white means never having to say you are sorry.

“If they’re old enough to be shot, they’re old enough to have an opinion about being shot”
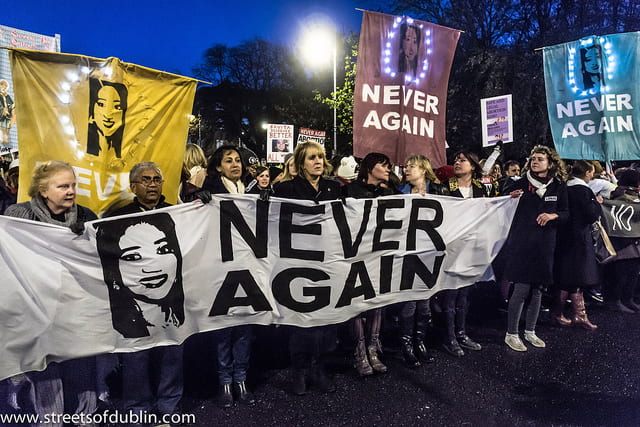
Reports occur daily of the ‘perceived threat of children’ when confronted by white people who feel a threat to their power or status. These reports extend beyond the scope of school shootings, and the requests to “stop killing us” commenced long before the Parkland shooting. The #NeverAgain movement includes the voices of the seemingly voiceless by including students from Chicago, Newtown, and 11-year-old Naomi Walder of Alexandria, VA. Walder, who highlights the deaths of Black girls forgotten by the media, organized her classmates during the National Walkout Day.
Political satirist and late-show comedy host Trevor Noah challenged the notion leveled by Fox News talking head Tucker Carlson after last week’s student walkout campaign. During a segment, Carlson questioned the validity of students making demands of lawmakers regarding guns by stating, “They’re not citizens; they’re children.” What’s interesting is that children are too young to make demands for gun control but not to find themselves in adult prison or forced into child marriage. Noah responded brilliantly stating, “…if kids are old enough to be shot, they’re old enough to have an opinion about being shot.” When processing the numbers provided by the CDF, it is time someone said something.
- 7,768 children and teens were killed in the US to gun violence during 2013-2015
- 113 children under five (5) died from guns in 2016, compared to 65 law enforcement officers killed by guns in the line of duty. Guns were used in criminal acts to kill 62 law enforcement officers while three (3) were killed in gun accidents.
- In 2016, 43% of gun deaths were among Black children and teens, although they made up only 14% of all children and teens.
- 1,335 Black children and teens were killed by guns in 2016, one every 6 hours and 34 minutes.
- The gun death rate for Black children and teens was nearly 4x that of White children and teens and more than 8x that of Asian and Pacific Islander children and teens.
- Most gun deaths among Black children and teens were by homicide. Most deaths by White children and teens were by suicide.
- Guns are more often used to cause harm than in self-protection. A gun in the home makes the likelihood of homicide 3x higher, suicide 3-5x higher, and accidental death 4x higher. For each time a gun in the home injures or kills in self-defense, there are 11 completed and attempted gun suicides, seven criminal assaults and homicides with a gun, and four unintentional shooting deaths or injuries.
- More than half of youth who committed suicide with a gun obtained the gun from their home, usually a parent’s gun.
Given the fact adults consistently prove children are not a priority in this country, children have made an opportunity to make themselves a priority.
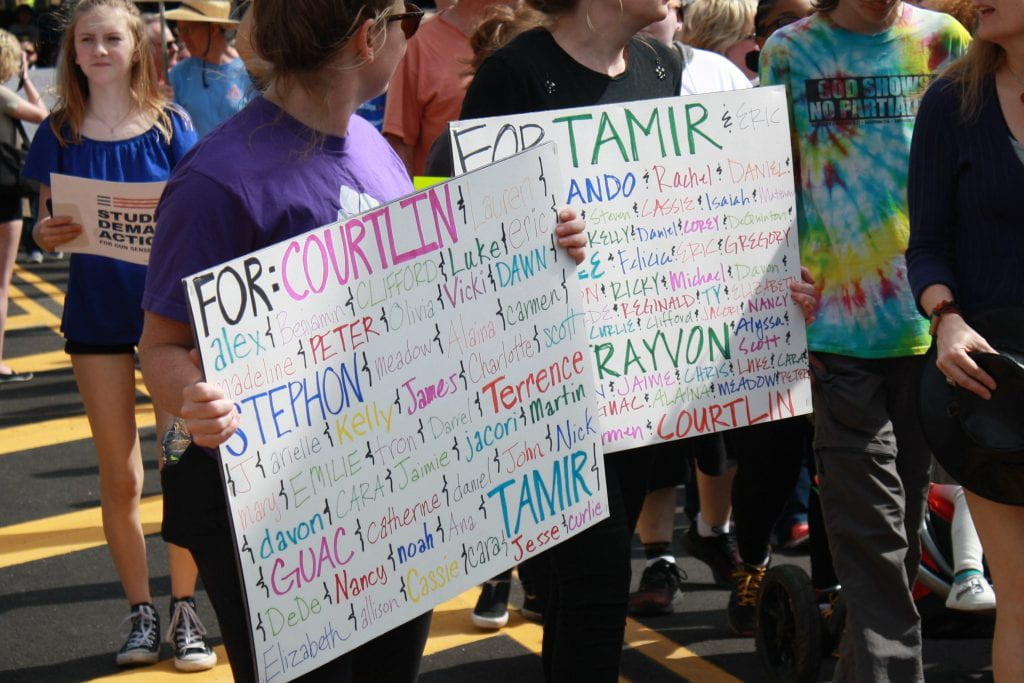
Today, millions of children and adults domestically and internationally, participated in the #NeverAgain movement by joining the March for Our Lives protest. The campaign is not to initiate a disarmament; however, it is to reinstate the ban on assault rifles like AR-15 used in several mass shootings, including Las Vegas and Orlando. Additional demands include an expansion of background checks and a rise of the minimum age to purchase. At the core of the demands and the purpose of the protest lies a peculiar request for the most important human right: the right to live.
A right to a life without fear and terror.
A right to a life where adults apologize for hurting, neglecting, and not prioritizing children who are reliant upon them.
A right to a life without the trauma of relieving the horrors of running to save myself.
A right to a life that does not include witnessing my friends and teachers die before my eyes.
A right to a life by enjoying the full scope of childhood and adolescence which includes mistakes that should not end life because of a perceived threat
A right to a life because adults believe that I and my future are worth fighting for… just as they do for the unborn.
March for Our Lives is a pro-life movement.






















