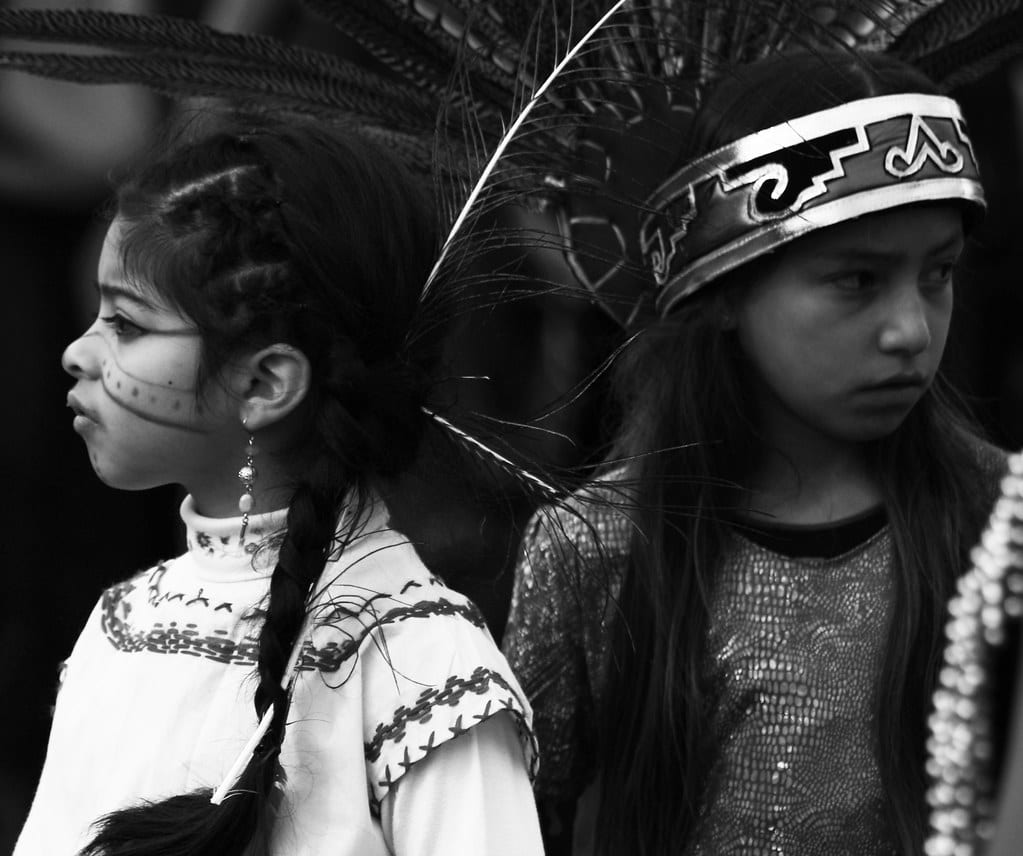
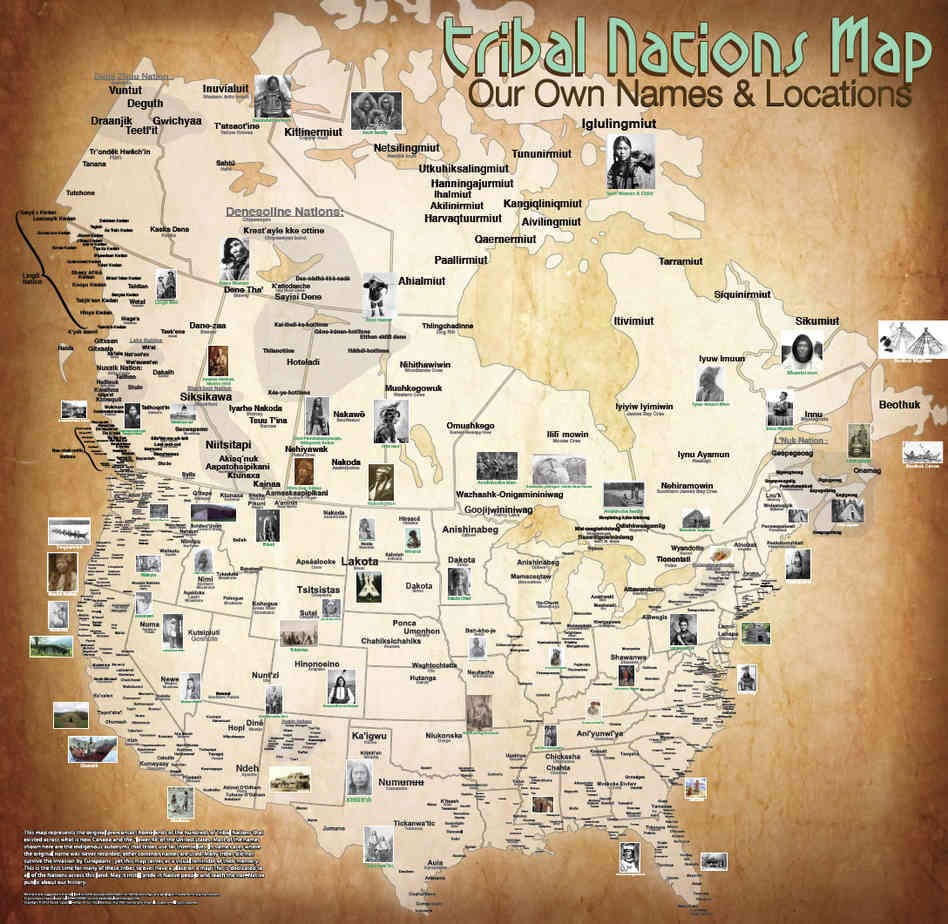
I would like to start this piece off with a land acknowledgment, where I acknowledge the truth of who the lands of America truly belong to. The land in which I sit to write this article, as well as the ones occupied by those who reside in America once belonged to the many diverse communities that existed long before America got its name. Once prosperous, thriving lands belonging to these various indigenous communities, (to the Creeks and Choctaw, in my case), the lands of America were respected and honored by the relationship that these various tribal communities held sacred between themselves and their environment. It is in honor of their stewardship and resilience that I hope to shed light on some of the more gruesome, nefarious betrayals they have experienced at the hands of colonizers from the time their tribal ancestors witnessed the colonizers’ arrival to their lands in 1492.
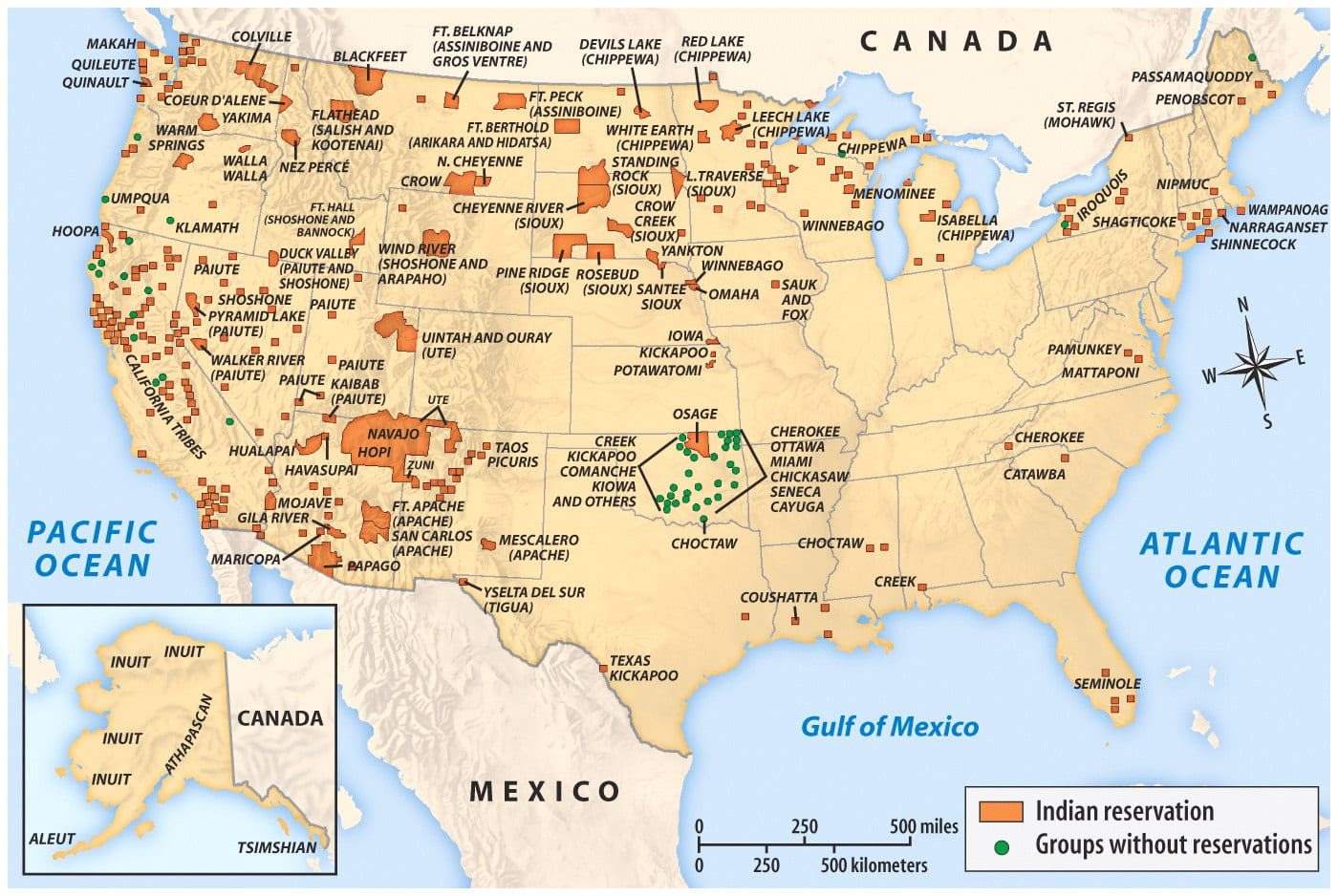
Before the European colonizers arrived on this land, there existed a diverse group of tribal communities, over a thousand different ones just in the mainland we call America today. Now, these tribes have been reduced to no more than 574 federally recognized ones, with dwindling tribal membership numbers, a fact that can only be blamed on the federally sanctioned behaviors of the colonists. So much has been stolen from the diverse groups of indigenous people since the colonization of the North American lands first began. The original indigenous peoples had offered the newly-arriving colonists hospitality and taught them how to cultivate the lands of America and brave the New Frontiers. Yet, what they received in gratitude was bloodshed, tears, death, and betrayals. So many treaties and promises were broken. According to Howard Zinn, the famous author of the book, “A People’s History of the United States,” the various indigenous communities that existed in the Americas by the time the famous explorers landed in the Americas were anywhere between 25-75 million individuals. They had moved into these fertile lands 25,000 years ago, long before the explorers “founded” the Americas. For those interested in learning a truthful history of America, please check out his book. The book begins in 1492 and continues to examine historical events until contemporary times and phenomena such as the “War on Terrorism”.
There is so much information to be covered on this topic, and the more I researched, the more I found. I want to do this topic justice, and I cannot do so until the historical context has been put in place. Hence, this will be a two-part deep dive into the Native American lands, their cultural lifestyles, their relationship with the environment, and what this means for their existence in a capitalist, contemporary society. Part one will focus on the history of Native American lands, the process of treaties and loss, and the cruel, scheming ways of the federal government that attempted to indirectly, yet forcibly, steal lands away from Native Americans by targeting the youngest members of their tribes. Part two will focus on the Indian Child Welfare Act, the fight (and entities involved) in support and against it, how the environment plays a role, and the vast consequences of the recent Supreme Court ruling on the matter, both in terms of the welfare of these indigenous children, as well as the issue of tribal sovereignty. There is a lot to unpack here, so without further ado, let’s begin with a deeper understanding of the relationship that indigenous communities share with their lands.
It’s All About the Land; It Always Has Been
The European settlers had a problem with the Native Americans from the moment they landed in America. For one, they thought the indigenous way of life to be “savagery” and believed that the Native Americans needed to be “civilized”, something they believed only Europeans could teach them about. They found the gods and spirituality of the various indigenous cultures to be blasphemous and nonsensical, and many Europeans attempted to convert the Natives to Christianity, a more “proper” religious belief. Most of all, though, the Europeans and the indigenous communities had vastly different concepts of property and land ownership. To the settlers, who came from the feudal systems of Europe, land was a commodity, purchased and sold by individuals, and prosperity (and social status) was determined by who owned the most properties, and the most prosperous lands. They became lords and could employ the less fortunate to work under them, paying them a fraction of their profits, while keeping the rest for themselves. This was how things worked in Europe back home, and this is the system they brought with them when settling in the New World.
Native Americans, however, had a different lifestyle and concept of ownership. To them, the thought of owning a piece of land was bizarre, as they viewed the land to belong to the various energies and life forms that existed in the said land. The tribal lands of an indigenous community not only fed and nurtured the tribal members but also protected the tribe’s history and held the ancestral burials of their people. The indigenous communities had a spiritual and emotional connection with their tribal lands, one that cannot be sold to another, similar to how you cannot sell to someone else the relationship you hold with your family. Many (if not most), Native tribes even practiced animism, a belief system that accepts all living and non-living things (and natural phenomena) as being capable of having a life force (or soul). For Native Americans, land ownership was a foreign concept, and everyone that existed in their community held rights to the land their tribes lived on. In fact, when European settlers began purchasing lands from the Native Americans, the indigenous people believed they were only “leasing” the lands to the settlers, not giving up their rights to them. For the indigenous communities, the land was just as much a right of every human as sunlight, water, or air.
The Native Americans’ relationship with their lands was also threatening to the European lifestyle of land ownership and individualism. This struggle, between an individualistic view of community, versus the collective view of community, is, as they say, a “tale as old as time.” For Europeans, who believed individual merit and hard work to be the true characteristics of a successful individual, their success could only be displayed by the vastness of their empires, figuratively and physically. Hence, land ownership was a symbol of status and in a way, a testament of a person’s character. For Native Americans who focused on collective success rather than individually standing out, the strength of their tribe was a result of the part each individual tribal member played to ensure their success. This meant that everyone had a role, and if they played them right, everyone in the tribe benefited from the success. This was how tribes survived even as they warred against each other.
Treaties and Deals

Due to these differences between the indigenous communities and the European settlers, many struggles broke out between the two groups between 1492 and 1700. In an attempt to keep the peace between the settlers and the indigenous communities, the British Crown established the Proclamation of 1763, which awarded the colonists all the lands East of the Appalachian Mountains, and everything West was promised to the various different Native American populations that lived in those regions. This did not make the colonists happy, as they believed the King was preventing them from expanding their population, and it was one of the points they listed in the Declaration of Independence as a wrong that was done by the King. Many scholars claim that the Proclamation of 1793 led colonists to pursue a revolution against the crown. The diverse indigenous populations attempted to stay out of the Revolutionary War, as they believed it to be a family feud between the British King, and his colonial subjects. Yet, when they did take part in the War, their participation was diverse. Some joined the rebelling Americans, while others joined the forces of the monarchy. Still, others chose to remain neutral, not wanting to support either side of the struggle. Upon the loss of the Revolutionary War, as part of the treaty signed between Britain and the newly established United States, Britain had to give up all the lands they lay claim to in America, including many of the lands that were promised to the Native American tribes living West of the Appalachian Mountains. This happened without consent or discussion with the Native Americans who took residence in those parts. When the colonists came to take over much of the lands that were promised to the Native Americans through the Proclamation of 1763, they justified their brutality against the Native Americans by blaming them for supporting the British in the Revolutionary War, and when the Native Americans tried to fight back for their lands, the British were nowhere to be seen. This was yet another episode of betrayal experienced by the indigenous populations at the hands of the settlers and the British Crown. Yet, this was just the beginning; the atrocities and betrayals were far from over.
Following the Revolutionary War and the as a result of the resilience shown by the many indigenous communities protecting their lands, the United States decided to engage in creating treaties between the various indigenous tribes in an attempt to set boundaries to their lands, and “compensate” them for the lands taken from them. I have “compensate” in quotations because first of all, no amount of money or goods can compensate for lost lives, which is what many tribes experienced. Some tribes became extinct as a result. Second, these treaties were signed by members who did not have signatory authority to give permission to the lands on the side of many indigenous nations, and Congress seldom ratified the treaties that were signed on the part of the United States. This meant that this was more of a theatrical expression than anything else, and the United States continued to steal the lands of indigenous people. Thirdly, as discussed above, many indigenous people who did engage in treaty-making assumed they were simply “leasing” their lands to be used by the colonists, not selling their rights to it outright. So, there was miscommunication and misunderstandings as to what the treaties actually established. Finally, the United States Congress and Supreme Court established that the indigenous tribes were not capable of engaging in treaty-making, and as such, ended the whole process altogether in 1871, claiming that Congress had full control over “Native American Affairs.”

In an attempt to fasten the process of transferring lands from Native American tribes to the hands of the government, the United States passed the Dawes Act of 1887. Many of the treaties that were made between the US and the various nations included provisions in which tribes were expected to distribute their lands among their members so that lands were held by individuals rather than the tribal entities as a whole. For reasons explained earlier, the settlers were threatened by the communal lifestyles of the Native American tribes and believed that having individual members have rights over smaller portions of lands would make it easier for them to accept the European lifestyles and give up their “backward” ways. The Dawes Act forced these indigenous members to choose a parcel of land for themselves and their families (the size of the parcel of land was determined by the government), and any excess amount of land after this process would be sold to the government to be used by non-native residents and corporations alike. Millions of acres of land were stolen from various indigenous tribes as a result. This essentially acted as a way to separate the individual Native American member from their larger tribe and weaken their sense of community and tribal sovereignty as a whole.
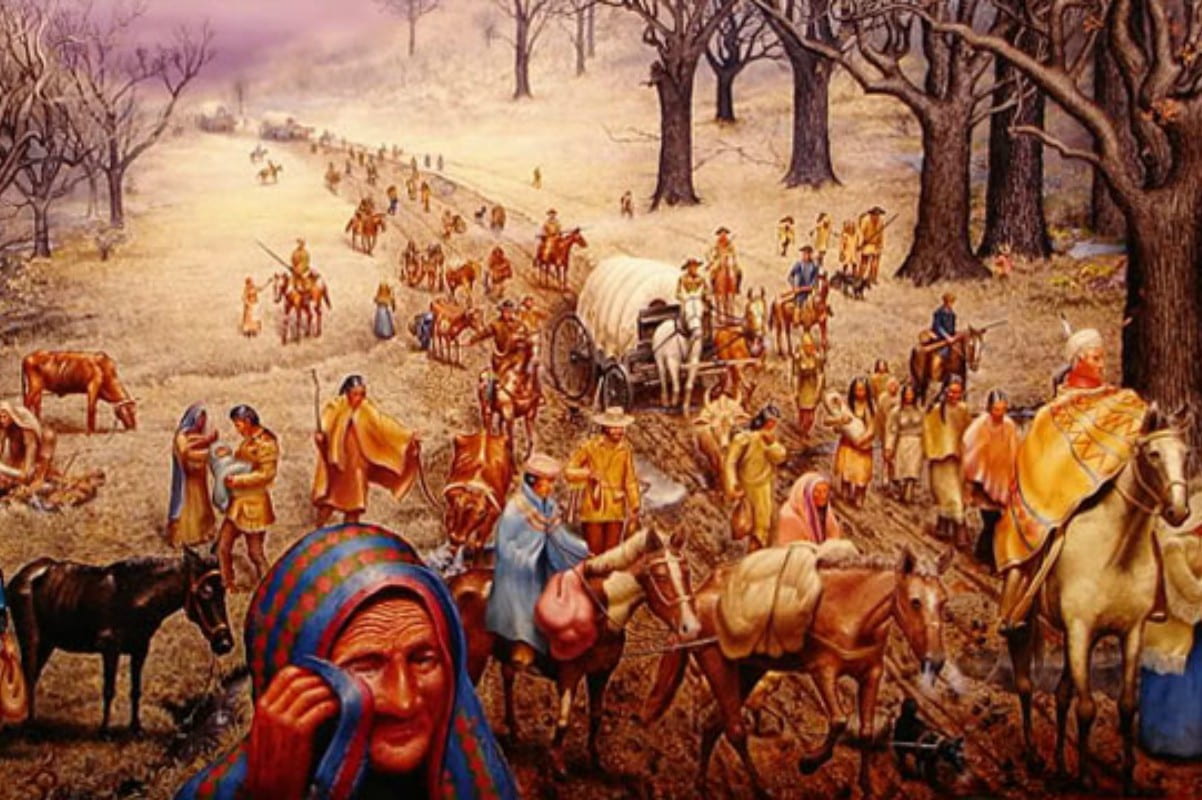
Since the end of the Revolutionary War, the United States government has made about 374 treaties with various indigenous nations across the country. The United States has either violated or fully broken nearly all of these treaties they created as a promise of peacekeeping. Many of these treaties that the United States obtained in the first place were either coerced or done so by forcible means such as threatening starvation on the communities that refused to sign the treaties. Of the various treaties that were violated and broken, one that comes to mind clearly for anyone even slightly familiar with American History is the actions of then president Andrew Jackson and his Indian Removal Act of 1830. Although he negotiated treaties with various tribes in the Southeast in an attempt to get them to move West of the Mississippi River voluntarily, when he became president of the United States, he passed the Indian Removal Act of 1830, forcibly removing almost 50,000 people from their homes. This forcible removal today would be recognized as a forceable deportation of a population, specifically as a crime against humanity. Under the United Nations Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court, this is one of the most heinous systematic crimes that has been committed throughout history. Jackson did this in an attempt to clear lands to cultivate cotton, which would lead to another atrocious event, the revamping of plantation slavery in the South.
History of the Forced Assimilation of Native American Children

Another tactic used by the government to acquire lands from the indigenous populations was through further treacherous means. Native American children were forcefully assimilated into American culture in an attempt to beat/torture their culture out of them. The existence of the Federal Indian Boarding School System was proof of this very thing. Recently, an internal investigation was conducted of the United States government’s treatment of Indigenous children following the incident in Canada, where they found over 215 unmarked graves at a school in 2021. This report, led by Deb Halland, the Secretary of Interior, highlighted many nefarious ways in which tribal lands were stolen from different indigenous nations and the atrocities that were forced upon the children from these nations.
To explore some of the details outlined in this report, (specifically from pages 20-40), the plans of forcible assimilation have been put in place since the days of George Washington. This plan to forcefully erase indigenous culture and assimilate the children into Western culture was seen as the “cheapest and safest way” to steal the tribal lands, ensure a less violent relationship between the colonists and the Native Americans, and transform the tribal economy so they would be prepared to live off of lesser and lesser parcels of land. They found a way to weaponize education in order to accomplish this task.
Elaborating on George Washington’s proposal, Thomas Jefferson, the third president of the United States, put forth a 2-step solution to acquire more lands for the colonists. First, he argued that Native Americans could be forcefully assimilated into European culture, where they could be discouraged to live out a nomadic lifestyle (which requires the use of vast areas of land) and to adopt an agricultural lifestyle similar to the colonists (which can be done with a few acres of land that are cultivated). Second, he proposed that the United States place indigenous populations in debt by encouraging their use of credits to purchase their goods. This, he presumed, would make them default on their debts, and when they were unable to pay back their loans, they would be forced to give up their lands as a result. This land acquired by the government would be sold to non-native settlers, and the profits from these land sales would be put back into the education programs for forceful assimilation of native children.
Sanctioned by the United States government, indigenous children were kidnapped from their homes, whether they wanted to go to boarding school or not (with or without parental permission), and placed in these schools that were located far away from their tribal lands. The plan was to erase the relationship these children had with their cultures, communities, and lands, and instead instill individualism in the children who they were attempting to assimilate in the hopes that they could break up the communal lands into individual parcels, making it easier to be ceased by the government and private entities alike. They called it the “Indian Problem”, which was the different lifestyle and relationship tribal members held with their land and their community. Thomas Jefferson’s two-part proposal was seen as a “key solution” to this “Indian problem.” If the Native American children were forced to become dependent on agricultural lifestyles, they assumed, they could be “civilized.” The government believed that if you separate the children from their families and their tribal connections at a very young age, what they were introduced to would be all they knew, and they would become strangers to the indigenous lifestyles. In turn, the government assumed, the children would not want to go back home and live on the reservations, but instead, would be much more likely to assimilate and live amongst the colonists.
As a result, indigenous families were broken apart, and indigenous children were placed with white families as part of the “outing system.” This meant that the children were forbidden to speak in their native languages and were required to speak English to communicate their needs. What’s worse, they were placed with children from other tribes, meaning that their common language of communication was English, and any children they would have would grow up learning English as their first language instead of the tribal languages of their ancestors.
To support the government in this endeavor, many churches were given legal power over reservations by the government. The military was called in to reinforce the orders of these religious institutions. Many times, the government paid these institutions if they operated a boarding school, paying them a sum for each child. The churches went along with it because they believed that the indigenous way of “paganism” kept them from becoming “civilized” and to fully do so, the indigenous children needed to accept Christianity. The government worked with churches from many denominations by funding them to build the Federal Indian Boarding School System.
Treatment of Indigenous children in these boarding school systems
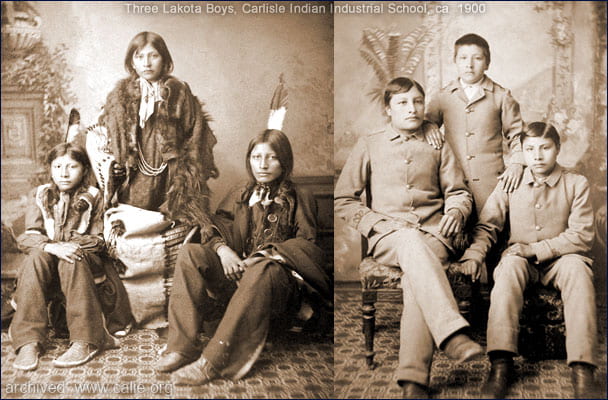

The Federal Indian Boarding School System was problematic in so many ways. Not only did it forcefully assimilate indigenous children, but the system also took a militaristic approach to education, abusing and mistreating these children in the process. The living conditions at these Boarding schools were terrible. There was no access to basic health care needs, and diseases ran rampant across the schools. The children were malnourished, as they were provided with food and water of poor quality. There was an overcrowding issue, with many facilities forcing multiple children to share one bed as a result. There were not enough toilets to serve the number of children at each facility, and the toilets were not properly maintained.
The infrastructure in these facilities was so poor because they were not built specifically to house these children as facilities for education. Rather, these children were placed in abandoned government buildings or military forts to carry out their education. There was also the issue of child labor, where the children were expected to provide all the services required to run the facilities. This included looking after the livestock, chopping wood, making bricks, sewing garments to clothe the other children, working on the railway, cooking, and cleaning for the others in the facility, and so much more.
The children were expected to take care of themselves and the other children at the facilities. They were also tasked with work from various fields like carpentry, plumbing, blacksmithing, fertilizing, helping with the irrigation system, helping make furniture for use in the facilities (such as tables, chairs, and beds), and anything else that involved physical labor. These jobs the children were trained in would forever keep them at a lower socioeconomic level than their White counterparts. Here too they tried to instill the patriarchal norms of Western society, making sure to teach and employ young girls to work as assistants and cooks, while the young boys were expected to be farmers and industrial workers.
The Indigenous children were forcefully assimilated into American culture. They were told to stop practicing their faiths and were stopped from performing any spiritual and/or religious rituals. The children were expected to go by the English names they were given at the boarding school instead of their Native names given to them at birth. They were forced to cut their hair (which was sacred to many indigenous people as it represented their cultural identity), and were forbidden to wear their cultural clothes and instead were put in military garb.
Those who resisted the assimilation or tried to run away were caught and severely abused and punished. They were put in solitary, whipped, slapped, starved, and abused for fighting to retain their culture. Many of the older children at the facilities were forced to punish the younger children, further dividing the children, and destroying any opportunity the children may have had to band together to resist the assimilation forces. As a result of what the Federal Indian Boarding School System put these children through, there were over 50 marked and unmarked burial sites found. These burial sites had found over 500 indigenous children dead and counting, and these numbers are expected to rise to thousands more. Many indigenous children that survived these boarding schools are reported to have long-lasting impacts on their health and their lives. These children that grew up to be adults reported having higher risks for cancer, diabetes, and Tuberculosis. They experienced heightened mental health issues, and many remain in a lower socioeconomic class as a result.
Cultural Genocide
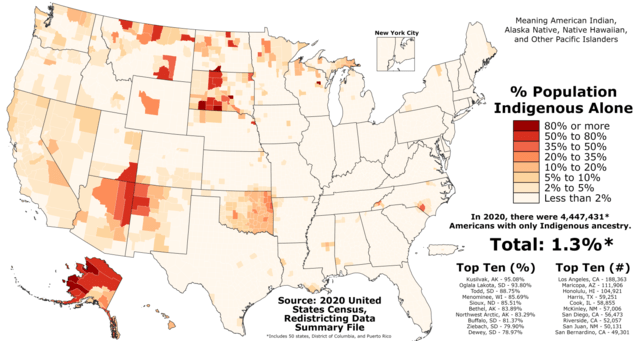
Many believe this forcible assimilation program conducted by the federal government to be a cultural genocide, in which a state-sanctioned attempt at the erasure of an entire culture took place. The official definition of genocide as established by the Genocide Convention in the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court reads as follows: “…any of the following acts committed with intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a national, ethnical, racial, or religious group, as such: killing members of the group; causing serious bodily or mental harm to members of the group; deliberately inflicting on the group conditions of life calculated to bring about its physical destruction in whole or in part; imposing measures intended to prevent births within the group; forcibly transferring children of the group to another group.” As per this definition, the acts carried out by the United States government against the children of various Native American tribes fulfill most, if not all these categories that define these acts to be considered genocidal. It is not a surprise that Native Americans have been killed by the federal government’s sanctions throughout history. There has been serious bodily harm and mental harm caused to members of these various indigenous groups throughout American history. The government deliberately placed young children in conditions of life that ensured their destruction as a member of the Native American tribe they each belonged to. The children within these facilities were not allowed to mingle with others from their own tribes, making it harder for them to retain and pass down their cultural identities, as well as procreate with members of their own tribe. Finally, they were forcibly taken away from their parents and placed in these facilities and other non-native homes in an attempt to erase their cultural backgrounds. All these actions, as was discovered by the recent report we explored at length in this blog, were done so with the intent to destroy the rich cultures of the various Native American tribes. So, the forcible assimilation of Native American children can, without a doubt, be characterized as cultural genocide.
The main goal of this blog was to establish the historical context of what the various Native American tribes endured, as well as the intentions of the federal government in terms of their dealings with the different native nations present in America. Part two of this conversation will focus on a specific piece of legislation that has gained a lot of attention in recent years, the Indian Child Welfare Act. At face value, this legislation is simply an act that addresses the long, detailed history of Native American children and sets guidelines to ensure that proper regulations are put in place to prevent a repetition of history. Yet, it’s now been challenged, partly with the help of very shady moneyed interest, and its fate (and the overarching consequences as a result) were placed in the hands of the nine Supreme Court justices of the United States. We will explore more about this legislation and the case in the next blog.