I was in 4th grade when I was asked if I was a terrorist. I was asked by a person who I thought was my friend. I was asked this horrible question because of the color of my skin. I was too young to realize I was being targeted along with another classmate of the Islam faith, and that my culture and Hindu background were gravely mistaken because of stereotypes and misinformation. While I have never been a victim of Islamophobia, that day I got a touch of what many Muslims face on an everyday basis. Some stories we hear, and some we don’t. Right now, cultural devastations and genocides are taking place in China due to widespread Islamophobia.
MODERN CONCENTRATION CAMPS
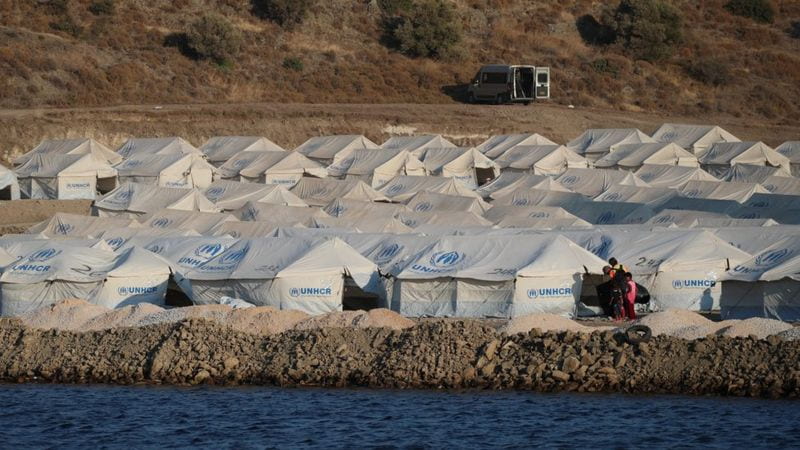
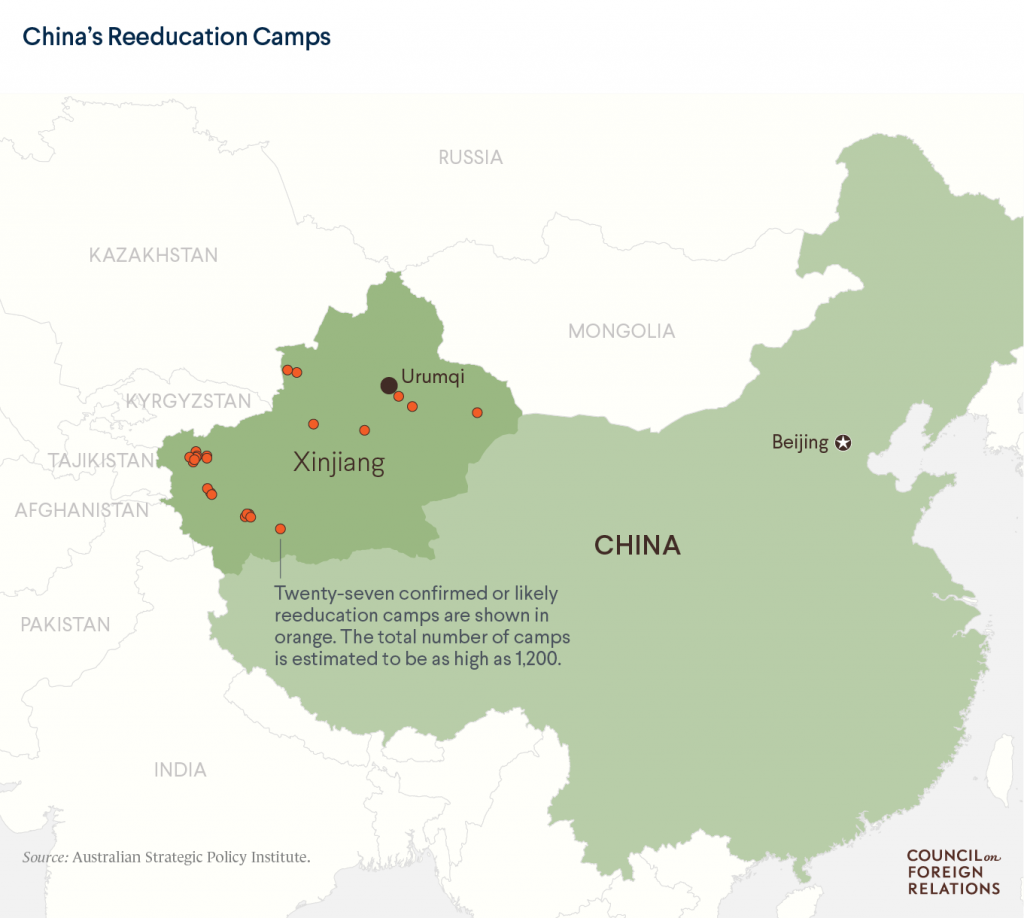
The Uyghurs are a Muslim minority in Xinjiang, China, which was once East Turkestan, but was annexed in 1949. Since 2017, more than 1 million of the 11 million Uyghurs have been places in 85 concentration camps, but China chooses to refer to these as re-education centers. Muslim anecdotes of life inside the camps consists of beatings, interrogations, and detainments for their religious beliefs and practices. Since the beginnings of these camps, the Xinjiang government has prohibited men from growing out the beards and women from wearing face coverings, while also destroying mosques, which are Muslim places of worship. Following United Nations probes, China claims that because the Uyghurs hold extremist views that are threatening to national security the concentration camps are justified.
For most of us, our views of a concentration camp typically include Nazi Germany and the atrocities that took place during World War II. But, our representative heuristic clouds our judgement when we try to compare what is currently going on in China to what was happening in World War II, but the bottom line is, “A concentration camp is a place where people are imprisoned not because of the crimes they committed but simply because of who they are.”

ETHNIC CLEANSING OF UYGHURS
Some of the stories that have been gathered from the concentration camps include reports of forced sterilizations on Uyghur women, bans against fasting during the holy month of Ramadan, and attending mosques. While China claims to be a democratic nation, the continuation of Uyghur persecution indicates that religions in China must be of Chinese orientation and the people should assimilate into a socialist society regardless of their own personal beliefs.
The Chinese government had “turned the Uighur autonomous region into something that resembles a massive internment camp.” After World War II, the nations of the world have promised to uphold and protect the rights of citizens globally. In light of recent events we are once again in the middle of another gross and egregious instance of human rights abuse.
A statement released from the Human Rights Watch states that, “A body of mounting evidence now exists, alleging mass incarceration, indoctrination, extrajudicial detention, invasive surveillance, forced labor, and the destruction of Uighur cultural statements, including cemeteries, together with other forms of abuse.”
ISLAMAPHOBIA
Islamophobia and unfounded fear of Muslims, and people from the Middle East, is something that has plagued the modern world since the 2001 September 11th attacks. The attacks have heightened the tension and awareness against minorities as well has the Uyghur separatist movement. To some extent, it can be argued that around the time the United States began its War on Terror in the Middle East, China spontaneously changed its rhetoric to labeling Uyghurs as “terrorists” in light of these attacks. The Uyghur separatist movement has been fighting for independence and has been protesting since the rise of the Beijing communist rule, and during this movement many lives have been lost. The Chinese government claims that this movement and the protests have led to bombings and politically calculated assassinations that have killed 162 people. Due to the separatist movement and the lives lost, the Chinese government is placing Uyghur Muslims in concentration camps in hopes of “re-educating them,” when really their methods have been identified as causes of cultural genocide. Almost two dozen countries are in tandem with concerns raised by an independent United Nations Committee on Elimination of Racial Discrimination concerning credible reports of mass detention; efforts to restrict cultural and religious practices; mass surveillance disproportionately targeting ethnic Uyghurs; and other human rights violations and abuses.
Disney’s Mulan
While many nations and corporations have identified the Uyghur crisis and have taken actions to bring it to light, Disney, one of the biggest corporations who has repeatedly prided itself on diversity, inclusivity, and decency, has somehow overlooked the genocide that is happening in China right now. Nine minutes into the credits of the film Mulan, Disney thanked the publicity department of the CPC Xinjiang Uyghur autonomous region committee which is exactly where the Uyghur genocide is currently taking place and where Muslims are being blatantly persecuted. In addition to that, the film’s lead Lui Yifei tweeted in support of the Hong Kong police who has been using police brutality to suppress the pro-democracy protestors. An internationally recognized company recently opened the Shanghai Disneyland Park and did so seamlessly without any government problems or much restriction, so how did this big company overlook the whitewashing of the ongoing Uyghur genocide?
What can I do?
Visit Uyghur Human Rights Project
Protest Beijing Olympics as “a key pressure point”
Educate yourself and the people you surround with on Islamophobia and its repercussions