Prentice Baptiste asserted in 1970 “Knowledge is socially distributed, what you know is what you have been allowed to know”. This holds true today. The human right to an education, though purportedly universal, has been applied in a culturally-specific manner, and oftentimes to the detriment of marginalized populations such as African-Americans (United Nations, 1976). Dr. Charles Drew is one of many whose profound contributions to the world could very well have been derailed if he were not afforded an opportunity to pursue advanced studies. Some argue opportunity is the test of a person’s mettle. I argue opportunity can be unfairly doled out to those in power. Dr. Drew persevered however, despite a structural bias against black students and the willful omissions of black scientists in history books and academia-at-large, including the very institution he so greatly benefited: the American medical complex.
The contributions of black scientists have, historically, been glossed over or explained by grievously inaccurate idioms such as “right place, right time” (Baptiste & Boyer, 2000). Researchers and advocates for human rights walk a fine line when memorializing contributions of all marginalized persons- including Dr. Charles R. Drew. On one hand, the challenges and struggles of these individuals must be contextualized (i.e. drawing upon the unique historical and sociocultural challenges resulting from their marginalizing status) to pay proper homage to both the brilliance of these individuals’ contributions and structural difficulties they faced. On the other hand, we must not indulge in “inspiration porn”, thereby overemphasizing marginalization status over these individuals’ work and benefit to society. With this conceptual framework in mind, this blog has two aims: 1) to provide a historical account of the life and work of Dr. Charles R. Drew and 2) contextualize the narrative of Dr. Drew through the lens of the ongoing struggle for equal human rights in America.
The Life of Dr. Charles R. Drew
Imagine for a moment being a teenager again. Some of us were pimply and awkward. Some were voted prom king or queen. Some teenagers hated school, while some earned straight A’s. What did you want to be when you were a teenager? A writer? An athlete? Charles Drew of Foggy Bottom, Washington DC, in his final year of high school, meekly wrote in his senior yearbook: “I want to be an electrical engineer”. Just as the future Dr. Charles R. Drew was no ordinary doctor, his extraordinary achievements began even in high school (US National Library of Medicine, 2017). After high school, Charles Drew attended Amherst University on an athletic scholarship, where he was an average student but an exceptional football player. At Amherst, he (not originally interested in the sciences) experienced two major losses: a severe hospitalization following a football injury and the death of his sister from tuberculosis prompting an interest in biology and medicine- an interest that compelled him to apply to medical school (US National Library of Medicine, 2017).
The majority of Black Americans were rarely afforded the opportunity to attend prestigious training programs in higher education during the 1920s and 1930s, although some schools did allow a handful of ‘colored’ students every year (US Library of Medicine, 2017). When Drew graduated from university, he was accepted to Harvard Medical School with the stipulation he defer his admission by one year. Drew refused. He attended McGill University in Montreal, Quebec Canada, beginning a path that would land his name and accomplishments in medical history books internationally (US Library of Medicine, 2017). At McGill and throughout his residency at Montreal General Hospital, he began research on fluid replacement in the human body. He then went on to study transfusion at Columbia University, one of the best medical institutions in the United States, and in 1940, Dr. Drew became the first African-American to earn a doctoral degree in medical science from Columbia (US Library of Medicine, 2017). Without reference to the sociocultural and historical experiences of Black Americans in the 1920’s and 1930’s, Dr. Drew’s attempts to enroll and successfully complete medical programs appear to reflect the struggle of any student wishing to break into higher education. Applying the conceptual framework of his marginalizing status (of African descent) plus the inherent and structural bias against black students and professionals, his accomplishments gain more depth. Drew not only overachieved scholastically (a difficult feat for anyone embarking on higher education), but he also successfully moved through a structure bent on forcing him out of the academy in the first place- the ingrained racism festering in all most aspects of American culture.
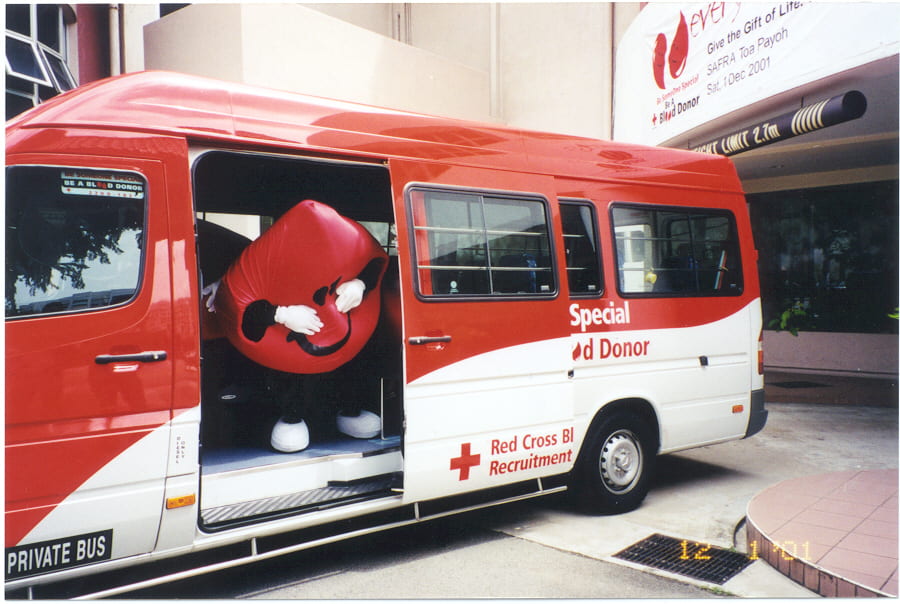

His Medical Legacy
Dr. Drew perfected the science of collecting, storing, and mobilizing blood donations (US National Library of Medicine, 2017). In 1940, he and his collaborators standardized these procedures, and this method soon became a critically necessary tool for the Red Cross during America’s involvement in World War II (US National Library of Medicine, 2017). As a leading expert in blood banking, he created “bloodmobiles” (mobile blood donation stations) and significantly helped America and its allies in the world war treat wounded soldiers and civilians on the battlefront (Gugliemo, 2010). Of tragic irony, Dr. Drew himself was unable to donate blood due to the fact he was of African descent. It is a testament to his character, both as a scientist and as a man, that Drew funneled his intellect and humanitarian spirit into a system that still viewed him as a second-class citizen.
Dr. Drew understood this injustice and the similar injustices of other race-based medical policies in the United States during the Jim Crow era. During the war, Drew practiced what some may consider nonviolent resistance of these policies. Historians of Drew and other medical professionals suspect these professionals would at times mislabel blood collection samples, thereby ensuring blood donated by black Americans reached the Red Cross and the injured people in need. Blood donations at this time (1940s) were required to be segregated along racial lines; ‘white’ blood could suit any medical needs while ‘colored’ blood was only allowed in ‘lesser’ facilities (local hospitals and the like; Guglielmo, 2010). While giving a speech to workers’ union in 1944, he proclaimed “the source of plasma was disregarded by physical and medical corpsmen on the front lines”, meaning ‘colored’ blood was being used in the exact same capacity to save lives as white blood (Guglielmo, 2010). These segregation plans imposed by the US were selectively followed, and others Drew worked with asserted “… these segregation plans were [not] carried through in in detail from beginning to end” (Guglielmo, 2010).
His Greatest Achievement
Drew’s accomplishments as a medical researcher, yes, are profound. However, a more interesting and little-known part of his story may outweigh his hematological inventions. As previously stated, when Drew attempted to begin his medical training, he faced institutional discrimination from the American higher education academy. Throughout his time as a researcher, he was not able to donate blood due to racist and discriminatory laws. His career, at every turn, was affected and slowed by systematic racism permeating throughout both the American academy and American medical industrial complex. However, these inequalities did not stop Dr. Drew and likely compelled him to use his stature in the medical profession to train and empower young African-American men and women hoping to study medicine. Until his untimely death in 1950, Dr. Charles R. Drew served as a mentor to young African-American doctors during his tenure as Chair of Department of Surgery at Howard University School of Medicine (Cornely, 1950). While the annals of history and medicine will likely remember him as the father of the bloodbank, the young black doctors he meticulously trained very well owe their intellectual lineage to Dr. Drew’s ferocity in achieving his dreams and a stark unwillingness to allow the same plight to slow those who came after him. It was not enough that Dr. Drew created a life-saving medical procedure for which the world will forever be indebted, but he also took it upon himself to train future black doctors. If we examine the ripples created from the life and work of Dr. Drew, we find academic prowess and personal resilience throughout his life. He is academically and medically renowned for his revolutionary paradigm of blood collection and storage- the first ripple. His students, mentees, and contemporaries revere him for his personal investment in the professional accomplishments of his students at Howard University- the second ripple. Finally, Drew is one of many marginalized individuals who successfully navigated a system attempting at every turn to inconvenience or diminish his work. Marginalized persons, of any marginalization status, possess the faculties to dismantle and undermine the antagonistic systems around them, such as the American academic and medical field was to Dr. Drew. Our goal as human rights advocates must be the empowerment of these persons, without indulging in ‘inspiration porn’ or glorifying marginalization status at the expense of losing sight of the actual person. The person, in this case Dr. Drew, must remain the central focus of historical accounts such as these. To overemphasize minority or marginalization statuses is to do a disservice to both the individual and to the very philosophy of human rights: dignity despite difference.
References
Baptiste, H. P. (1970). A black educator’s view: The pseudo-sacrosanct role of intelligence in education. Notre Dame Journal of Education, 1(2).
Baptiste, H. P. & Boyer, J. B. (2000). African American males and the scientific endeavor. Journal of African American Men, 4(4), 49-61.
Cornely, P. B. (1950). Charles R. Drew (1904-1950): An appreciation. Phylon, 11(2), 176-177.
Guglielmo, T. A. (2010). “Red Cross, double cross”: Race and America’s World War II-era blood donor service. The Journal of American History, 97(1), 63-90.
Haber, L. (1970). The Afro-American scientist- Why don’t we know him. The Science Teacher, 37(5), 46-48.
Janken, K. R. (1996). A legendary death, a legendary divide. Reviews in American History, 24(4), 657-662.
United Nations (1976). International Covenant on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights. http://www.ohchr.org/EN/ProfessionalInterest/Pages/CESCR.aspx
US National Library of Medicine (2017). The Charles R. Drew Papers. Online. https://profiles.nlm.nih.gov/ps/retrieve/Narrative/BG/p-nid/336